Cppcheck 1.54 C/C++静态代码分析工具
int main()
{
char a[10];
a[10] =0;
return 0;
}用此工具进行检测,结果如下图所示:
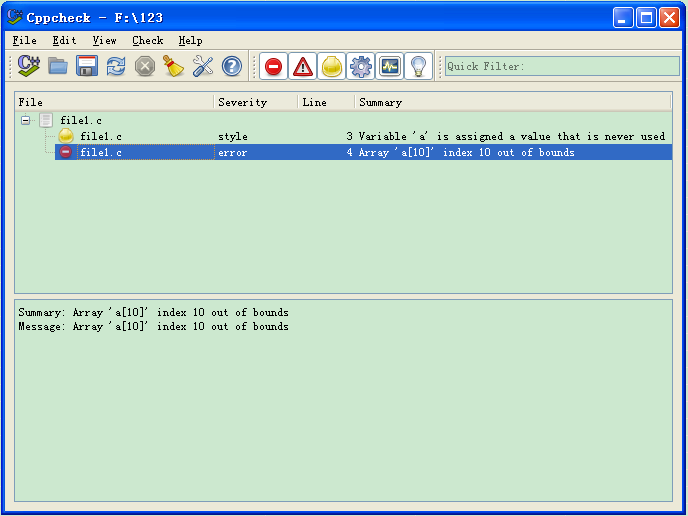
一下子就分析出了其中的警告和错误。用命令行检测的话,可以支持中文路径,效果如下图所示:
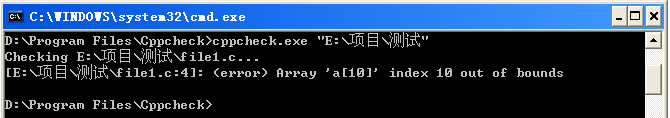
命令行方式,默认只显示错误的信息,使用--enable打开其他提示信息,如下:
在Visual Studio下使用的话,步骤如下: 1.在Visual Studio菜单栏"工具"→"外部工具",点击"添加",内容如下:
标题:Cppcheck
命令:D:\Program Files\Cppcheck\cppcheck.exe
参数:--enable=all--template=vs $(SolutionDir)
勾选"使用输出窗口" 2.使用时,点击"工具"→"Cppcheck"即可,如下图所示:
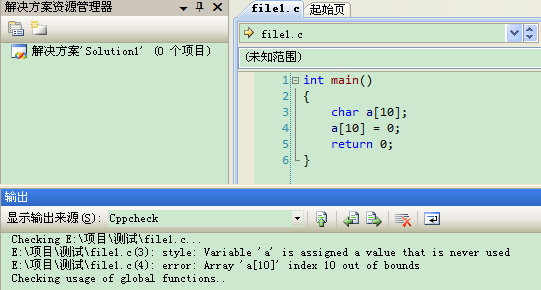
双击提示内容,即可定位到所在行。
cppcheck [OPTIONS] [files or paths] If a directory is given instead of a filename, *.cpp, *.cxx, *.cc, *.c++, *.c, *.tpp, and *.txx files are checked recursively from the given directory.
--append= file This allows you to provide information about functions by providing an implementation for them.
--check-config Check cppcheck configuration. The normal code analysis is disabled by this flag.
-D ID By default Cppcheck checks all configurations. Use -D to limit the checking to a particular configuration.
Example: -DDEBUG=1 -D__cplusplus.
-U ID By default Cppcheck checks all configurations. Use -U to explicitly hide certain #ifdef ID code paths from checking.
Example: -UDEBUG
--enable= id Enable additional checks. The available ids are:
* all
Enable all checks
* style
Enable all coding style checks. All messages with the severities style, performance and portability are enabled.
* performance
Enable performance messages
* portability
Enable portability messages
* information
Enable information messages
* unusedFunction
Check for unused functions
* missingInclude
Warn if there are missing includes. For detailed information, use --check-config.
Several ids can be given if you separate them with commas. See also --std
--error-exitcode= n If errors are found, integer [n] is returned instead of the default 0. 1 is returned if arguments are not valid or if no input files are provided. Note that your operating system can modify this value, e.g. 256 can become 0.
--exitcode-suppressions= file Used when certain messages should be displayed but should not cause a non-zero exitcode.
--file-list= file Specify the files to check in a text file. Add one filename per line. When file is -, the file list will be read from standard input.
-f, --force Force checking of all configurations in files. If used together with --max-ifdefs=, the last option is the one that is effective.
-I dir Give path to search for include files. Give several -I parameters to give several paths. First given path is searched for contained header files first. If paths are relative to source files, this is not needed.
--includes-file= file Specify directory paths to search for included header files in a text file. Add one include path per line. First given path is searched for contained header files first. If paths are relative to source files, this is not needed.
-i dir or file Give a source file or source file directory to exclude from the check. This applies only to source files so header files included by source files are not matched. Directory name is matched to all parts of the path.
--inline-suppr Enable inline suppressions. Use them by placing one or more comments, like: // cppcheck-suppress warningId on the lines before the warning to suppress.
--max-configs= limit Maximum number of configurations to check in a file before skipping it. Default is 12. If used together with --force, the last option is the one that is effective.
--platform= type Specifies platform specific types and sizes. The available platforms are:
* unix32
32 bit unix variant
* unix64
64 bit unix variant
* win32A
32 bit Windows ASCII character encoding
* win32W
32 bit Windows UNICODE character encoding
* win64
64 bit Windows
-rp, --relative-paths
-rp= paths , --relative-paths= paths Use relative paths in output. When given, paths are used as base. You can separate multiple paths by ;. Otherwise path where source files are searched is used. We use string comparison to create relative paths, so using e.g. ~ for home folder does not work. It is currently only possible to apply the base paths to files that are on a lower level in the directory tree.
--rule-file= file Use given rule file. For more information, see: https://sourceforge.net/projects/cppcheck/files/Articles/
--std= id Enable some standard related checks.
The available options are:
* posix
Checks related to POSIX-specific functionality
* c99
C99 standard related checks
* c++11
C++11 standard related checks
Example to enable more than one checks:
cppcheck --std=c99 --std=posix file.cpp
--suppress= spec Suppress warnings that match spec . The format of spec is:
[error id]:[filename]:[line]
The [filename] and [line] are optional. If [error id] is a wildcard *, all error ids match.
--suppressions-list= file Suppress warnings listed in the file. Each suppression is in the same format as spec above.
--template= text Format the error messages. E.g.
{file}:{line},{severity},{id},{message} or {file}({line}):({severity}) {message}
Pre-defined templates: gcc, vs, edit.
--xml-version= version Select the XML file version. Currently versions 1 and 2 are available. The default version is 1.
Example usage: # Recursively check the current folder. Print the progress on the screen and write errors to a file: cppcheck . 2 err.txt # Recursively check ../myproject/ and dont print progress: cppcheck --quiet ../myproject/ # Check only files one.cpp and two.cpp and give all information there is: cppcheck -v -s one.cpp two.cpp # Check f.cpp and search include files from inc1/ and inc2/: cppcheck -I inc1/ -I inc2/ f.cpp
A pointer to a variable is only valid as long as the variable is in scope. Check:
returning a pointer to auto or temporary variable assigning address of an variable to an effective parameter of a function returning reference to local/temporary variable returning address of function parameter Boost usageCheck for invalid usage of Boost:
container modification during BOOST_FOREACH Bounds checkingout of bounds checking
ClassCheck the code for each class.
Missing constructors Are all variables initialized by the constructors? Warn if memset, memcpy etc are used on a class If its a base class, check that the destructor is virtual Are there unused private functions operator= should return reference to self operator= should check for assignment to self Constness for member functions Exception SafetyChecking exception safety
Throwing exceptions in destructors Throwing exception during invalid state Throwing a copy of a caught exception instead of rethrowing the original exception exception caught by value instead of by reference Match assignments and conditionsMatch assignments and conditions:
Mismatching assignment and comparison = comparison is always true/false Mismatching lhs and rhs in comparison = comparison is always true/false Detect matching if and else if conditions Memory leaks (address not taken)Not taking the address to allocated memory
Memory leaks (class variables)If the constructor allocate memory then the destructor must deallocate it.
Memory leaks (function variables)Is there any allocated memory when a function goes out of scope
Memory leaks (struct members)Dont forget to deallocate struct members
Non reentrant functionsWarn if any of these non reentrant functions are used:
crypt ctermid fgetgrent fgetpwent fgetspent getgrent getgrgid getgrnam gethostbyaddr gethostbyname gethostbyname2 gethostent getlogin getnetbyaddr getnetbyname getnetgrent getprotobyname getpwent getpwnam getpwuid getrpcbyname getrpcbynumber getrpcent getservbyname getservbyport getservent getspent getspnam gmtime localtime readdir strtok tempnam ttyname Null pointerNull pointers
null pointer dereferencing Obsolete functionsWarn if any of these obsolete functions are used:
asctime asctime_r bcopy bsd_signal bzero ctime ctime_r ftime getcontext gethostbyaddr gethostbyname getwd index makecontext pthread_attr_getstackaddr pthread_attr_setstackaddr rand_r rindex scalbln swapcontext tmpnam tmpnam_r ualarm usleep utime vfork wcswcs OtherOther checks
Assigning bool value to pointer (converting bool value to address) bad usage of the function sprintf (overlapping data) division with zero using fflush() on an input stream scoped object destroyed immediately after construction assignment in an assert statement sizeof for array given as function argument sizeof for numeric given as function argument using sizeof(pointer) instead of the size of pointed data incorrect length arguments for substr and strncmp invalid usage of output stream. For example: std::cout std::cout; wrong number of arguments given to printf or scanf; double free() or double closedir() C-style pointer cast in cpp file casting between incompatible pointer types redundant if bad usage of the function strtol unsigned division Dangerous usage of scanf passing parameter by value Incomplete statement check how signed char variables are used variable scope can be limited condition that is always true/false unusal pointer arithmetic. For example: "abc" + d redundant assignment in a switch statement redundant strcpy in a switch statement look for sizeof sizeof .. look for calculations inside sizeof() assignment of a variable to itself mutual exclusion over || always evaluating to true Clarify calculation with parentheses using increment on boolean comparison of a boolean with a non-zero integer comparison of a boolean expression with an integer other than 0 or 1 suspicious condition (assignment+comparison) suspicious condition (runtime comparison of string literals) suspicious condition (string literals as boolean) duplicate break statement unreachable code testing if unsigned variable is negative testing is unsigned variable is positive using bool in bitwise expression Suspicious use of ; at the end of if/for/while statement. incorrect usage of functions from ctype library. optimisation: detect post increment/decrement STL usageCheck for invalid usage of STL:
out of bounds errors misuse of iterators when iterating through a container mismatching containers in calls dereferencing an erased iterator for vectors: using iterator/pointer after push_back has been used optimisation: use empty() instead of size() to guarantee fast code suspicious condition when using find redundant condition common mistakes when using string::c_str() using auto pointer (auto_ptr) useless calls of string functions Uninitialized variablesUninitialized variables
using uninitialized variables and data Unused functionsCheck for functions that are never called
UnusedVarUnusedVar checks
unused variable allocated but unused variable unred variable unassigned variable unused struct member Using postfix operatorsWarn if using postfix operators ++ or -- rather than prefix operator
C++ Json工具--Jsoncpp用法简介 Json简介 JSON(JavaScript Object Notation, JS 对象简谱) 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,可读性强,易扩展,很适合做通信协议,下面主要介绍一款C++的Json库:Jsoncpp.
Android C++ 系列:Linux 常用函数和工具 如果times是非空指针,则存取时间和修改时间被设置为 times所指向的结构中的值。此 时,进程的有效用户ID必须等于该文件的所有者 ID,或者进程必须是一个超级用户进程。对 文件只具有写许可权是不够的
C/C++ 库函数查询工具MSDN 当我们学习C/C++ 总会用到库函数,而面对陌生的函数时,我们就要去查询它的作用,参数,头文件,返回值等等。但是我们在查询它们的用用法时可能会耗费时间和精力,所以我将为大家提供一个好用的查询软件MSDN(注:不需要联网使用)
实现无入侵式C++代码mock工具 为了实现真正无侵入式的mock,我们基于开源Hook框架Frida-gum提供的API,利用C++模板进行封装,作者编写了一个简单实用的mock工具,在此开源分享(代码详见附录)。
相关文章
- 【c++STL——第十一讲】iterator系列 (常用知识点总结)
- c++中类的构造函数的初始化成员列表详解
- 47 C++ - 继承中的静态成员特性
- 26 C++ - 静态成员
- C++第7周任务3-输出星号图详解示例
- C++位操作中按位置0、置1、取反操作
- c++中vector的用法详解
- C++静态成员和非静态成员的区别 及修饰
- C++常用类型转换
- c++终极螺旋丸:₍˄·͈༝·͈˄*₎◞ ̑̑“类与对象的结束“是结束也是开始
- 《C++编程规范:101条规则、准则与最佳实践》——1.5做代码审查
- 《C++编程剖析:问题、方案和设计准则》——第一章泛型编程与C++标准库1.1:vector的使用
- 《C++编程风格(修订版)》——3.1 编程风格示例:堆栈
- C++学习必备网站推荐收藏
- 静态链接库与动态链接库----C/C++
- C++中编译静态库与动态库
- C++静态库与动态库详解
- 【华为OD机试真题 java、python、c++】静态扫描(100%通过+复盘思路)
- C++模板中的静态
- C/C++教程 第十章 —— 静态库与动态库

