Android NIO 系列教程(八) --NIO简易聊天室
2023-09-27 14:28:04 时间
Android NIO 系列教程(一) NIO概述
Android NIO 系列教程(二) – Channel
Android NIO 系列教程(三) – Buffer
Android NIO 系列教程(四) – Selector
Android NIO 系列教程(五) – FileChannel
Android NIO 系列教程(六) – SocketChannel
Android NIO 系列教程(七) – ServerSocketChannel
Android NIO 系列教程(八) --NIO简易聊天室
从上面几章,我们已经知道了 NIO 的 SocketChannel ,ServerSocketChannel,Selector 等知识,这章我们来做个总结,实现一个简易的聊天室。
今天要实现的效果如下:
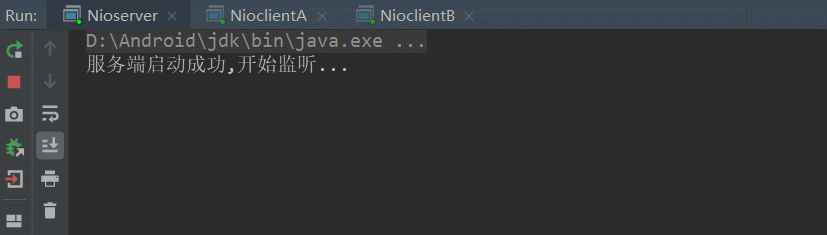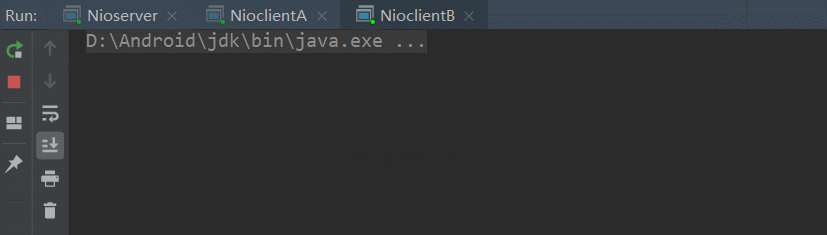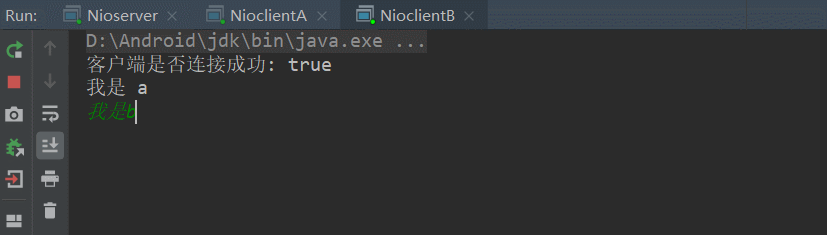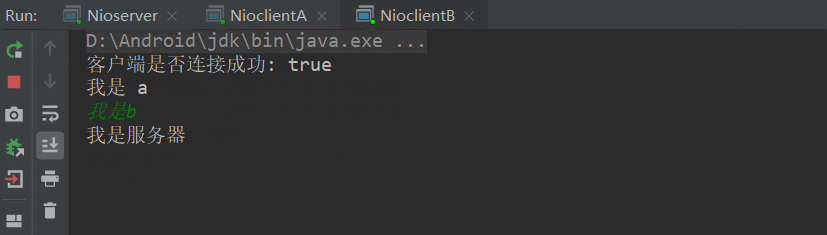
首先,先构建服务器,从上面几章的理解,我们总结出以下步骤
- 创建 selector
- 创建ServerSocketChannel
- 创建非阻塞模式
- 绑定要监听的端口
- 向selector注册 channel
- 通过 selectionKeys 拿到想要监听的事件
所以服务端的代码如下:
首先是初始化:
//1.创建 selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//2.创建 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//3.绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(Constants.PORT));
//4.设置为非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//5.将channel注册到selector中
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
System.out.println("服务端启动成功,开始监听...");
接着监听感兴趣的事件,比如客户端接入和客户端的数据:
// 7.通过selectedKeys() 拿到 selectedKeys 集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//拿到 selectedKeys 实例
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
//移除 selectedKeys 实例
iterator.remove();
/**
* 如果是接入事件
*/
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()){
handleAccept(serverSocketChannel,selector);
}
/**
* 如果是可读事件
*/
if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
handleRead(selectionKey,selector);
}
}
如果是 accept 事件,我们处理的比较简单,就打印个提示即可:
/**
* 处理接受事件
* @param serverSocketChannel
* @param selector
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void handleAccept(ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel,Selector selector) throws IOException {
//拿到 SocketChannel 客户端
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("新客户端连接:"+socketChannel.getRemoteAddress().toString());
//设置 socketchannel 为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//客户端注册读事件,这样我们才能接收到客户端的信息
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//发送 conected 提示服务端已经接收到
// ByteBuffer buf = Charset.forName("utf-8").encode(Constants.CLIENT_CONNECTED);
// socketChannel.write(buf);
}
注意到对 socketChannel 注册成 read 模式,这样,客户端的数据我们才能接收到。
接着是监听:
/**
* 处理客户端读事件,并广播出去
* @param selectionKey
* @param selector
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void handleRead(SelectionKey selectionKey,Selector selector) throws IOException {
//拿到已经就绪的 channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
if (channel != null) {
//读取channel的数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int readByte = channel.read(buf);
while (readByte > 0) {
//切换为读模式
buf.flip();
String msg = String.valueOf(Charset.forName("utf-8").decode(buf));
sb.append(msg);
readByte = channel.read(buf);
}
buf.clear();
//将 channel 继续注册为可读事件
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
if (sb.length() > 0) {
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress().toString()+" : " + sb.toString());
//返回数据
//String responeMsg = sb.length();
//channel.write(Charset.forName("utf-8").encode(responeMsg));
//广播
broadcastMsg(selector,channel,sb.toString());
}
}
}
注释已经很清楚了,这里就不过多解释了。然后广播的代码为:
/**
* g
* @param selector
* @param targetChannel
* @param msg
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void broadcastMsg(Selector selector,SocketChannel targetChannel,String msg) throws IOException {
//拿到已连接的客户端个数
Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.keys();
for (SelectionKey selectionKey : keys) {
Channel channel = selectionKey.channel();
//不是自己本身,其他通道才需要拿到信息
if (channel instanceof SocketChannel){
if (targetChannel != null &&
channel == targetChannel ){
continue;
}
((SocketChannel) channel).write(Charset.forName("utf-8").encode(msg));
}
}
}
接着是客户端,我们也总结了以下步骤:
- 创建 selector
- 创建 SocektChannel
- 设置非阻塞模式
- 使用 connect 连接服务器
- 通过 read() 或 write() 读写数据
首先,首先初始化为:
//1.创建 selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//2.创建SocketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
//3.设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4.连接服务器
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", Constants.PORT));
//注册读事件,读取服户端信息
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
接着,读取终端的信息,并发送给服务端:
if (socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
while (!isFinish) {
String msg = br.readLine();
if ("bye".equals(msg)) {
isFinish = true;
sendData(socketChannel,"客户端A退出了");
readerThread.exit();
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("服务端已退出");
break;
} else {
sendData(socketChannel,msg);
}
}
}
其中 sendData 如下:
/**
* 给服务器发送数据
* @param channel
* @param msg
* @throws IOException
*/
private static void sendData(SocketChannel channel,String msg) throws IOException {
if (channel.isConnected()){
channel.write(Charset.forName("utf-8").encode(msg));
}
}
而读取服务端的信息,则另开一个线程去监听数据即可:
static class ReaderThread extends Thread{
private Selector selector;
private boolean isFinish = false;
public ReaderThread(Selector selector) {
this.selector = selector;
}
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
while (!isFinish){
//调用 select 方法,拿到 channel
int channels = selector.select();
if (channels == 0){
continue;
}
//如果能拿到,则通过 selectedKeys() 方法,拿到 selectedKeys 的集合
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//拿到 selectedKeys 实例
SelectionKey selectionKey = iterator.next();
//如果是可读事件
if (selectionKey.isReadable()){
//拿到 就绪的 SocketChannel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
if (channel != null) {
//读取channel的数据
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (channel.read(buf) > 0) {
//切换为读模式
buf.flip();
String msg = String.valueOf(Charset.forName("utf-8").decode(buf));
sb.append(msg);
}
//将 channel 继续注册为可读事件
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
if (Constants.CLIENT_CONNECTED.equals(sb.toString())){
sendData(channel,"我是客户端A");
}else {
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
exit();
}
}
public void exit(){
isFinish = true;
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这样,我们一个简易的聊天室就完成了。
可能你会问到,这样并没有体现 NIO 的单个 selector 和 多个channel 的优势啊,还有其他等问题,这些,等我们后面再去优化。
相关文章
- 精通Android自定义View(十三)事件分发简述
- Android入门之ActionBar实现Tab导航
- 《Android游戏开发详解》一2.15 改进程序
- 《Android应用开发从入门到精通》——第1章,第1.3节小结
- 关于Android中根据ID名动态获取资源的两个方法
- android:Android中用文件初始化sqlite数据库
- 详解Android中AsyncTask的使用
- Android Backup功能之全面实战
- Flutter iOS风格文本输入框CupertinoTextField光标在Android中未与提示文本对齐
- Android学习站点推荐
- 常见Android测试工具简介
- 【Android学习】kotlin语言基础知识学习

