1.1、基于增量式生成遮挡与对抗抑制的行人再识别(论文阅读与理解)
[5]. Cairong Zhao, Xinbi Lv, Shuguang Dou, Shanshan Zhang, Jun Wu, Liang Wang.
Incremental Generative Occlusion Adversarial Suppression Network for Person ReID(基于增量式生成遮挡与对抗抑制的行人再识别).
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021. [pdf][code]
基于增量式生成遮挡与对抗抑制的行人再识别
赵才荣 , 吕心铋 , 窦曙光 , 张珊珊 , 吴俊 , 王亮
同济大学, 南京理工大学, 复旦大学, 中科院自动化所
TIP 2021
撰稿人:赵才荣,吕心铋,窦曙光
推荐理事:林宙辰
原文标题:Incremental Generative Occlusion Adversarial Suppression Network for Person ReID
原文地址:https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9397375
代码链接:https://github.com/Vill-Lab/IGOAS
可用于以下应用:行人重识别、找相似图(谷歌识图)...
◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆
本文贡献:
1) The IGOAS network first generates easy-to-hard occluded data through the IGO block and then suppresses the generated occluded region with the adversarial suppression branch. In this process of adversarial learning, the IGOAS learns a more discriminative and robust feature for the occlusion problem.
IGOAS网络首先通过IGO块生成由易到难的遮挡数据,然后用对抗性抑制分支抑制生成的遮挡区域。在这种对抗学习的过程中,IGOAS学习到遮挡问题的更具鉴别性和鲁棒性的特征。
2) We propose an incremental generative block to generate easy-to-hard occlusion data. It makes the network more robust to occlusion by gradually learning harder occlusion instead of hardest occlusion directly.
3) We develop an occlusion suppression module in the G&A framework. By suppressing the occlusions, our model can focus less on the background and more on the foreground.
摘要
在遮挡场景下,行人图像包含遮挡和较少具有辨别力的行人信息。之前的工作设计复杂的模块来捕捉隐性信息(包含人体姿态关键点, 掩码图和空间信息)来实现有效地对齐。少量研究工作专注于数据增强,只带来有限的性能提升。为了解决遮挡问题,我们提出一种新增量式生成遮挡与对抗抑制(Incremental Generative Occlusion Adversarial Suppression ,IGOAS)方法。在遮挡数据Occluded-DukeMTMC上,我们的方法在Rank-1和mAP指标上分别达到了60.1%和49.4%。
行人重识别(ReID【Re-identification】)的几种类型介绍:

背景
为了解决遮挡问题,现有的方法不断地试图设计复杂的模块来捕捉隐含的信息(如姿态关键点和掩码图)。这样做是为了迫使网络将重点放在非遮挡身体区域的具有辨别力的特征上并进一步实现空间错位下的匹配。
使用数据增强有它的弊端
一般来说,数据增强不需要任何额外的参数学习并且能有效提高模型对数据变化(包括遮挡)鲁棒性。然而,由于困难训练样本的随机生成策略,其带来的性能提升有限。此外,传统的基于单样本的数据增强方法对单张图像进行随机裁剪[3]、随机擦除[4]等操作,有时会使训练数据更加复杂多样。
在由易到难的学习策略和对抗性思想的启发下,我们提出了一种新颖的增量生成式遮挡对抗性抑制(IGOAS)网络来解决这个具有挑战性的问题。
具体来说,我们首先提出一个增量生成遮挡(IGO)模块。不同于传统的基于单样本的数据增强方法,IGO采用了一种由易到难的方法来生成遮挡数据而不是随机的,这使得网络对遮挡更加鲁棒。其次,我们提出了一个全局与对抗抑制(G&A)框架,使模型忽略了生成的遮挡区域,这产生一个对抗性的过程。该方法的示意图如图1所示。
全局与对抗抑制(G&A)框架的整体结构:
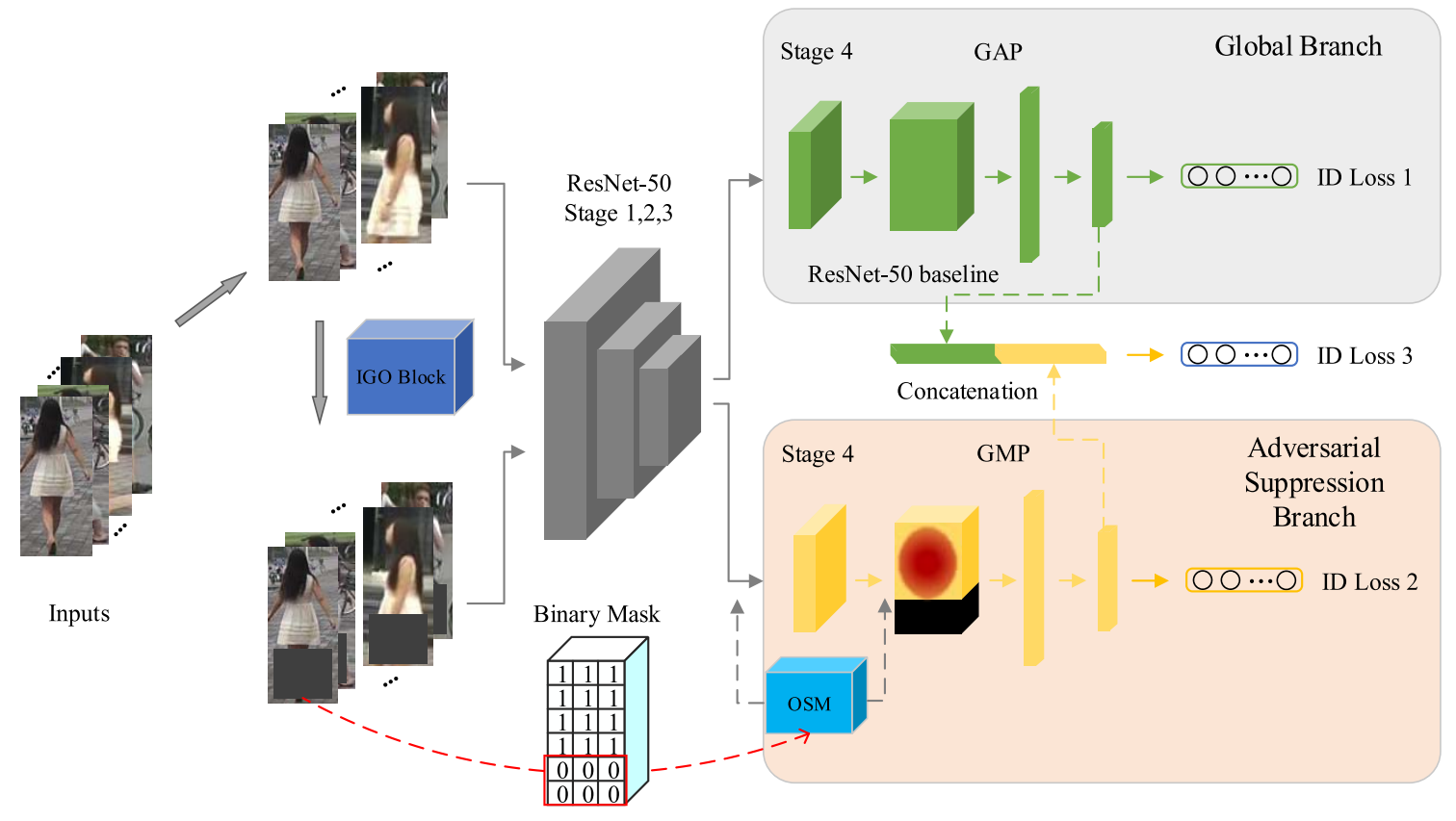
Fig. 2. The flowchart of the proposed IGOAS network:
As shown in Fig. 2, the G&A framework is composed of a backbone network, a global branch(提取图像稳定的全局特征), and an adversarial suppression branch(使用OSM通过将生成的遮挡区域的响应抑制为零,从而对前景信息给予更多关注).
1) Backbone Network: We use the ResNet-50 Stages 1, 2, and 3 as a backbone network. We modify the Stage 4 and do not employ down-sampling operation in the first residual block for a fair comparison with the recent works. In this way, we get a larger feature map of size 2048 × 24 × 8. In our framework, Stages 1, 2, and 3 share weights for fewer parameters learning, and Stage 4 does not. We need Stage 4 to focus on a specific task in each branch.
2) Global Branch: We need the global branch to learn steady global features(提取图像稳定的全局特征).Thus, we adopt the ResNet-50 baseline structure as the global branch, considering its competitive performance to re-id.
- Specifically, following Stage 4, we employ a global average pooling (GAP) to get a 2048-d feature vector.
- The vector is further reduced to 512-d via a fully connected layer,
- a batch normalization (BN) layer ,
- and a ReLU layer. Finally,
- a 512-d global feature vector is output for calculating classification loss.
3) Adversarial Suppression Branch: The adversarial suppression branch aims to pay more attention to foreground information by suppressing the response of the generated occlusion region to zero.(使用OSM通过将生成的遮挡区域的响应抑制为零,从而对前景信息给予更多关注)
We develop an occlusion suppression module (OSM) to achieve this goal.
运行步骤:
1、Specifically, in the training phase, the IGO block converts the raw input into occluded data,
2、and then the raw data and the occluded data are entered into the respective branch of the frame for feature extraction.
- In global branch, we retain the ResNet-50 baseline to extract steady global features of the raw data.
- In adversarial suppression branch, the OSM and a global max pooling operation are employing to force this branch to suppress the occlusion’s response and strengthen discriminative feature representation on non-occluded regions of the pedestrian.
3、Finally, we get a more robust pedestrian feature descriptor by concatenating two branches’ features. And in the test phase, the incremental occlusion block won’t be performed.
如何生成ReID中的mask?
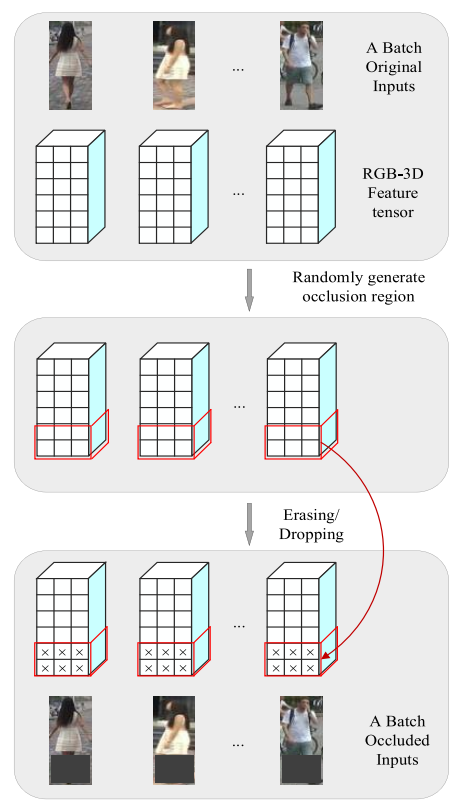
Fig. 4. Simple flow of the batch-based incremental occlusion block in a batch: A cuboid represents the RGB-3D feature tensor of one image.
For a batch image, the block randomly generates uniform size and position of occlusion region, such as the red cuboid region.
All the units inside will be erasing(擦除) with random value in [0, 255] to simulate images suffer from occlusions.
Notably, the size of occlusion increases with the number of training iterations.
生成mask的过程:
image
--> RGB-3D feature tensor
--> randomly generate occlusion region( partical region of the image is erased )
--> reased region is filled with random value in [0, 255](这里的遮挡区域是所有的像素点都是一个值,而不是说每个像素点随机为[0-255])
全局与对抗抑制框架
G&A框架由一个主干网络、一个全局分支和一个对抗性抑制分支组成。
我们使用全局分支来学习稳健的全局特征。
而对抗抑制分支旨在通过将生成的遮挡区域的响应抑制为零,从而对前景信息给予更多关注。
我们设计一个遮挡抑制模块(OSM)来实现这一目标。
OSM的结构如图2所示:

步骤:
- 输入的特征
首先被送入注意力模块以获得精炼的特征
。在本文中,我们使用CBAM[8]作为OSM的注意力模块。
- 然后,通过对二进制掩码和
进行元素级的操作乘法得到
。其中二进制掩码是通过缩放人工设计的图像遮挡掩码得到。
- 最后,
通过掩码损失来监督
(通过掩码损失对
进行监督),这样模型在反向传播的过程中就能学会忽略背景区域(图2中
的黑色部分)。
掩码损失可以被表述为:
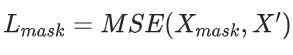
其中 代表均方误差。更具体地说。掩码损失函数使区域内的特征对应于遮挡的区域内的特征尽可能为零。由于遮挡的位置是已知的和随机的,它可以作为注意力模块的监督信息来学习抑制生成的遮挡反应。
介绍:(a)基于单个随机遮挡块与(b)基于批量的增量遮挡块
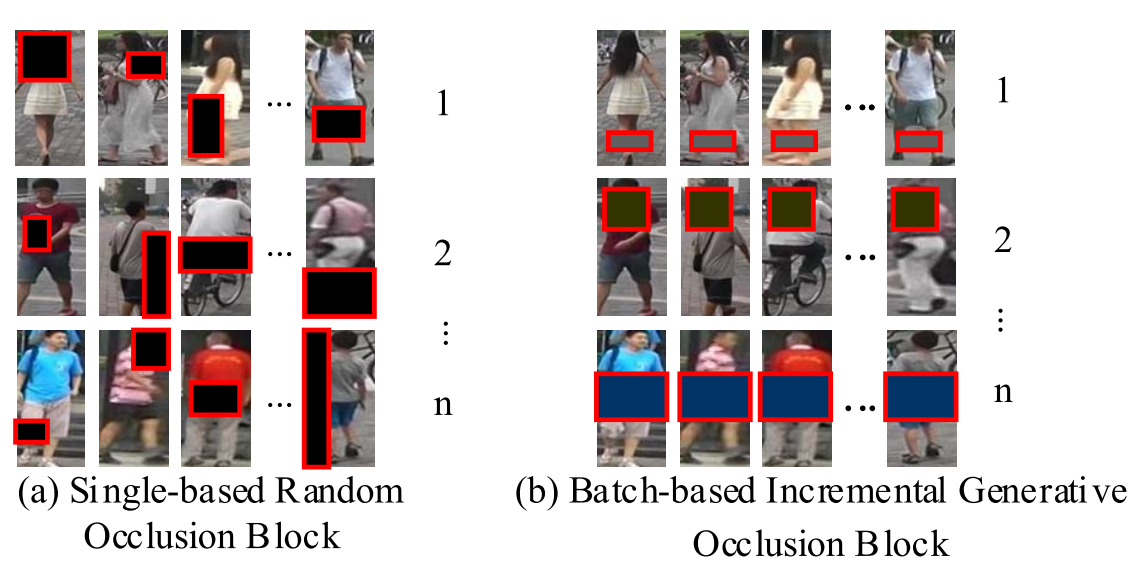

Fig. 5. Comparison of (a) single-based random occlusion block, (b) batch-based incremental occlusion block.
In (a), each data in the batch suffers from a variable-size and variable-position occlusion.(随机位置、随机大小)
In (b), all data in the batch suffer from occlusions with a uniform size and position. But as the number of iterations increases, it allows to generate variable-size, variable-position, and easy-to-hard occlusions.(多尺寸、多位置、由易到难的遮挡)
是否可以在IGOB的基础上增加为一幅图像上有多个遮挡,而不是仅仅一个遮挡?
增量式生成遮挡模块
为了加强网络应对遮挡行人再识别,我们提出了一个基于批量样本的数据增强方法-增量式生成遮挡模块。我们随机生成从易到难的遮挡数据来模拟遭受遮挡的图像,通过逐渐学习更难的遮挡而不是直接学习最难的遮挡,使网络对遮挡更加鲁棒。算法细节如下所示:

与其它数据增强方法Batch DropBlock[11], Slow-Drop Block[14]和Batch Random Erasing Block的对比如下图所示:
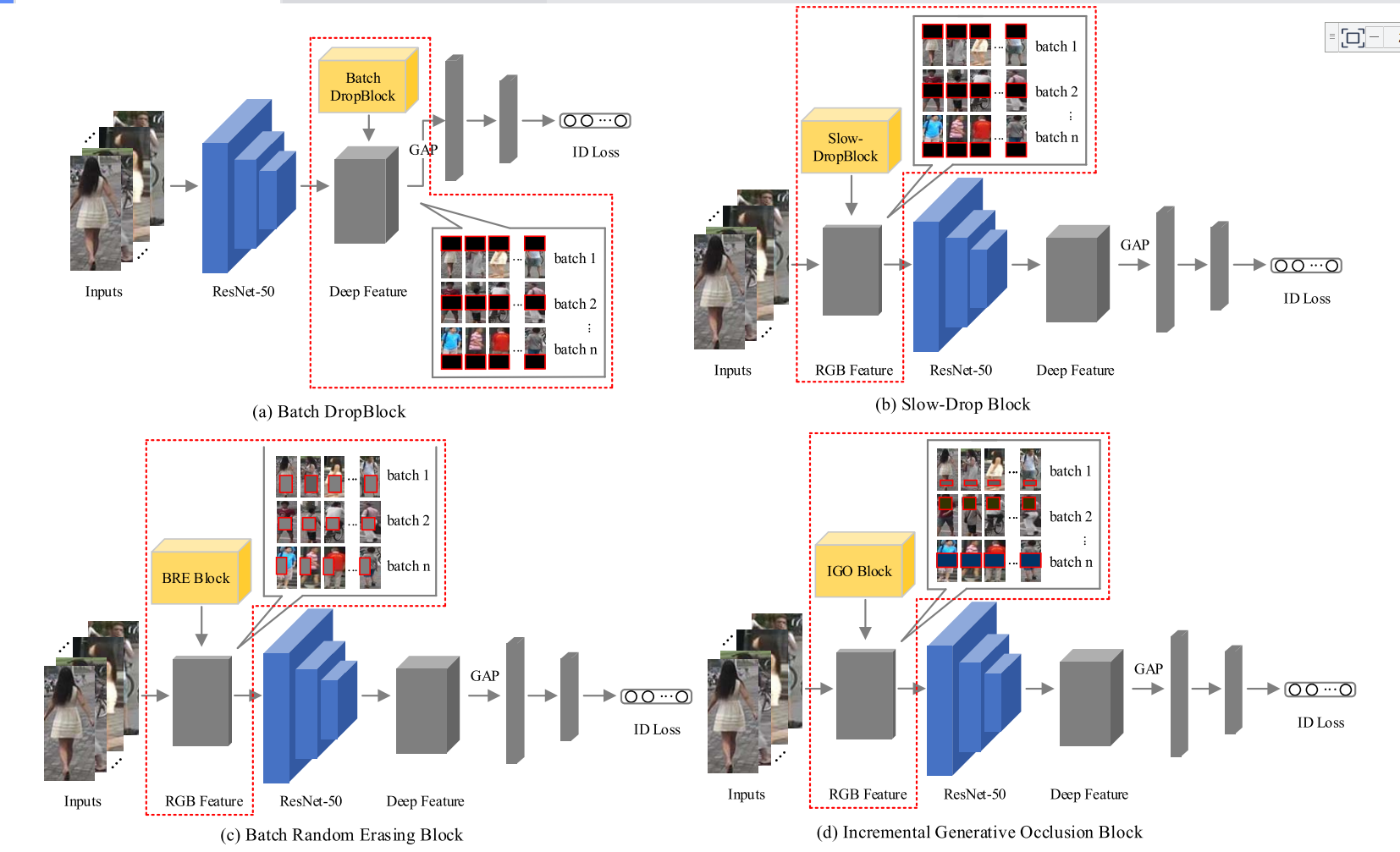
Fig. 6. Comparison of (a) Batch DropBlock, (b) Slow-Drop Block, (c) Batch-based Random Erasing Block and (d) Incremental Generative Occlusion Block.
In (a), batch dropblock randomly drops the same region (fixed-size) of all deep features to reinforce the attentive feature learning on local regions. In (b), slow-dropblock moves the dropping operation from the deep feature layer towards the input images ensure inputs diversity for feature learning.
In (c), batch-based random erasing block generates the occlusion mask of random size and random position and replaces the original image with mean of ImageNet.(随机尺寸、随机位置)
In (d), our incremental occlusion block generates variable-position(可变位置) and easy-to-hard occlusions(由易到难的遮挡) to enrich the diversity of occlusions, more various images under occlusion can be generated. The easy-to-hard learning strategy also make the network more robust to occlusion by gradually learning harder occlusion instead of hardest occlusion directly.(可变位置、遮挡由少逐渐变多):在(d)中,这种数据增强方法宣称可以生成更多的遮挡图像【与c相比,能有更多的遮挡图像吗?】,同时easy-to-hard使network more robust【what is the reason of more robust?】。
Fig. 9. 在阶段4被不同的遮挡方法学到的特征图的可视化结果

The first, second, third, and fourth rows show the results for the baseline (ResNet-50) without occlusion simulation, the IGOAS joint with single-based random occlusion, the IGOAS joint with batch-based random occlusion, and the IGOAS joint with batch-based incremental occlusion.
实验结果
图8:不同分支学习的阶段4特征图的可视化
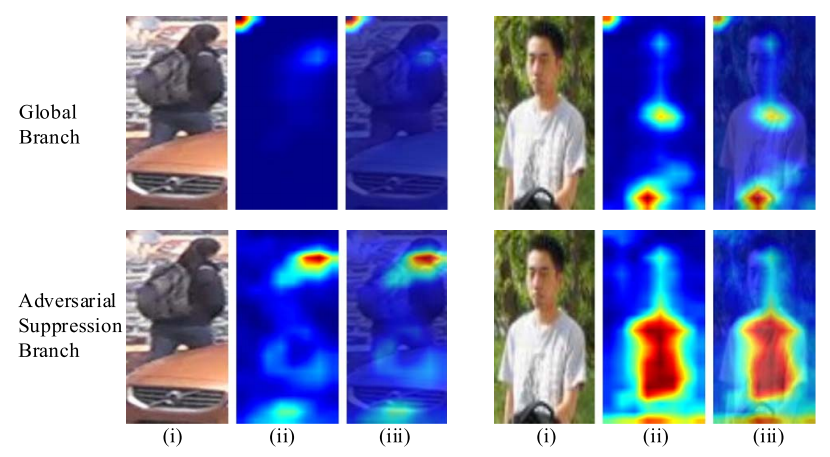
The first and second rows show the results for the global branch and the attentive branch.
From left to right, (i) Original images, (ii) Activation map, and (iii) Overlapped image.
In the heat map, the response increases from blue to red.
我们在两个遮挡行人数据集-Occluded-DukeMTMC和Occluded-REID和两个完整行人数据集-Market-1501和DukeMTMC-reID上评价提出的算法。为了证明我们提出方法的有效性,我们提出一个IGOAS的基础版本。一方面我们直接使用基于批量样本的随机擦除模块来生成遮挡,另一方面,我们使用CBAM来替换OSM在网络中的位置。我们将这种组合的方法称为BRE+CBAM。
表1. 在Occluded-DukeMTMC上的性能
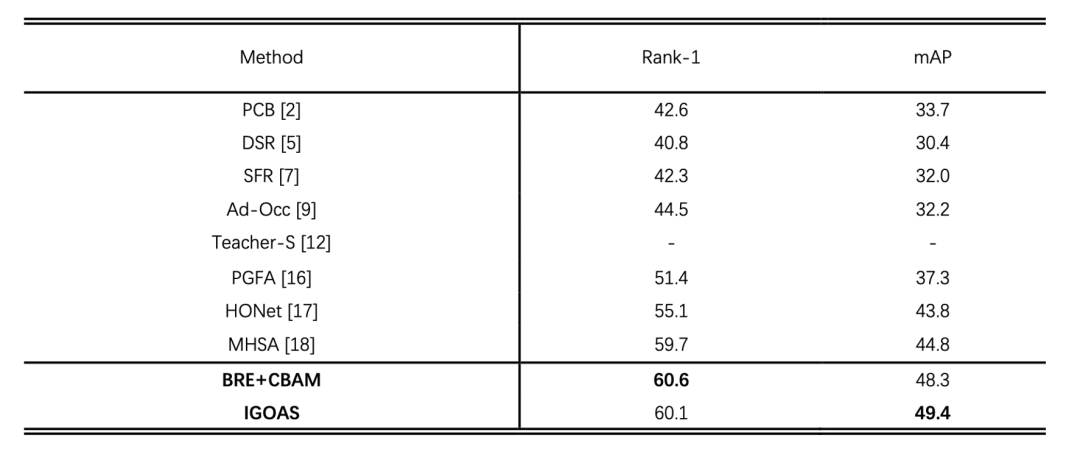
表 2. 在Occluded-ReID上的性能

表 3. 在两个完整行人数据集上的性能

实验结果表明,我们的方法相比最先进的遮挡方法HONet和MHSA能获得更好的效果。在完整的行人数据集中,IGOAS也表现出具有竞争力的性能。值得注意的是,以上方法大多使用额外的信息和复杂的网络结构。我们的方法没有使用任何额外信息,仅通过生成遮挡再抑制生成的遮挡来解决行人再识别中的遮挡问题。
相关文章
- java 图片识别 tess4j_JAVA使用Tess4J进行ocr识别
- C++版OpenCV使用神经网络ANN进行mnist手写数字识别[通俗易懂]
- 反光衣实时识别检测系统
- 基于ArduinoUNO的LD3320语音识别+SYN6288语音合成的智能分类垃圾桶
- opencv lsd算法_opencv目标识别
- 【顶刊论文分享】识别恶意bot
- 自制正方软件系统验证码的识别程序(1/4)
- 如何识别文章是ChatGPT AI写的,还是人写的?
- [Bioinformatics | 论文简读] csORF-finder:用于准确识别多物种编码短开放阅读框架的有效集成学习框架
- [Brief. Bioinformatics | 论文简读] CReSIL:从长读序列中准确识别染色体外环状DNA
- [Genome Biology | 论文简读] metaMIC:从头宏基因组组装的无参考错误组装识别和校正
- 内置AI算法的智能分析网关,如何将智能识别技术应用到生活场景中?
- 水面漂浮物垃圾识别检测系统 智慧水利
- 公开课笔记 | 如何运用商品识别技术重塑新零售关键节点?
- PRICAI 2016 论文精选 | 基于稀松K-SVD算法的自发性微表情识别
- 深圳南山区人民医院+腾讯:如何把 AI 应用在电子健康记录、肿瘤影像、医保欺诈识别中
- Oracle遇到硬盘问题无法识别(oracle 不识别硬盘)
- uSens与台湾厂商LEAPSY合作AR头显,内嵌自然手势识别

