一、hadoop部署
一、Java环境
yum 安装方式安装
1、搜索JDK安装包
yum search java|grep jdk

2、安装
yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-src.x86_64
3、查看安装结果
java -version 通过yum默认安装的路径为 /usr/lib/jvm 可以通过cd /usr/lib/jvm 命令 查看
4、配置环境变量
JDK默认安装路径/usr/lib/jvm
4.1 查看JDK默认安装路径/usr/lib/jvm
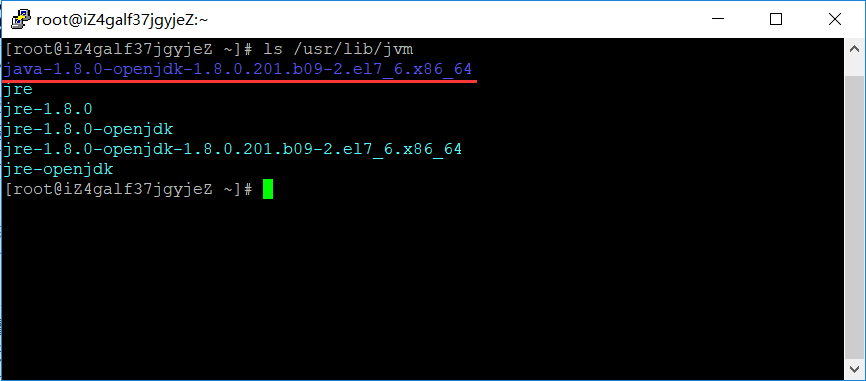
4.2在/etc/profile文件添加如下命令
# set java environment JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.181-3.b13.el7_5.x86_64 PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar export JAVA_HOME CLASSPATH PATH
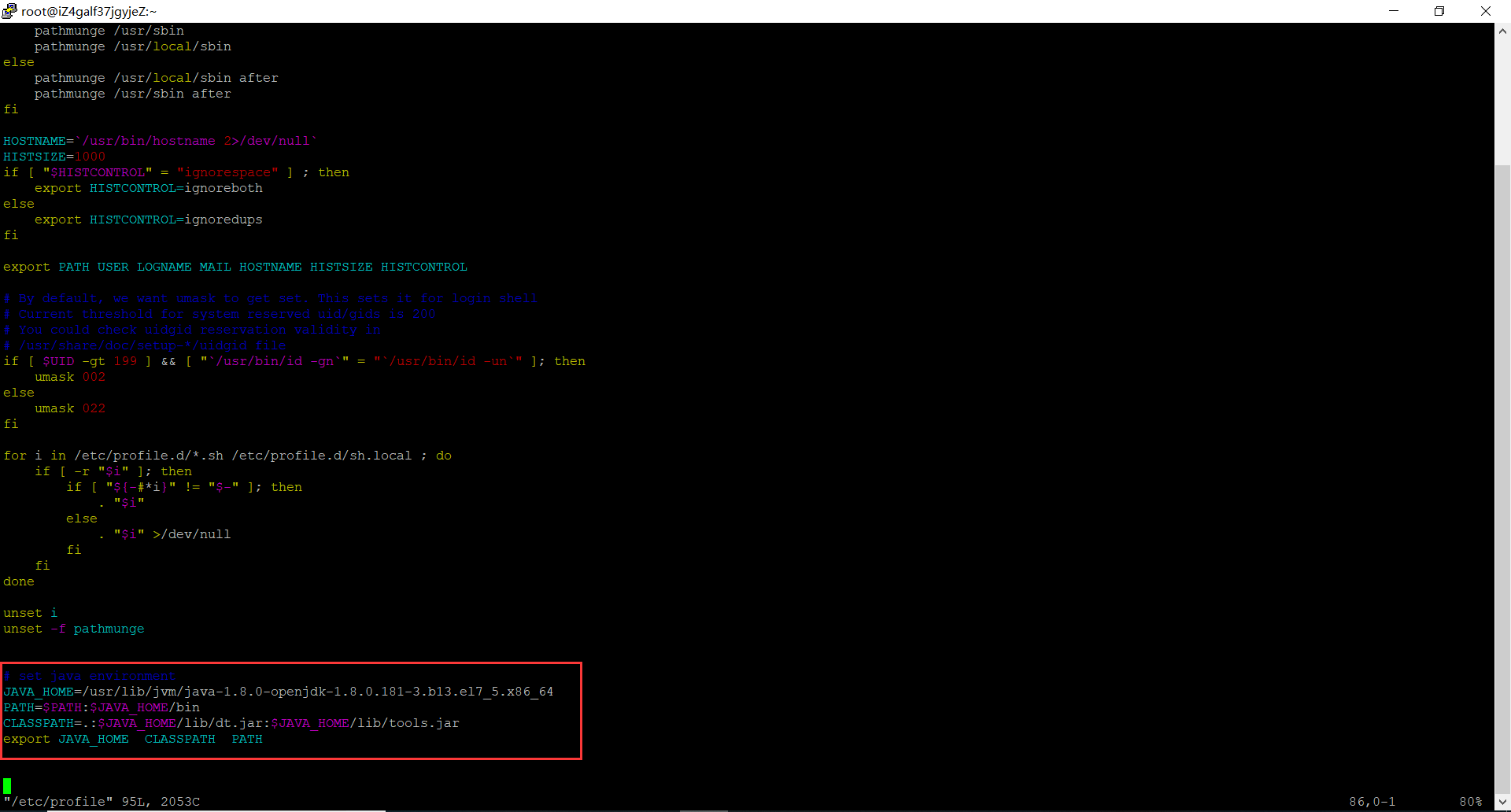
4.3保存关闭profile文件,执行如下命令生效
source /etc/profile
4.4使用如下命令,查看JDK变量
echo $JAVA_HOME echo $PATH echo $CLASSPATH
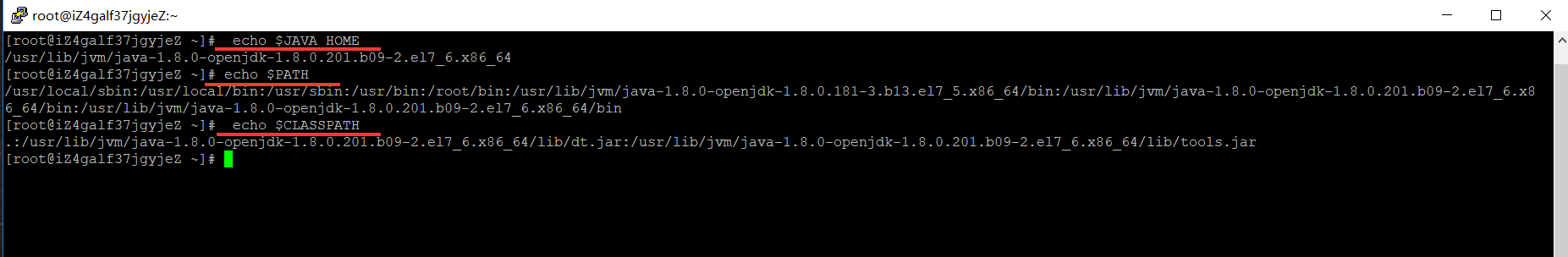
二、SSH 无密码验证配置
1、SSH介绍
1.1 SSH的好处:
在linux系统中,ssh是远程登录的默认工具,因为该工具的协议使用了RSA/DSA的加密算法.该工具做linux系统的远程管理是非常安全的。telnet,因为其不安全性,在linux系统中被搁置使用了。
1.2 SSH的原理:
Master(NameNode | JobTracker)作为客户端,要实现无密码公钥认证,连接到服务器Salve(DataNode | Tasktracker)上时,需要在Master上生成一个密钥对,包括一个公钥和一个私钥,而后将公钥复制到所有的Slave上。当Master通过SSH连接Salve时,Salve就会生成一个随机数并用Master的公钥对随机数进行加密,并发送给Master。Master收到加密数之后再用私钥解密,并将解密数回传给Slave,Slave确认解密数无误之后就允许Master进行连接了。这就是一个公钥认证过程,其间不需要用户手工输入密码。重要过程是将客户端Master复制到Slave上。
1.3 SSH的为什么要使用无密码验证设置:
Hadoop启动以后,NameNode是通过SSH(Secure Shell)来启动和停止各个DataNode上的各种守护进程的。
节点之间执行指令的时候是不需要输入密码的形式,故我们需要配置SSH运用无密码公钥认证的形式,这样NameNode使用SSH无密码登录并启动DataName进程,同样原理,DataNode上也能使用SSH无密码登录到NameNode。
2、配置
那么我们想要的结果是在 master 机器上能不输入密码直接登录到 slave1 和 slave2 机器上。反之在 slave1 上能不输入密码登录到 master 和 slave2 机器上。
首先我们配置从 master 机器上不输入密码登录到 slave1 机器上。
第一步:确认系统已经安装了 SSH
我们需要两个服务,ssh和rsync。可以通过下面命令查看结果显示如下:
rpm –qa | grep openssh rpm –qa | grep rsync

则表示没安装,通过以下命令安装
master 机器上生成 秘钥对
在 master 机器上输入一下命令:
ssh-keygen -t rsa -P ''
这条命令是生成无密码秘钥对,rsa 是加密算法,-P '' 表示密码为空。询问其保存路径时直接回车采用默认路径。生成的密钥对:id_rsa和id_rsa.pub,默认存储在"/root/.ssh"目录下。
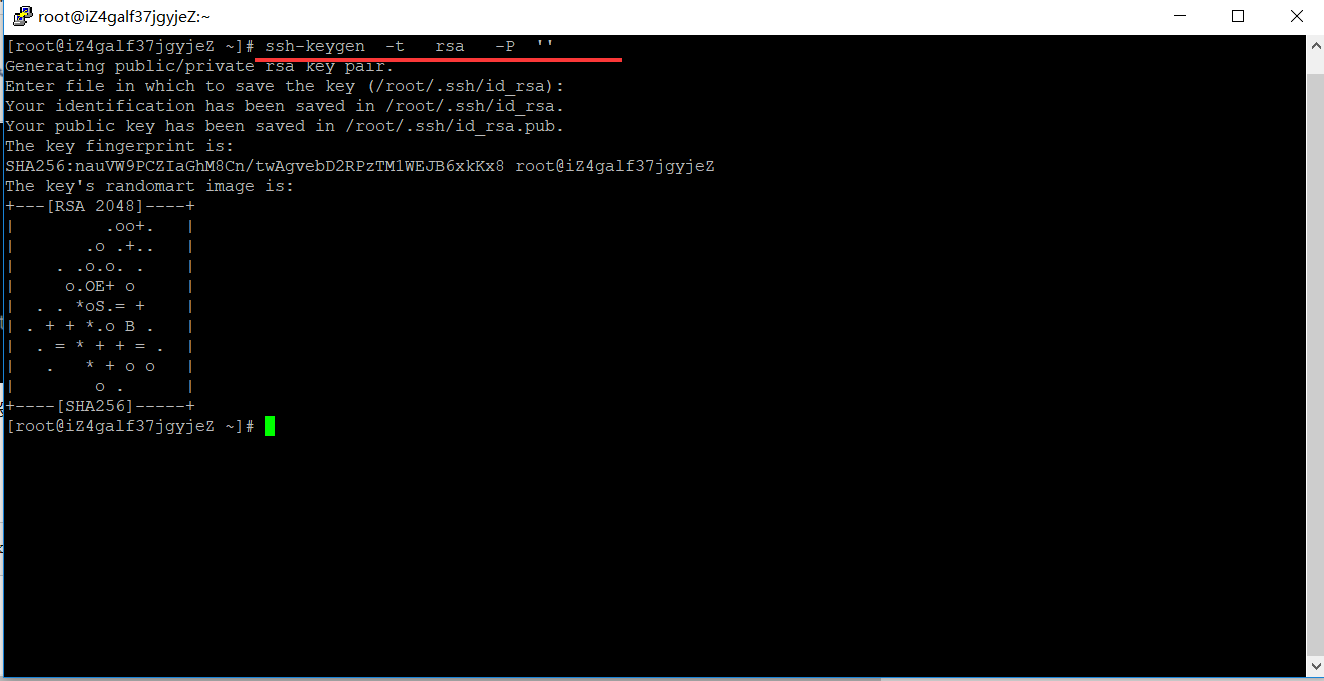
查看"/home/hadoop/"下是否有".ssh"文件夹,且".ssh"文件下是否有两个刚生产的无密码密钥对。
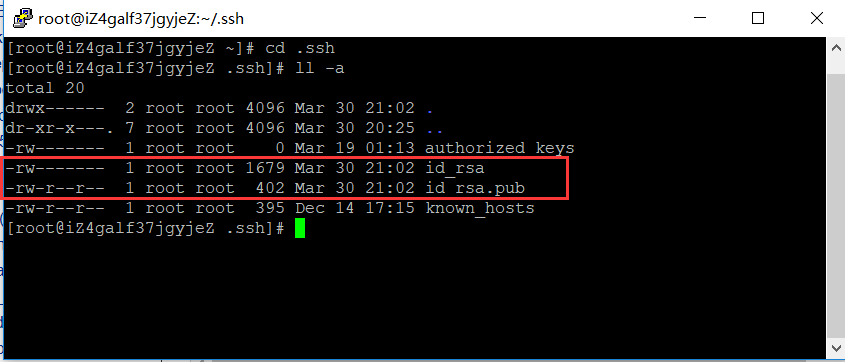
创建authorized_keys文件并将密钥写入
touch /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
查看下,是否创建成功
[root@hadoop01 .ssh]# ls /root/.ssh/ authorized_keys id_rsa id_rsa.pub [root@hadoop01 .ssh]#
或者把公钥 id_rsa.pub追加到授权的key里面去。
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
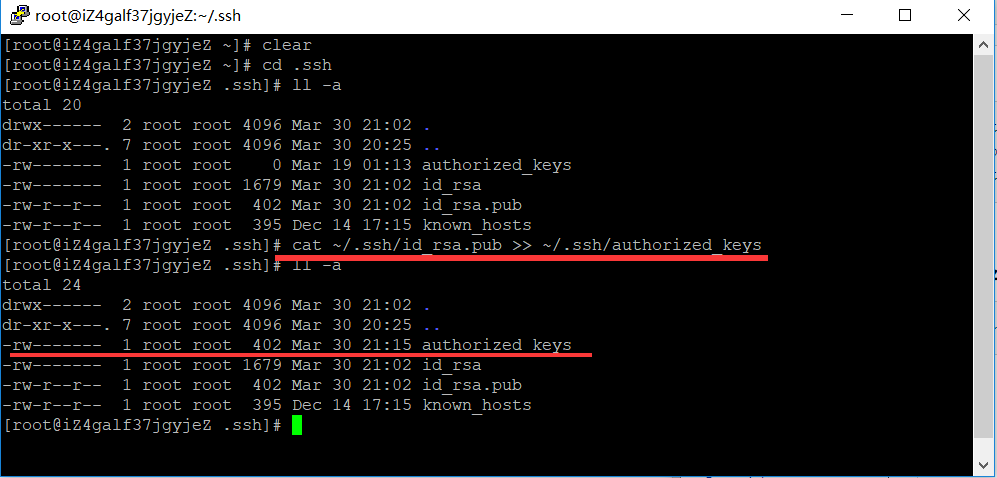
对比查看写入是否一致
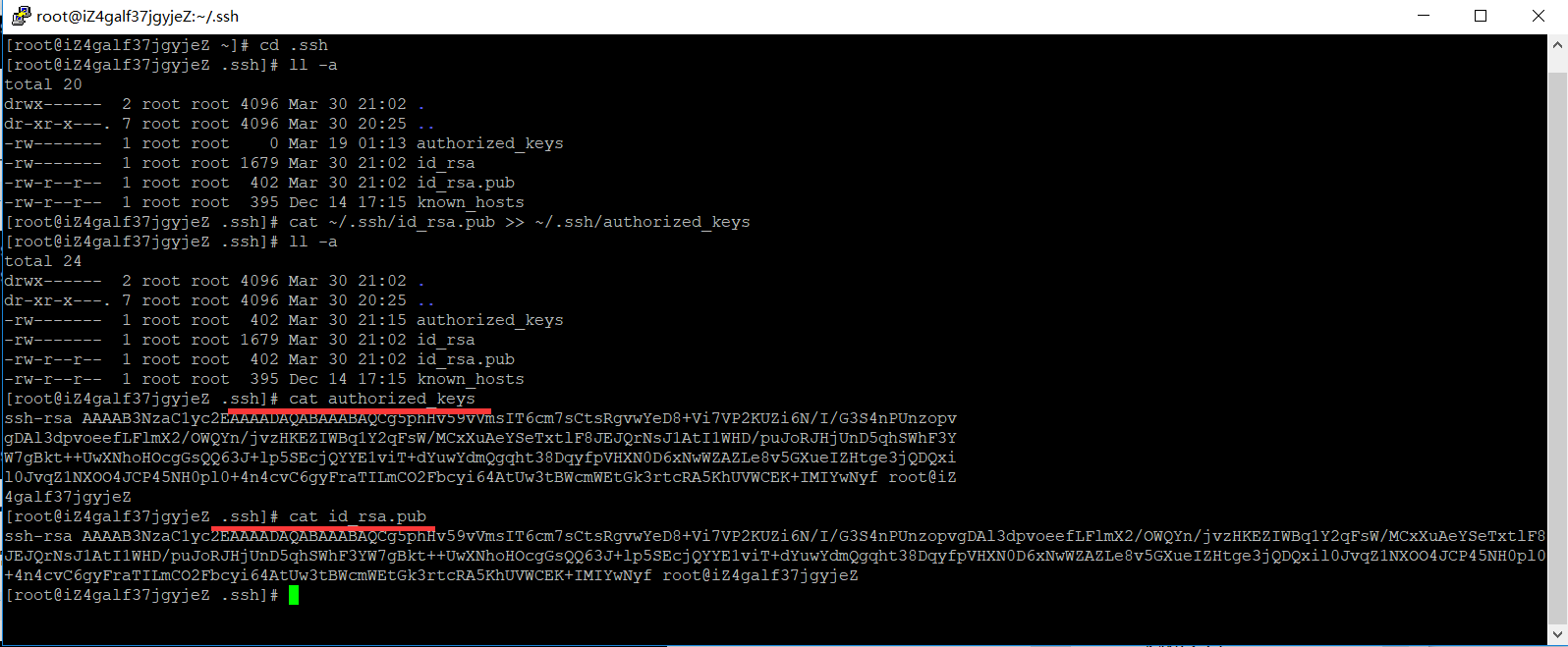
授权authorized_keys文件
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
三、用root用户登录服务器修改SSH配置文件
cat /etc/ssh/sshd_config
# $OpenBSD: sshd_config,v 1.100 2016/08/15 12:32:04 naddy Exp $ # This is the sshd server system-wide configuration file. See # sshd_config(5) for more information. # This sshd was compiled with PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin # The strategy used for options in the default sshd_config shipped with # OpenSSH is to specify options with their default value where # possible, but leave them commented. Uncommented options override the # default value. # If you want to change the port on a SELinux system, you have to tell # SELinux about this change. # semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp #PORTNUMBER # Port 22 #AddressFamily any #ListenAddress 0.0.0.0 #ListenAddress :: HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key #HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ecdsa_key HostKey /etc/ssh/ssh_host_ed25519_key # Ciphers and keying #RekeyLimit default none # Logging #SyslogFacility AUTH #LogLevel INFO # Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m #PermitRootLogin yes #StrictModes yes #MaxAuthTries 6 #MaxSessions 10 #PubkeyAuthentication yes # The default is to check both .ssh/authorized_keys and .ssh/authorized_keys2 # but this is overridden so installations will only check .ssh/authorized_keys AuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys #AuthorizedPrincipalsFile none #AuthorizedKeysCommand none #AuthorizedKeysCommandUser nobody # For this to work you will also need host keys in /etc/ssh/ssh_known_hosts #HostbasedAuthentication no # Change to yes if you don't trust ~/.ssh/known_hosts for # HostbasedAuthentication #IgnoreUserKnownHosts no # Don't read the user's ~/.rhosts and ~/.shosts files #IgnoreRhosts yes # To disable tunneled clear text passwords, change to no here! #PermitEmptyPasswords no # Change to no to disable s/key passwords #ChallengeResponseAuthentication yes ChallengeResponseAuthentication no # Kerberos options #KerberosAuthentication no #KerberosOrLocalPasswd yes #KerberosTicketCleanup yes #KerberosGetAFSToken no #KerberosUseKuserok yes # GSSAPI options GSSAPIAuthentication yes GSSAPICleanupCredentials no #GSSAPIStrictAcceptorCheck yes #GSSAPIKeyExchange no #GSSAPIEnablek5users no # Set this to 'yes' to enable PAM authentication, account processing, # and session processing. If this is enabled, PAM authentication will # be allowed through the ChallengeResponseAuthentication and # PAM authentication via ChallengeResponseAuthentication may bypass # the setting of "PermitRootLogin without-password". # If you just want the PAM account and session checks to run without # and ChallengeResponseAuthentication to 'no'. # WARNING: 'UsePAM no' is not supported in Red Hat Enterprise Linux and may cause several # problems. UsePAM yes #AllowAgentForwarding yes #AllowTcpForwarding yes #GatewayPorts no X11Forwarding yes #X11DisplayOffset 10 #X11UseLocalhost yes #PermitTTY yes #PrintMotd yes #PrintLastLog yes #TCPKeepAlive yes #UseLogin no #UsePrivilegeSeparation sandbox #PermitUserEnvironment no #Compression delayed #ClientAliveInterval 0 #ClientAliveCountMax 3 #ShowPatchLevel no #UseDNS yes #PidFile /var/run/sshd.pid #MaxStartups 10:30:100 #PermitTunnel no #ChrootDirectory none #VersionAddendum none # no default banner path #Banner none # Accept locale-related environment variables AcceptEnv LANG LC_CTYPE LC_NUMERIC LC_TIME LC_COLLATE LC_MONETARY LC_MESSAGES AcceptEnv LC_PAPER LC_NAME LC_ADDRESS LC_TELEPHONE LC_MEASUREMENT AcceptEnv LC_IDENTIFICATION LC_ALL LANGUAGE AcceptEnv XMODIFIERS # override default of no subsystems Subsystem sftp /usr/libexec/openssh/sftp-server # Example of overriding settings on a per-user basis #Match User anoncvs # X11Forwarding no # AllowTcpForwarding no # PermitTTY no # ForceCommand cvs server UseDNS no AddressFamily inet SyslogFacility AUTHPRIV PermitRootLogin yes PasswordAuthentication yes
重启服务
service sshd restart
验证
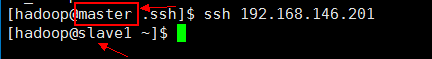
注意看我们两个箭头,说明已经无密码登录到 slave1 机器上了。那么这样就算大功告成。
相关文章
- Hadoop部署记录
- 如何用鲲鹏弹性云服务器部署《Hadoop伪分布式》
- Hadoop伪分布式集群的安装部署
- Cloudera Manager 5 和 CDH5 本地(离线)安装指南(Hadoop集群搭建)
- 高可用Hadoop平台-Ganglia安装部署
- 高可用Hadoop平台-Ganglia安装部署
- HADOOP:WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable终于解决了
- Hadoop的环境搭建,和编写一个简单的hadoop job
- hadoop 2.X HA详细配置
- Hadoop 生态系统
- helm部署hadoop报错解决方法
- Hadoop MapReduce入门程序wordcount代码示例及打包部署运行结果演示
- Hadoop Java客户端操作hdfs实现文件上传操作
- hadoop 使用Avro排序
- Hadoop伪分布式集群的安装部署
- 9.2.2 hadoop全排序实例详解
- java.io.IOException: Could not locate executable nullbinwinutils.exe in the Hadoop binaries.
- Caused by: org.xml.sax.SAXParseException; systemId: file:/home/hadoop/hive-0.12.0/conf/hive-site.xml; lineNumber: 5; columnNumber: 2; The markup in the document following the root element must be well
- 一脸懵逼学习Hadoop分布式集群HA模式部署(七台机器跑集群)
- 一脸懵逼学习hadoop之HDFS的java客户端编写
- Hadoop阅读笔记(五)——重返Hadoop目录结构
- 008-Hadoop Hive sql语法详解3-DML 操作:元数据存储
- Hadoop 搭建分布式环境 hadoop-3.0.0.tar.gz
- Hadoop之—— CentOS Warning: $HADOOP_HOME is deprecated解
- 通过Hadoop安全部署经验总结,开发出以下十大建议,以确保大型和复杂多样环境下的数据信息安全。
- MapReduce与Hadoop之比较
- 大数据Hadoop之——部署hadoop+hive环境(window10)
- 大数据Hadoop之——实时计算流计算引擎Flink(Flink环境部署)
- 大数据Hadoop之——EFAK安全认证实现(kafka+zookeeper)
- 大数据Hadoop之——Hadoop HDFS多目录磁盘扩展与数据平衡实战操作
- 大数据Hadoop之——Spark集群部署(Standalone)
- 大数据Hadoop之——任务调度器Oozie(Oozie环境部署)
- Hadoop之hadoop-mapreduce-examples测试执行及报错处理
- Root cause: BlockMissingException【查看修复HDFS中丢失的块】ORG.APACHE.HADOOP.HDFS.BLOCKMISSINGEXCEPTION: COULD
- 101_Hadoop安装部署
- Hadoop HA 部署
- Apache Hadoop 3.x 版本的HA高可用配置和部署
- Hadoop(18):MapReduce框架原理之数据清洗(ETL)
- Hadoop(3):Hadoop安装和部署过程中的常见问题

