【面试题】实现文件夹中文件的遍历输出
2023-09-27 14:27:40 时间
<p> </p>
<p>在之前的文章中:https://www.cnblogs.com/leiziv5/p/7411091.html,分享了基于python去递归查找文件中的文件。在后续的接触中,可以基于深度遍历和广度遍历来实现
</p>
<p>1.深度遍历实现
对应实现思路:
1.创建栈
2.增加路径
3.当栈不为空,处理栈的一个路径
4.遍历路径下面的每一项
5.遇到文件夹加入到栈中
6.知道栈中元素为空,退出
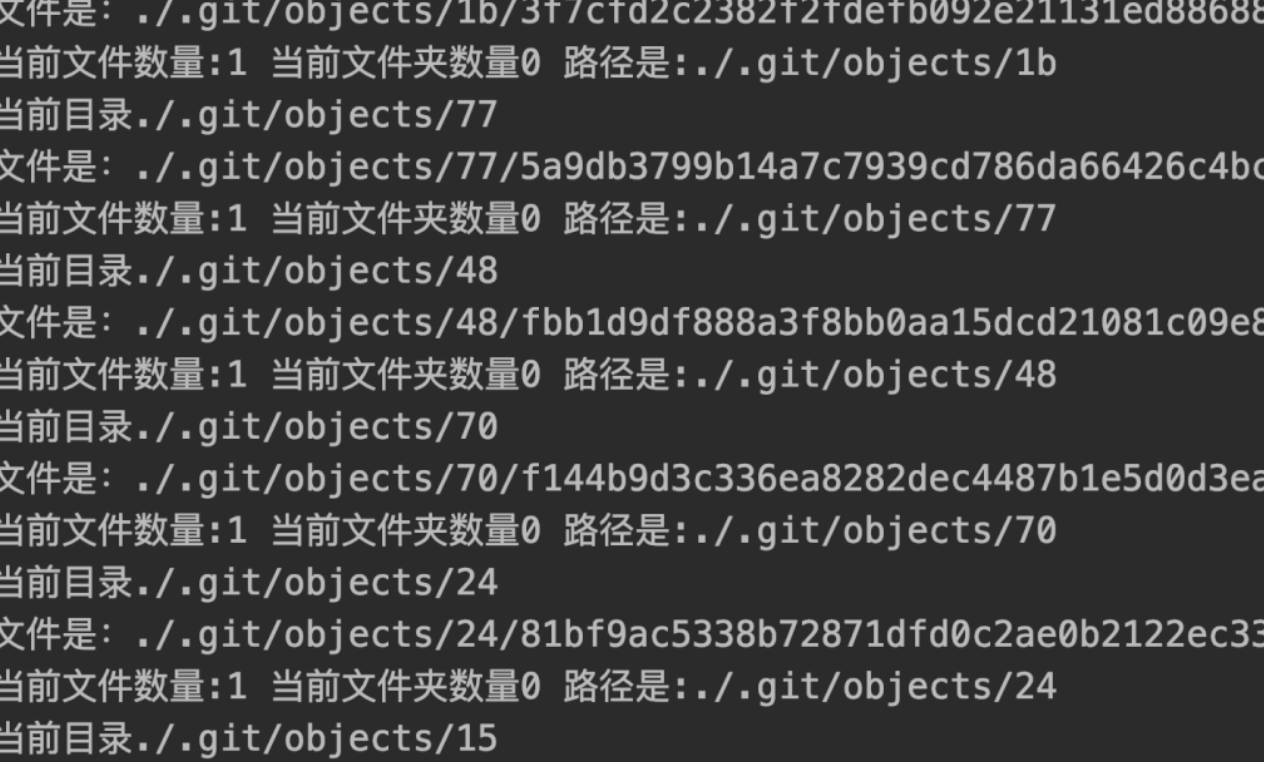
import os
path = '.'
def GetAllDeep(path):
stack = []
stack.append(path)
# 处理栈,当栈为空时结束循环
while len(stack) != 0:
# 从栈里取出数据
DirPath = stack.pop()
# 目录下所有文件
num = 0
file_num = 0
FileList = os.listdir(DirPath)
# 循环处理每个文件
for FileName in FileList:
FileAbsPath = os.path.join(DirPath,FileName)
if os.path.isfile(FileAbsPath) == True:
print("是文件",FileAbsPath)
num += 1
else:
# print("是目录",FileAbsPath)
stack.append(FileAbsPath)
file_num += 1
print('当前文件数量:%s' % num, '当前文件夹数量%s' % file_num, '路径是:%s' % (FileAbsPath))
我们看下最后的结果
2.广度优先遍历实现
思路
1.创建一个队列 2.队列增加文件路径 3.当队列不为空,获取队列 4.遍历某个路径,判断是文件输出,是文件夹加入队列 5.直到队列为空,程序终止运行。
看下最后的代码实现
import os, collections
# 广度遍历目录
def Get_All_Dir_Scope(path:str):
#创建队列
queue = collections.deque()
# 进队
queue.append(path)
print("queue =", queue)
while len(queue) != 0:
# 出队数据
File_Path = queue.popleft()
# print(FilePath)
# 找出所有的文件
num = 0
file_num = 0
FileNameList = os.listdir(File_Path)
for fileName in FileNameList:
fileAbsPath = os.path.join(File_Path, fileName)
if os.path.isfile(fileAbsPath):
print("是文件", fileAbsPath)
num += 1
else:
file_num += 1
queue.append(fileAbsPath)
print('当前文件数量:%s' % num, '当前文件夹数量%s' % file_num, '路径是:%s' % (fileAbsPath))
我们去传递一个路径,遍历里面文件
path = '.' Get_All_Dir_Scope(path)
最后打印结果
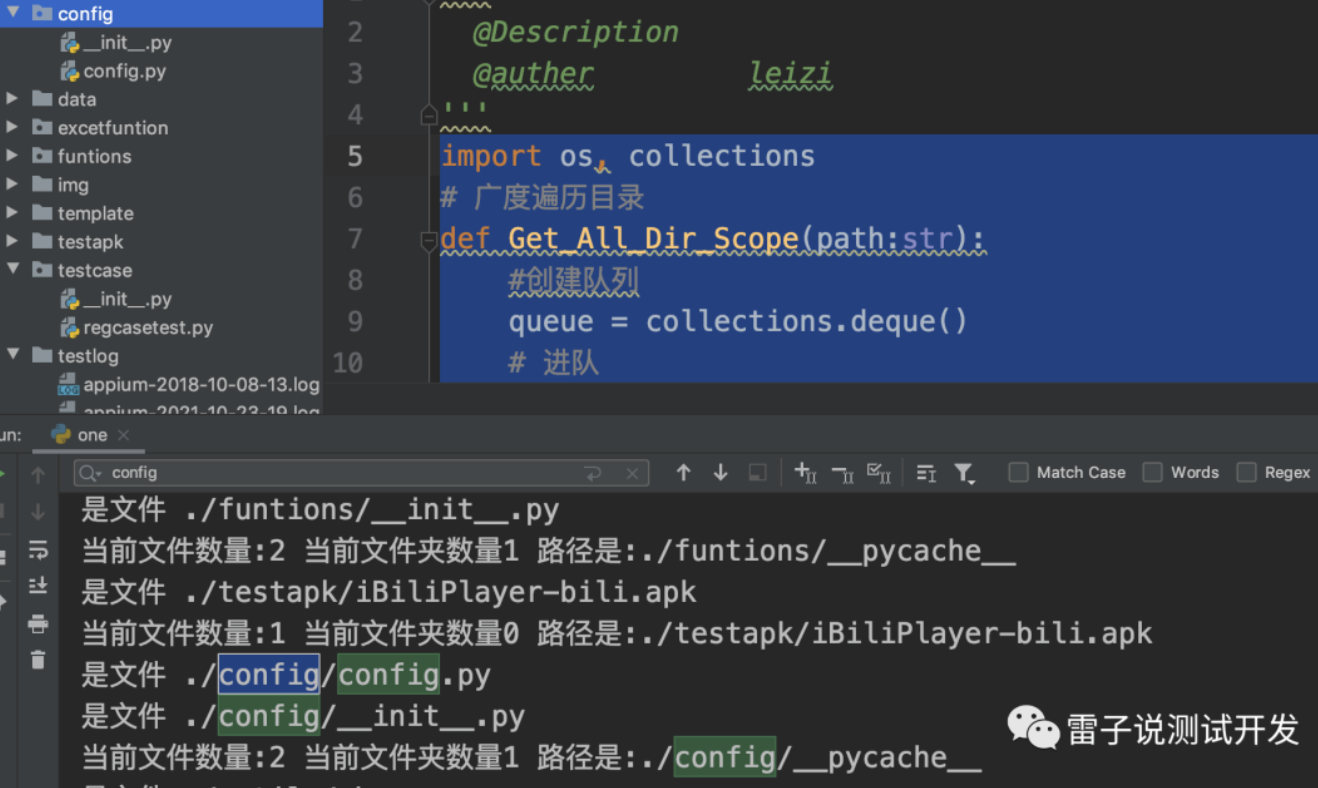
可以看到上面的结果,和我们想要的输出是一致的。
基于广度遍历的方式就实现完毕。其实很简单。


