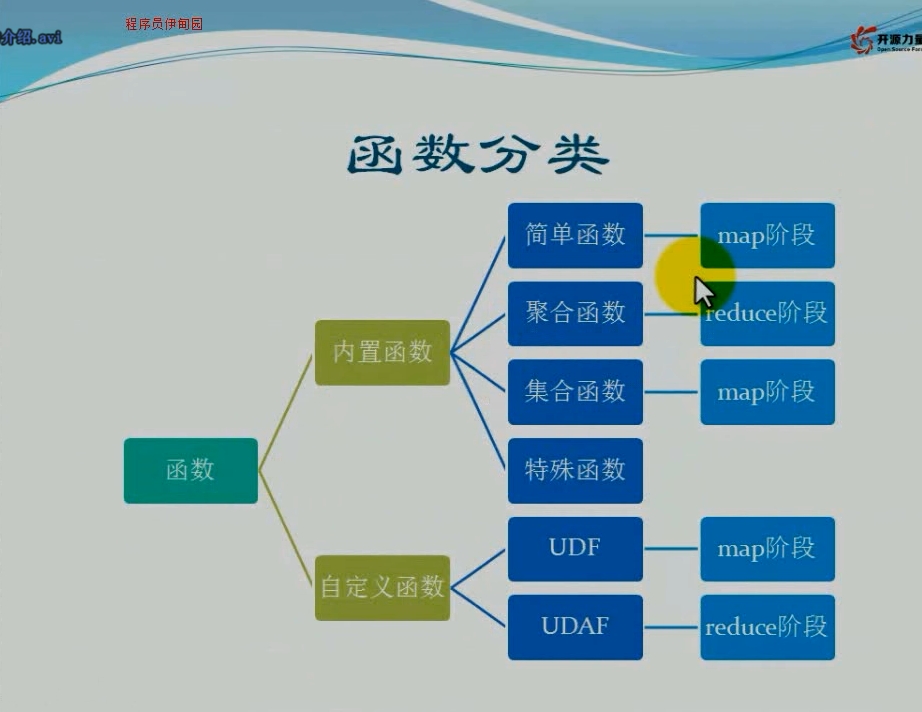
hive内置函数详解(分析函数、窗口函数)
cli命令
show functions;
desc function concat;
desc function extended concat;查看某个函数怎么使用的例子
nvl函数
coalesce(v1,v2,...)返回参数中第一个非空值,如果所有值都为null返回null;
set.cli.print.header=true;
winfunc
员工 工资 标识
id money type
关系型运算符优先级高到低为:not and or
and or 优先级
select id ,money from winfunc where id=1001 or id=1002
and money =100;
结果
1001 100
1001 150
1001 200
1001 150
1002 100
正确的sql应该是
select id ,money from winfunc where (id=1001 or id=1002) and money =100;
结果
1001 100
1002 100
if(con,v1,v2)
select if(2 1,v1,v2) from dual;
v1
case when
select case when id=1001 then v1 when id=1002 then v2 else v3 end from winfunc;
get_json_object
select get_json_object({"name":"jack","age":"20"},$.name) from dual;
jack
parse_url
select parse_url(http://facebook.com/path1/p.php?k1=v1 k2=v2#Ref1, HOST) from
lxw_dual;
facebook.com
select parse_url(http://facebook.com/path1/p.php?k1=v1 k2=v2#Ref1, QUERY, k1)
from lxw_dual;
v1
concat_ws比concat多了个拼接字符串之间的分隔符
concat_ws(string SEP,array string )对数组里的值处理
collect_set(id)去重返回数组
select collect_set(id) from winfunc;
["1001","1002","1003","1004"]
collect_list(id)不去重返回数组
select collect_list(id) from winfunc;
partition by关键字是oracle中分析性函数的一部分,它和聚合函数不同的地方在于它能返回一个分组中的多条记录,而聚合函数一般只有一条反映统计值的记录
sum() over (PARTITION BY ...) 是一个分析函数。 他执行的效果跟普通的sum ...group by ...不一样,它计算组中表达式的累积和,而不是简单的和。
Group By 和 Having, Where ,Order by这些关键字是按照如下顺序进行执行的:Where, Group By, Having, Order by。
在这四个关键字中,只有在Order By语句中才可以使用最终视图的列名,如:
SELECT FruitName, ProductPlace, Price, ID AS IDE, Discount
FROM T_TEST_FRUITINFO
WHERE (ProductPlace = Nchina)
ORDER BY IDE
这里只有在ORDER BY语句中才可以使用IDE,其他条件语句中如果需要引用列名则只能使用ID,而不能使用IDE。
ORDER BY 子句中的列必须包含在聚合函数或 GROUP BY 子句中。
GROUP BY 和 ORDER BY一起使用时,ORDER BY要在GROUP BY的后面。
一、窗口函数
first_value(求组的第一个值)
select id,money,
first_value(money) over (partition by id order by money
rows between 1 preceding and 1 following)
from winfunc
每行对应的数据窗口是从第一行到最后一行
rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following
lead(money,2) 取后面距离为2的记录值,没有就取null
select id,money,lead(money,2) over(order by money) from winfunc
lag(money,2)于lead相反
rank()排序函数与row_number()
select id,money, rank() over (partition by id order by money) from winfunc
结果
1001 100 1
1001 150 2
1001 150 2
1001 200 4
dense_rank()
select id,money, dense_rank() over (partition by id order by money) from winfunc
结果
1001 100 1
1001 150 2
1001 150 2
1001 200 3
cume_dist()
计算公式:CUME_DIST 小于等于当前值的行数/分组内总行数–比如,统计小于等于当前薪水的人数,所占总人数的比例
select id,money, cume_dist() over (partition by id order by money) from winfunc
结果
1001 100 0.25
1001 150 0.75
1001 150 0.75
1001 200 1
percent_rank(),第一个总是从零开始
PERCENT_RANK() = (RANK() – 1) / (Total Rows – 1)
计算公式:(相同值最小行号-1)/(总行数-1)
结果
1001 100 0
1001 150 0.33
1001 150 0.33
1001 200 1
ntile(2) 分片
asc时, nulls last为默认
desc时, nulls first为默认
select id,money, ntile(2) over (order by money desc nulls last) from winfunc;
混合函数(使用java里面的方法)
java_method和reflect是一样的
select java_method("java.lang.Math","sqrt",cast(id as double)) from winfunc;
UDTF表函数explode()配合lateral view关键字
select id ,adid from winfunc lateral view explode(split(type,B)) tt as adid
1001 ABC
列转行
1001 A
1001 C
正则表达式函数
like 字符"_"表示任意单个字符,而字符"%"表示任意数量的字符
rlike后面跟正则表达式
select 1 from dual where footbar rlike ^f.*r$;
正则表达式替换函数
regexp_replace(string A,string B,string C)
将字符串A中符合java正则表达式B的部分替换为C
select regexp_replace(foobar,oo|ar,) from dual;
返回fb
regexp_extract(string subject,string pattern,int index)
select regexp_extract(foothebar,foo(.*?)(bar),1) from dual;
返回the,()正则表达式中表示组,1表示第一个组的索引
1.贪婪匹配(.*), |一直匹配到最后一个|
select regexp_extract(979|7.10.80|8684,.*\\|(.*),1) from dual;
返回8684
2.非贪婪匹配(.*?)加个问号告诉正则引擎,尽可能少的重复上一个字符
select regexp_extract(979|7.10.80|8684,(.*?)\\|(.*),1) from dual;
本文出自 “点滴积累” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://tianxingzhe.blog.51cto.com/3390077/1710582
hive的窗口函数、分析函数有哪些? 窗口函数FIRST_VALUE:取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,第一个值LAST_VALUE: 取分组内排序后,截止到当前行,最后一个值LEAD(col,n,DEFAULT) :用于统计窗口内往下第n行值。第一个参数为列名,第二个参数为往下第n行(可选,默认为1),第三个参数为默认值(当往下第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)LAG(col,n,DEFAULT) :与lead相反,用于统计窗口内往上第n行值。第一个参数为列名,第二个参数为往上第n行(可选,默认为1),第三个参数为默认值(当往上第n行为NULL时候,取默认值,如不指定,则为NULL)OVER从句1、使用标准的聚
SQL、Pandas、Spark:窗口函数的3种实现 窗口函数是数据库查询中的一个经典场景,在解决某些特定问题时甚至是必须的。个人认为,在单纯的数据库查询语句层面【即不考虑DML、SQL调优、索引等进阶】,窗口函数可看作是考察求职者SQL功底的一个重要方面。 前期个人以求职者身份参加面试时被问及窗口函数的问题,近期在作为面试官也提问过这一问题,但回答较为理想者居少。所以本文首先窗口函数进行讲解,然后分别从SQL、Pandas和Spark三种工具平台展开实现
相关文章
- PHP 5.4 已废弃 magic_quotes_gpc,PHP安全转义函数详解(addslashes 、htmlspecialchars、htmlentities、mysql_real_escape_string、strip_tags)
- Linux C 字符函数 getchar()、putchar() 与 EOF 详解
- Linux C fcntl()函数详解
- 详解JMeter函数和变量
- Uploadify 3.2 参数属性、事件、方法函数详解
- 从零开始入门 K8s| 详解 Pod 及容器设计模式
- 分区函数Partition By的与row_number()的用法以及与排序rank()的用法详解(获取分组(分区)中前几条记录)
- OpenGL ES 详解纹理生成和纹理映射步骤以及函数
- linux日志管理命令详解
- MySQL explain执行计划详解
- KestrelServer详解[2]: 网络连接的创建
- 一文详解Java日志框架JUL
- Greenplum 架构详解 & Hash Join 算法介绍
- 016-Hadoop Hive sql语法详解6-job输入输出优化、数据剪裁、减少job数、动态分区
- Kubernetes集群Pod资源钩子函数详解(十一)
- C# 泛型详解
- Linux下MongoDB安装和配置详解
- 通信协议演进与JCE协议详解
- UICC 之 USIM 详解全系列——常用命令详解与实例说明
- Linux命令详解之vi
- 【Kubernetes】 DaemonSet 详解
- 手把手调参 YOLOv8 模型之 训练|验证|推理配置-详解
- Java8之Function函数、BiFunction函数详解
- java8 函数编程Consumer使用详解
- L2TP详解(一)
- Oracle的学习心得和知识总结(三)|Oracle数据库重要函数详解 单行函数(一)(建议收藏 持续更新...)
- linux内核radeon gpu源码解析4 —— drm_get_pci_dev函数详解1

