Python 实现个人博客系统(附零基础python学习资料)
前言
项目描述
开发环境:PyCharm、python3.7、MySQL5.5
使用技术:服务端是使用Flask开发的,前端是使用的Layui和Markdown编辑器所实现的。
项目包含功能如下:(文末送读者福利)
注册:注册账号
登录:通过账号密码进行登录
写博客:写博客采用的Markdown编辑器完成的。可以发布自己的博客
我的博客:查看自己发布的博客并对其管理
我的评论:查看自己的所有评论并对其管理
修改密码
查看博客列表:查看所有已发布的博客
博客详情页:查看博客内容及评论信息,可以对当前博客进行评论
关于
项目目录

数据库设计
数据库一共设计了三张表:用户表、博客表、评论表。(文末送读者福利)
表之间的映射关系如下:

用户表和博客表一对多关系;用户和评论表一对多关系;博客表和评论表一对多关系。
其表的模型类代码如下:
class User(db.Model):
# 设置表名
__tablename__ = 'tb_user';
# id,主键并自动递增
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True)
username = db.Column(db.String(64), unique=True)
password = db.Column(db.String(256), nullable=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(64))
# 设置只可写入,对密码进行加密
def password_hash(self, password):
self.password = generate_password_hash(password);
class Blog(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'blog'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True)
title = db.Column(db.String(128))
text = db.Column(db.TEXT)
create_time = db.Column(db.String(64))
#关联用户id
user_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey('tb_user.id'))
user = db.relationship('User', backref='user')
class Comment(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'comment'
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True, autoincrement=True)
text = db.Column(db.String(256)) # 评论内容
create_time = db.Column(db.String(64))
# 关联博客id
blog_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey("blog.id"))
# 关联用户id
user_id = db.Column(db.Integer, db.ForeignKey("tb_user.id"))
blog = db.relationship("Blog", backref="blog")
user = db.relationship("User", backref="use")
功能实现
页面基本模板实现
页面使用的是Jinja2模板,Jinja2支持页面继承,所以导航栏重复性的页面代码,我们都可以写在一个文件中。这里我们先创建一个base.html文件,编写页面大致的框架。其他模块直接继承使用即可。
"en">
"UTF-8">
"stylesheet" href="/static/layui/css/layui.css">
"stylesheet" href="/static/css/base.css">
"/static/js/jquery.js">
"/static/layui/layui.js">
{% block css %}
{% endblock %}
"bg">
"layui-nav" lay-filter="">
"layui-nav-item">"/">在线博客平台
{% if username %}
"layui-nav-item{% block updatepwd_class %}{% endblock %}">"/updatePwd">修改密码
{% endif %}
"layui-nav-item{% block blog_class %}{% endblock %}">"/blog/blogAll">博客
"layui-nav-item{% block about_class %}{% endblock %}">"/about">关于
{% if username %}
"layui-nav-item" style="float: right; margin-right: 30px;">
"javascript:;">{{ name }}
"layui-nav-child">
"/blog/myBlog">我的博客
"/blog/myComment">我的评论
"/logout">注销
"layui-nav-item{% block write_class %}{% endblock %}" style="float: right">"/blog/writeBlog">写博客
{% else %}
"layui-nav-item{% block register_class %}{% endblock %}" style="float: right">"/register">注册
"layui-nav-item{% block login_class %}{% endblock %}" style="float: right">"/login">登录
{% endif %}
"content">
{% block content %}
{# 其他页面内容 #}
{% endblock %}
这里页面使用了Layui定义了一个导航栏,展示了对应的功能模块。其中{% if username %},username为后台存放在session中的一个键值对,用于判断用户是否登录了,有些功能登录后才显示。
base.html模板文件完成后,我们在定义一个index.html来做项目的首页,直接继承base.html。这样首页index.html就节省了很多代码。如下:
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"margin: 35vh;">在线博客平台
{% endblock %}
首页效果如下:

登录与注册功能
登录
先定义一个登录的视图函数,可以接收GET、POST请求,GET请求为跳转到登录页面,POST请求为处理登录提交的请求,验证是否登录成功,登录成功后把当前登录对象的用户名存入session会话中。
# 登录请求
@index.route('/login', methods=['POST', 'GET'])
def login():
if request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('login.html')
if request.method == 'POST':
username = request.form.get('username')
password = request.form.get('password')
user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first();
# check_password_hash比较两个密码是否相同
if (user is not None) and (check_password_hash(user.password, password)):
session['username'] = user.username
session.permanent = True
return redirect(url_for('index.hello'))
else:
flash("账号或密码错误")
return render_template('login.html');
登录页面是用Layui写的一组form表单,也是基础的base.html,代码如下:
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台.登录
{% endblock %}
{% block css %}
"stylesheet" href="/static/css/register.css">
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"register">
登录
"tip">
{% for item in get_flashed_messages() %}
{{ item }}
{% endfor %}
"layui-form" action="login" method="post">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-form-label">用户名
"layui-input-block">
type="text" name="username" required lay-verify="required" placeholder="请输入用户名" class="layui-input">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-form-label">密 码
"layui-input-block">
type="password" name="password" required lay-verify="required" placeholder="请输入密码" class="layui-input">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-input-block">
"layui-btn" lay-submit lay-filter="formDemo">立即提交
type="reset" class="layui-btn layui-btn-primary">重置
{% endblock %}
{% block login_class %}
layui-this
{% endblock %}
效果如下(账号和密码错误后,会有相应的提示信息):

注册和登录差不多,页面都是使用的同一个css样式文件,所以这里就贴代码出来了,需要的可以自行下载完整项目代码:GitHub地址。
修改密码
修改密码模块,因为数据库存放明文密码很不安全,所以这里使用了Werkzeug对密码进行了加密存储。对于WerkZeug密码加密想进一步了解的,可以访问Flask 使用Werkzeug实现密码加密。
因为数据库中存储的是加密后的密码,所以这里判断原密码是否正确需要使用check_password_hash函数进行判断。
定义一个修改密码的视图函数。
# 修改密码
@index.route("/updatePwd", methods=['POST', 'GET'])
@login_limit
def update():
if request.method == "GET":
return render_template("updatePwd.html")
if request.method == 'POST':
lodPwd = request.form.get("lodPwd")
newPwd1 = request.form.get("newPwd1")
newPwd2 = request.form.get("newPwd2")
username = session.get("username");
user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first();
if check_password_hash(user.password, lodPwd):
if newPwd1 != newPwd2:
flash("两次新密码不一致!")
return render_template("updatePwd.html")
else:
user.password_hash(newPwd2)
db.session.commit();
flash("修改成功!")
return render_template("updatePwd.html")
else:
flash("原密码错误!")
return render_template("updatePwd.html")
页面样式文件和登录注册引入的样式文件一致(原密码不正确或两次新密码不同,会给出相应的提示信息),代码如下:
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台.修改密码
{% endblock %}
{% block css %}
"stylesheet" href="/static/css/register.css">
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"register">
修改密码
"tip">
{% for item in get_flashed_messages() %}
{{ item }}
{% endfor %}
"layui-form" action="updatePwd" method="post">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-form-label">原密码
"layui-input-block">
type="password" name="lodPwd" required lay-verify="required" placeholder="请输入原密码" class="layui-input">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-form-label">新密码
"layui-input-block">
type="password" name="newPwd1" required lay-verify="required" placeholder="请输入新密码" class="layui-input">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-form-label">确认新密码
"layui-input-block">
type="password" name="newPwd2" required lay-verify="required" placeholder="请再次输入新密码" class="layui-input">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-input-block">
"layui-btn" lay-submit lay-filter="formDemo">立即提交
{% endblock %}
{% block updatepwd_class %}
layui-this
{% endblock %}
效果如下:

写博客
写博客,博客表中会保存标题、博客内容、当前时间等字段。如下是写博客的视图函数。
# 写博客页面
@blog.route('/writeBlog', methods=['POST', 'GET'])
@login_limit
def writeblog():
if request.method == 'GET':
return render_template('writeBlog.html')
if request.method == 'POST':
title = request.form.get("title")
text = request.form.get("text")
username = session.get('username')
# 获取当前系统时间
create_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first()
blog = Blog(title=title, text=text, create_time=create_time, user_id=user.id)
db.session.add(blog)
db.session.commit();
blog = Blog.query.filter(Blog.create_time == create_time).first();
return render_template('blogSuccess.html', title=title, id=blog.id)
保存博客时会获取到当前系统时间,当做博客的发布时间。博客保存成功后,会返回保存成功页面,下面会有讲解。
写博客对应的html文件,代码如下。
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台.写博客
{% endblock %}
{% block css %}
"stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/static/editor/css/editormd.css"/>
"/static/editor/editormd.js" type="text/javascript">
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"main">
"/blog/writeBlog" class="layui-form" method="post">
"layui-form-item">
"layui-form-label">标 题
"layui-input-block">
type="text" name="title" lay-verify="required" placeholder="请输入标题" class="layui-input">
"editormd">
"text" lay-verify="required" style="display:none;" >
"layui-form-item">
"layui-input-block">
"layui-btn" style="width: 150px" lay-submit lay-filter="formDemo">保存
type="text/javascript">
layui.use('form', function(){
var form = layui.form;
form.on('submit(formDemo)', function(data){
});
});
$(function() {
editormd("editormd", {
width: "100%",
height: 600,
syncScrolling: "single",
path: "/static/editor/lib/", //依赖lib文件夹路径
emoji: true,
taskList: true,
tocm: true,
imageUpload: true, //开启本地图片上传
imageFormats: ["jpg", "jpeg", "gif", "png"], //设置上传图片的格式
imageUploadURL: "/blog/imgUpload" //上传图片请求路径
});
});
{% endblock %}
{% block write_class %}
layui-this
{% endblock %}
写博客这里采用的是Markdown编辑器,对于Markdown编辑器之前写过一篇Markdown的使用方法,只不过后端用的是Java语言,感兴趣的小伙伴可以看看,Markdown的基本使用。Flask与之不同的是,后端接收Markdown上传图片时的语句不同,Flask接收Markdown上传图片的语句:
file = request.files.get('editormd-image-file');
其他的基本相同,毕竟Markdown是属于前端的知识,后端只要求根据规定个格式返回数据即可。
因为Markdown支持图片上传,那就必须的有文件上传的方法了。如下定义一个文件上传的视图函数(这里需要注意的是Markdown上传图片是使用的POST方法)。
# 上传图片
@blog.route('/imgUpload', methods=['POST'])
@login_limit
def imgUpload():
try:
file = request.files.get('editormd-image-file');
fname = secure_filename(file.filename);
ext = fname.rsplit('.')[-1];
# 生成一个uuid作为文件名
fileName = str(uuid.uuid4()) + "." + ext;
filePath = os.path.join("static/uploadImg/", fileName);
file.save(filePath)
return {
'success': 1,
'message': '上传成功!',
'url': "/" + filePath
}
except Exception:
return {
'success': 0,
'message': '上传失败'
}
如果对上述的文件上传代码比较陌生,可以访问Flask 文件上传与下载,对Flask文件上传与下载进一步了解。
效果如下:

保存成功后,会返回保存成功页面,可以在写一篇,或者查看当前发布的文章。

查看博客列表
查看博客列表就是遍历所有已发布的博客。先定义一个视图函数,查询所有已发布的博客,传递到前端进行遍历显示。视图函数代码如下:
# 展示全部博客
@blog.route("/blogAll")
def blogAll():
# order_by按照时间倒序
blogList = Blog.query.order_by(Blog.create_time.desc()).all();
return render_template('blogAll.html', blogList=blogList)
因为最新发布的博客在数据库的最后一条,所以这里根据发布时间倒序查询。
页面代码如下:
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台.博客
{% endblock %}
{% block css %}
"stylesheet" href="/static/css/blogAll.css">
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"main">
{% for blog in blogList %}
"title" href="/blog/showBlog/{{ blog.id }}">{{ blog.title }}
发布人:{{ blog.user.name }} 发布时间:{{ blog.create_time }}
{% endfor %}
{% endblock %}
{% block blog_class %}
layui-this
{% endblock %}
效果如下:

博客详情页面
在博客列表中点击博客的标题可以进入博客的详情页面,详情页面展示了博客的详细内容以及评论内容。
因为数据库中保存博客内容的是Markdown格式的,所以在这里需要解析成HTML格式,解析代码如下。
"/static/editor/lib/marked.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/prettify.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/raphael.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/underscore.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/sequence-diagram.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/flowchart.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/jquery.flowchart.min.js">
"/static/editor/editormd.js">
editormd.markdownToHTML("test", {
htmlDecode: "style,script,iframe",
emoji: true,
taskList: true,
tex: true, // 默认不解析
flowChart: true, // 默认不解析
sequenceDiagram: true // 默认不解析
});
评论
在博客详情页面可以进行评论,评论使用的是Layui的编辑器,比较简约也可以达到想要的效果。

看上去是不是还可以,和页面也很搭。评论需要先登录才可以评论,如果没有登录则会提示登录。

如果登录评论后,会发送保存评论请求,携带当前博客的id和评论内容进行保存。
保存评论的视图函数。
# 评论
@blog.route("/comment", methods=['POST'])
@login_limit
def comment():
text = request.values.get('text')
blogId = request.values.get('blogId')
username = session.get('username')
# 获取当前系统时间
create_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first()
comment = Comment(text=text, create_time=create_time, blog_id=blogId, user_id=user.id)
db.session.add(comment)
db.session.commit();
return {
'success': True,
'message': '评论成功!',
}
上述的博客内容解析与评论都在一个页面中,完整代码如下。
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台.博客
{% endblock %}
{% block css %}
"stylesheet" type="text/css" href="/static/editor/css/editormd.css"/>
"stylesheet" href="/static/css/showBlog.css">
"/static/editor/lib/marked.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/prettify.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/raphael.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/underscore.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/sequence-diagram.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/flowchart.min.js">
"/static/editor/lib/jquery.flowchart.min.js">
"/static/editor/editormd.js">
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"main">
{{ blog.title }}
发布人:{{ blog.user.name }} 发布时间:{{ blog.create_time }}
"test">
{{ blog.text }}
"layui-elem-field layui-field-title">
发表评论
type="hidden" id="blog_id" name="blogId" value="{{ blog.id }}">
"lay_edit" lay-verify="content" name="text">
type="button" class="layui-btn comSub">提交评论
"margin-top: 30px; margin-bottom: 20px;">
"comment">
{% for com in comment %}
"myText">{{ com.text }}
评论人:{{ com.user.name }} 发布时间:{{ com.create_time }}
{% endfor %}
type="text/javascript">
$(function (){
$(".myText").each(function () {
$(this).html($(this).text());
});
})
editormd.markdownToHTML("test", {
htmlDecode: "style,script,iframe",
emoji: true,
taskList: true,
tex: true, // 默认不解析
flowChart: true, // 默认不解析
sequenceDiagram: true // 默认不解析
});
layui.use(['layedit', 'form'], function () {
var form = layui.form;
var layedit = layui.layedit;
//创建一个编辑器
var index = layedit.build('lay_edit', {
height: 150,
tool: [
'face', //表情
'|', //分割线
'link' //超链接
]
});
$(".comSub").click(function (){
layui.use('layer', function(){
var layer = layui.layer;
{% if username %}
//获取评论内容
var text = layedit.getContent(index);
var blogId = $("#blog_id").val();
if(text == "" || text == undefined){
layer.msg("评论不能为空哦!", {icon: 0});
}else {
$.post("/blog/comment", {text: text, blogId: blogId}, function (result) {
if (result.success) {
window.location.href = '/blog/showBlog/' + blogId;
}
})
}
{% else %}
layer.confirm('登录后在评论哦!', {
btn: ['取消','登录']
}, function(index){
layer.close(index);
}, function(){
window.location.href = '/login';
});
{% endif %}
});
})
});
{% endblock %}
我的博客
登录之后在右上角导航栏可以查看我的博客,查看个人已经发布过的博客并进行管理。

定义一个视图函数,查询当前登录的用户发布的所有博客。
# 查看个人博客
@blog.route("/myBlog")
@login_limit
def myBlog():
username = session.get('username')
user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first()
# order_by按照时间倒序
blogList = Blog.query.filter(Blog.user_id == user.id).order_by(Blog.create_time.desc()).all()
return render_template("myBlog.html", blogList=blogList)
页面与博客列表基本相似,但可以对其博客进行修改与删除。

修改博客
在我的博客中,有修改博客的链接,把当前的博客id当做参数传递到后台,查询当前这条博客的数据,进行修改。
# 博客修改
@blog.route("/update/", methods=['POST', 'GET'])
@login_limit
def update(id):
if request.method == 'GET':
blog = Blog.query.filter(Blog.id == id).first();
return render_template('updateBlog.html', blog=blog)
if request.method == 'POST':
id = request.form.get("id")
title = request.form.get("title")
text = request.form.get("text")
blog = Blog.query.filter(Blog.id == id).first();
blog.title = title;
blog.text = text;
db.session.commit();
return render_template('blogSuccess.html', title=title, id=id)
修改页面和写博客的页面基本一样,在textarea标签中设置markdown编辑器的默认值。
"text" lay-verify="required" style="display:none;" >{{ blog.text }}
删除博客
删除博客和修改一样,把博客的id传到后端,根据id删除数据库中对应的数据。
# 删除博客
@blog.route("/delete/")
@login_limit
def delete(id):
blog = Blog.query.filter(Blog.id == id).first();
db.session.delete(blog);
db.session.commit();
return {
'state': True,
'msg': "删除成功!"
}
删除成功后,使用JS删除页面上对应的DOM元素。
function del(url, that){
layui.use('layer', function(){
var layer = layui.layer;
layer.confirm('您确定要删除吗?', {
btn: ['取消','确定']
}, function(index){
layer.close(index);
}, function(){
$.get(url, function (data){
if(data.state){
$(that).parent().parent().parent().remove();
layer.msg(data.msg, {icon: 1});
}
})
});
});
}
我的评论
在页面的右上角不仅可以查看个人已发布的博客,也可以看到自己的所有评论信息。

根据评论列表,可以点击评论或博客,可以进入评论的博客详情页中;也可以对评论的内容进行删除操作。
定义一个视图函数,查询所有的评论内容,返回给前台遍历展示(同样根据时间倒序查询)。
# 用户所有的评论
@blog.route('/myComment')
@login_limit
def myComment():
username = session.get('username')
user = User.query.filter(User.username == username).first()
# order_by按照时间倒序
commentList = Comment.query.filter(Comment.user_id == user.id).order_by(Comment.create_time.desc()).all();
return render_template("myComment.html", commentList=commentList)
前端页面展示代码。
{% extends 'base.html' %}
{% block title %}
在线博客平台.我的评论
{% endblock %}
{% block css %}
"stylesheet" href="/static/css/blogAll.css">
{% endblock %}
{% block content %}
"main">
{% for comment in commentList %}
"title" href="/blog/showBlog/{{ comment.blog_id }}">{{ comment.text }}
博客:"/blog/showBlog/{{ comment.blog_id }}">{{ comment.blog.title }} 评论时间:{{ comment.create_time }}
"operation">
"javascript:;" onclick="del('/blog/deleteCom/{{ comment.id }}', this)">删除
{% endfor %}
type="text/javascript">
$(function (){
$(".title").each(function () {
$(this).html($(this).text());
});
})
function del(url, that){
layui.use('layer', function(){
var layer = layui.layer;
layer.confirm('您确定要删除吗?', {
btn: ['取消','确定']
}, function(index){
layer.close(index);
}, function(){
$.get(url, function (data){
if(data.state){
$(that).parent().parent().parent().remove();
layer.msg(data.msg, {icon: 1});
}
})
});
});
}
{% endblock %}
页面样式和博客列表样式一致。
删除评论
在评论列表中有删除评论的链接,根据评论的id删除当前条评论,删除后,对应博客中的评论也随之删除。
# 删除评论
@blog.route('/deleteCom/')
def deleteCom(id):
com = Comment.query.filter(Comment.id == id).first()
db.session.delete(com);
db.session.commit();
return {
'state': True,
'msg': "删除成功!"
}
关于页面
关于页面可以简单的描述一下网站的设计及作用等,这里就没有写过多的内容了,可以自行设计。

注销
注销只需要清除session中的数据,返回首页即可。
# 退出
@index.route('/logout')
def logout():
session.clear()
return redirect(url_for('index.hello'))
定义错误页面
系统在平时使用中难免会遇到一些错误,但又不能直接让用户看到这些错误,所以我们可以定义一个错误页面,使其报错后都跳转到此页面。Flask中有两个视图函数处理404和500错误的,这里直接使用即可,这里两个视图函数都是跳转到了同一个页面(也可以跳转不同的页面)。
# 404页面
@app.errorhandler(404)
def page_not_found(e):
return render_template('404.html'), 404;
# 500页面
@app.errorhandler(500)
def internal_server_error(e):
return render_template('404.html'), 500;
错误页面这里就简单的插入了一张图片,添加了一个返回首页的链接。
"en">
"UTF-8">
type="text/css">
body{
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
height: 100vh;
background: url('/static/img/404.gif') no-repeat;
background-size: cover;
z-index: -1;
}
a{
width: 65px;
display: inherit;
margin: 0 auto;
margin-top: 87vh;
padding: 5px 20px;
border: 1px solid;
border-radius: 8px;
}
"/">返回首页
效果如下:

读者福利:知道你对Python感兴趣,便准备了这套python学习资料,
对于0基础小白入门:
如果你是零基础小白,想快速入门Python是可以考虑的。
一方面是学习时间相对较短,学习内容更全面更集中。
二方面是可以找到适合自己的学习方案
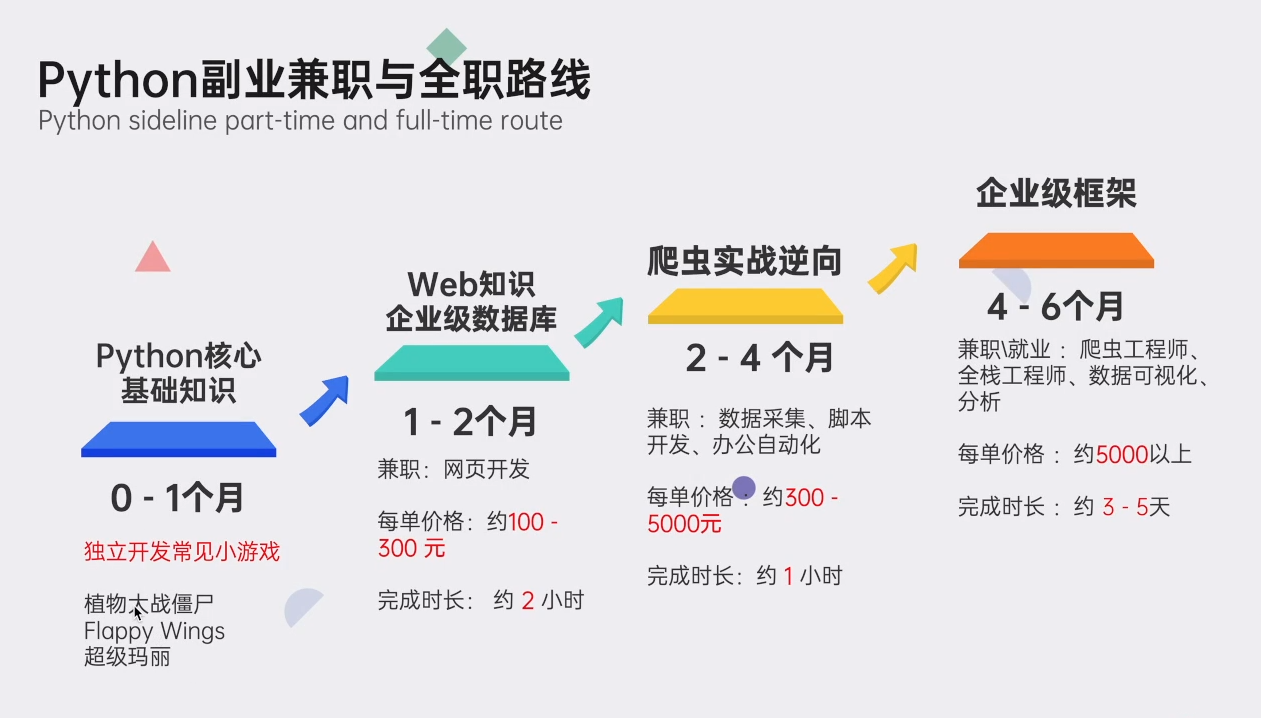
零基础Python学习资源介绍
👉Python学习路线汇总👈
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。(学习教程文末领取哈)

👉Python必备开发工具👈
温馨提示:篇幅有限,已打包文件夹,获取方式在:文末
👉Python学习视频600合集👈
观看零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
👉实战案例👈
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
👉100道Python练习题👈
检查学习结果。
👉面试刷题👈
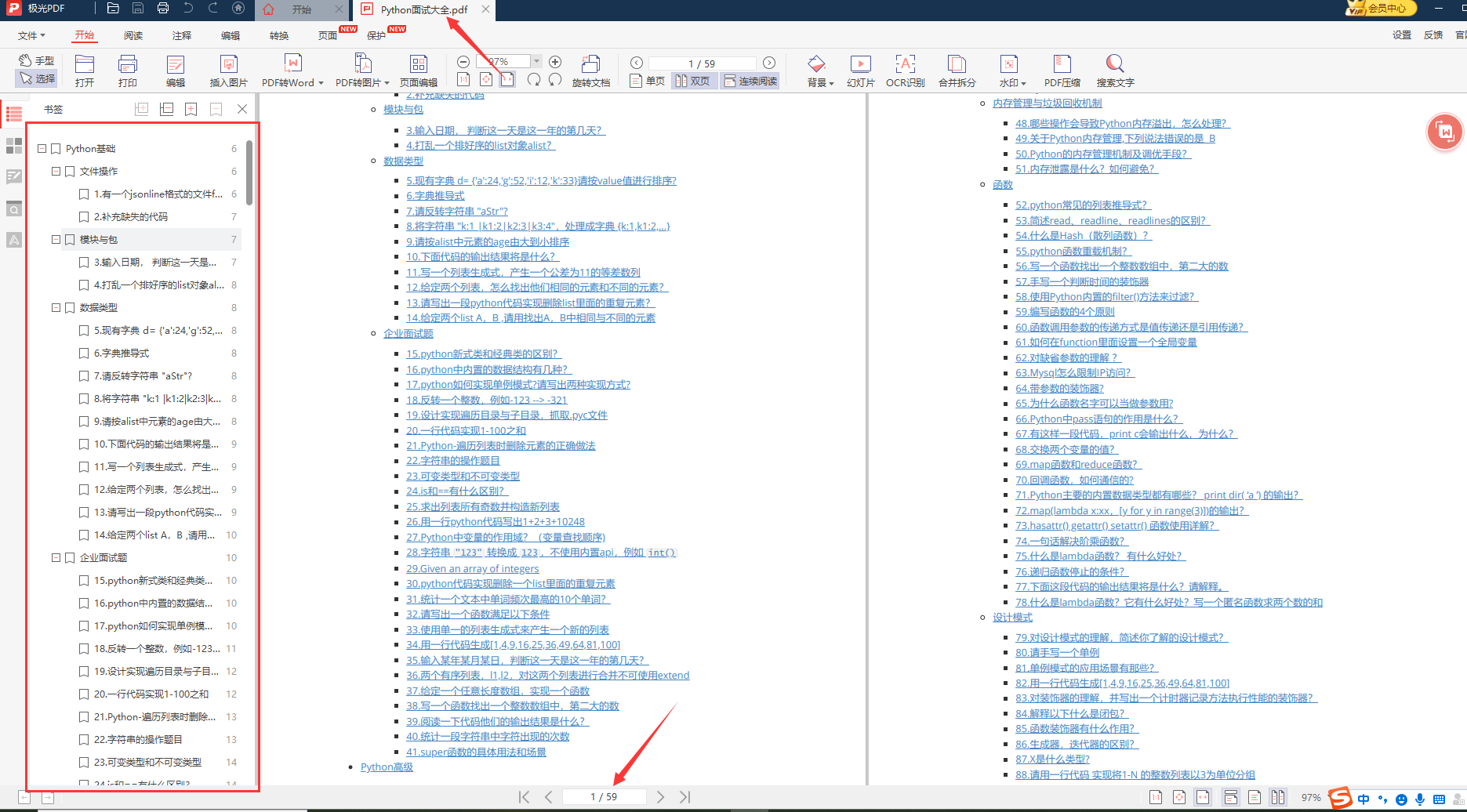
资料领取
这份完整版的Python全套学习资料已为大家备好,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方二维码添加,输入"领取资料" 可免费领取全套资料【有什么需要协作的还可以随时联系我】朋友圈也会不定时的更新最前言python知识。

好文推荐
了解python的前景: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49892805/article/details/127196159
python有什么用: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_49892805/article/details/127214402
相关文章
- Python以及Pycharm的matplotlib和xlrd安装方法[通俗易懂]
- python语言变量命名规则有什么_Python变量命名规则(超级详细)
- python jieba库_Python jieba库的使用说明「建议收藏」
- python安装不了whl文件_Python安装whl文件过程图解
- Python 数字图像处理-从 scikit-image 库开始学习
- 利用python实现易班疫情自动签到
- python getopt方法_python的getopt
- Python快速编程入门课后习题答案「建议收藏」
- python语言一般用于什么_PYthon
- lua sort排序_python中列表排序的用法
- python全局变量赋值_Python全局变量和局部变量[通俗易懂]
- 【说站】python关闭文件的两种方法
- 【说站】python中异步非阻塞如何实现
- Python静态代码检查工具Flake8
- 【硬核书】数学和Python机器学习的核心方法:构建逻辑的100个练习
- python抛出异常写法_零基础学 Python(32):如何抛出和捕获异常?「建议收藏」
- Python文件名后缀_python获取目录下所有文件的文件名
- Python 命令行cmd指定颜色设置
- python计算windows的cpu使用率详解编程语言
- 在Linux上学习Python——你的编程之路(linux学python)
- Connecting to MSSQL with Python: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners(python连接mssql)
- 利用Neo4j和Python进行无缝图形数据库支持(neo4j python)
- 在Linux系统中使用Python编程语言(linux中python)
- Linux下Python编程:从入门到精通(linux下python编程)
- Python中使用MySQL数据库的操作技巧(mysql_python)

