MYSQL简单安装配置
2023-09-14 08:59:37 时间
http://www.cnblogs.com/zeroone/articles/2298942.html
http://blog.csdn.net/h1017597898/article/details/9815987
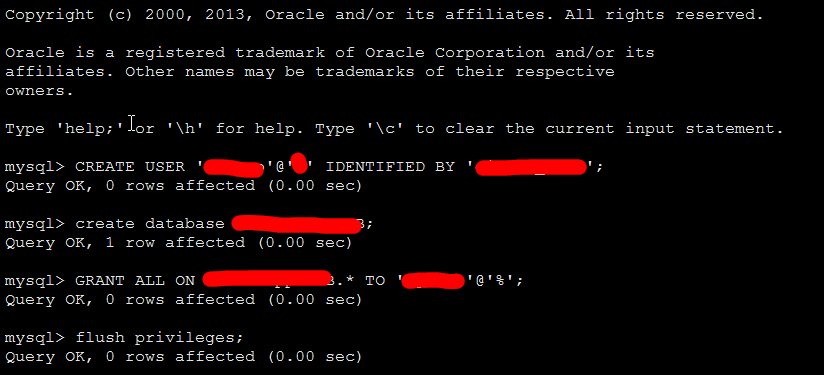
安装之后,新建用户及密码,新建数据库,分配权限

mysql CREATE USER user@% IDENTIFIED BY password; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) mysql create database DB; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql create database DB default character set utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; (为了DJANGO操作中文不乱码)
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql GRANT ALL ON DB.* TO user@%;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)

YUM安装的MYSQL之后,第一次启动时的安全配置:

PLEASE REMEMBER TO SET A PASSWORD FOR THE MySQL root USER ! To do so, start the server, then issue the following commands: /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root password new-password /usr/bin/mysqladmin -u root -h cnsz141539 password new-password Alternatively you can run: /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation which will also give you the option of removing the test databases and anonymous user created by default. This is strongly recommended for production servers. See the manual for more instructions. You can start the MySQL daemon with: cd /usr ; /usr/bin/mysqld_safe You can test the MySQL daemon with mysql-test-run.pl cd /usr/mysql-test ; perl mysql-test-run.pl Please report any problems with the /usr/bin/mysqlbug script!

如果要将MYSQL放入SERVICE服务,相应的脚本为:

#!/bin/sh # mysqld This shell script takes care of starting and stopping # the MySQL subsystem (mysqld). # chkconfig: - 64 36 # description: MySQL database server. # processname: mysqld # config: /etc/my.cnf # pidfile: /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: mysqld # Required-Start: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named $syslog $time # Required-Stop: $local_fs $remote_fs $network $named $syslog $time # Short-Description: start and stop MySQL server # Description: MySQL database server ### END INIT INFO # Source function library. . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions # Source networking configuration. . /etc/sysconfig/network
# Set timeouts here so they can be overridden from /etc/sysconfig/mysqld STARTTIMEOUT=120 STOPTIMEOUT=60 [ -e /etc/sysconfig/$prog ] . /etc/sysconfig/$prog lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/$prog
# extract value of a MySQL option from config files # Usage: get_mysql_option SECTION VARNAME DEFAULT # result is returned in $result # We use my_print_defaults which prints all options from multiple files, # with the more specific ones later; hence take the last match. get_mysql_option(){ result=`/usr/bin/my_print_defaults "$1" | sed -n "s/^--$2=//p" | tail -n 1` if [ -z "$result" ]; then # not found, use default result="$3" get_mysql_option mysqld datadir "/var/lib/mysql" datadir="$result" get_mysql_option mysqld socket "$datadir/mysql.sock" socketfile="$result" get_mysql_option mysqld_safe log-error "/var/log/mysqld.log" errlogfile="$result" get_mysql_option mysqld_safe pid-file "/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid" mypidfile="$result"
MYSQLPID=`cat "$mypidfile" 2 /dev/null` if [ -n "$MYSQLPID" ] [ -d "/proc/$MYSQLPID" ] ; then MYSQLDRUNNING=1 RESPONSE=`/usr/bin/mysqladmin --socket="$socketfile" --user=UNKNOWN_MYSQL_USER ping 2 1` if [ $MYSQLDRUNNING = 1 ] [ $? = 0 ]; then # already running, do nothing action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/true ret=0 elif [ $MYSQLDRUNNING = 1 ] echo "$RESPONSE" | grep -q "Access denied for user" then # already running, do nothing action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/true ret=0 else # prepare for start touch "$errlogfile" 2 /dev/null if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then # failed to touch log file, probably insufficient permissions action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/false return 4 chown mysql:mysql "$errlogfile" chmod 0640 "$errlogfile" [ -x /sbin/restorecon ] /sbin/restorecon "$errlogfile" if [ ! -d "$datadir/mysql" ] ; then # First, make sure $datadir is there with correct permissions if [ ! -e "$datadir" -a ! -h "$datadir" ] then mkdir -p "$datadir" || exit 1 chown mysql:mysql "$datadir" chmod 0755 "$datadir" [ -x /sbin/restorecon ] /sbin/restorecon "$datadir" # Now create the database action $"Initializing MySQL database: " /usr/bin/mysql_install_db --datadir="$datadir" --user=mysql ret=$? chown -R mysql:mysql "$datadir" if [ $ret -ne 0 ] ; then return $ret chown mysql:mysql "$datadir" chmod 0755 "$datadir" # We check if there is already a process using the socket file, # since otherwise this init script could report false positive # result and mysqld_safe would remove the socket file, which # actually uses a different daemon. if fuser "$socketfile" /dev/null ; then echo "Socket file $socketfile exists. Is another MySQL daemon already running with the same unix socket?" action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/false return 1 # Pass all the options determined above, to ensure consistent behavior. # In many cases mysqld_safe would arrive at the same conclusions anyway # but we need to be sure. (An exception is that we dont force the # log-error setting, since this script doesnt really depend on that, # and some users might prefer to configure logging to syslog.) # Note: set --basedir to prevent probes that might trigger SELinux # alarms, per bug #547485 $exec --datadir="$datadir" --socket="$socketfile" \ --pid-file="$mypidfile" \ --basedir=/usr --user=mysql /dev/null 2 1 safe_pid=$! # Spin for a maximum of N seconds waiting for the server to come up; # exit the loop immediately if mysqld_safe process disappears. # Rather than assuming we know a valid username, accept an "access # denied" response as meaning the server is functioning. ret=0 TIMEOUT="$STARTTIMEOUT" while [ $TIMEOUT -gt 0 ]; do RESPONSE=`/usr/bin/mysqladmin --socket="$socketfile" --user=UNKNOWN_MYSQL_USER ping 2 1` mret=$? if [ $mret -eq 0 ]; then break # exit codes 1, 11 (EXIT_CANNOT_CONNECT_TO_SERVICE) are expected, # anything else suggests a configuration error if [ $mret -ne 1 -a $mret -ne 11 ]; then echo "$RESPONSE" echo "Cannot check for MySQL Daemon startup because of mysqladmin failure." ret=1 break echo "$RESPONSE" | grep -q "Access denied for user" break if ! /bin/kill -0 $safe_pid 2 /dev/null; then echo "MySQL Daemon failed to start." ret=1 break sleep 1 let TIMEOUT=${TIMEOUT}-1 done if [ $TIMEOUT -eq 0 ]; then echo "Timeout error occurred trying to start MySQL Daemon." ret=1 if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/true chmod o+r $mypidfile /dev/null 2 1 touch $lockfile else action $"Starting $prog: " /bin/false return $ret stop(){ if [ ! -f "$mypidfile" ]; then # not running; per LSB standards this is "ok" action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/true return 0 MYSQLPID=`cat "$mypidfile" 2 /dev/null` if [ -n "$MYSQLPID" ]; then /bin/kill "$MYSQLPID" /dev/null 2 1 ret=$? if [ $ret -eq 0 ]; then TIMEOUT="$STOPTIMEOUT" while [ $TIMEOUT -gt 0 ]; do /bin/kill -0 "$MYSQLPID" /dev/null 2 1 || break sleep 1 let TIMEOUT=${TIMEOUT}-1 done if [ $TIMEOUT -eq 0 ]; then echo "Timeout error occurred trying to stop MySQL Daemon." ret=1 action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/false else rm -f $lockfile rm -f "$socketfile" action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/true else action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/false else # failed to read pidfile, probably insufficient permissions action $"Stopping $prog: " /bin/false ret=4 return $ret restart(){ stop start condrestart(){ [ -e $lockfile ] restart || :
echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload}" exit 2 exit $?

相关文章
- Ubuntu安装Navicat 12 for MySQL
- Ubuntu 安装配置MySQL,并使用VS的Server Explorer UI界面远程管理MySQL
- mysql的备份与还原,安装(window)
- Mac Pro 解压安装MySQL二进制分发版 mysql-5.6.30-osx10.11-x86_64.tar.gz(不是dmg的)
- Cubieboard A10 安装Nand系统,配置nginx,php,mysql,samba详细教程
- 通过yum安装nginx-mysql-php-fastcgi配置LNMP
- centos7下使用yum安装mysql
- python-django-linux上mysql的安装和配置_20191124
- 【问题解决方案】MySQL安装后无法启动-net start mysql服务名无效
- Ubuntu 13.04 MySQL Proxy 安装与配置
- python-django-linux上mysql的安装和配置_20191124
- Linux下MySQL源码编译安装(eg:mysql-5.6.27.tar.gz )
- linux -安装mysql,配置密码,开启远程访问
- MySQL Study之--Mysql无法启动“mysql.host”
- windows s2019安装mysql 5.7并配置
- CentOS在安装配置 Ngnix_tomcat_PHP_Mysql
- 如何测试mysql是否安装成功
- Mysql之rpm方式安装
- mysql-installer-community-8.0.22.0安装教程
- 迁移SpringCloude微服务 安装和配置数据存储仓库MySQL

