kubernetes 的日志解决方案
概述
对于一个分布式平台来说 日志收集处理是一个不可或缺的功能。目前 ELK Stack 已经成为最流行的集中式日志解决方案。本文主要梳理一下ELK的一些理论知识 并针对K8S容器云平台探讨一下集中式日志解决方案的可行性 并做一下简单实践。
ELK Stack
ELK Stack主要包括以下组件
Elasticsearch 分布式搜索和分析引擎 基于 Apache Lucene构建 用于对大容量的数据进行接近实时的存储 搜索和分析。具有高可伸缩 高可靠 易管理等特点。通常用作某些应用的基础搜索引擎 使其具有复杂的搜索功能。
Logstash: 数据收集引擎。支持动态的从各种数据源搜集数据 并对数据进行过滤、分析、丰富、统一格式等操作 然后存储到用户指定的位置。
Kibana 数据分析和可视化平台。通常与 Elasticsearch配合使用 对其中数据进行搜索、分析和以统计图表的方式展示
Filebeat ELK 协议栈的新成员 一个轻量级开源日志文件数据搜集器 基于 Logstash-Forwarder 源代码开发 是对它的替代 Logstash占用内存太大 。在需要采集日志数据的 server 上安装 Filebeat 并指定日志目录或日志文件后 Filebeat 就能读取数据 迅速发送到 Logstash 进行解析 亦或直接发送到 Elasticsearch 进行集中式存储和分析。
ELK 的架构设计是跟业务息息相关的 如果是数据量比较小 可靠性要求不高 允许数据丢失的情况可以直接布单实例的ELK 大致如下
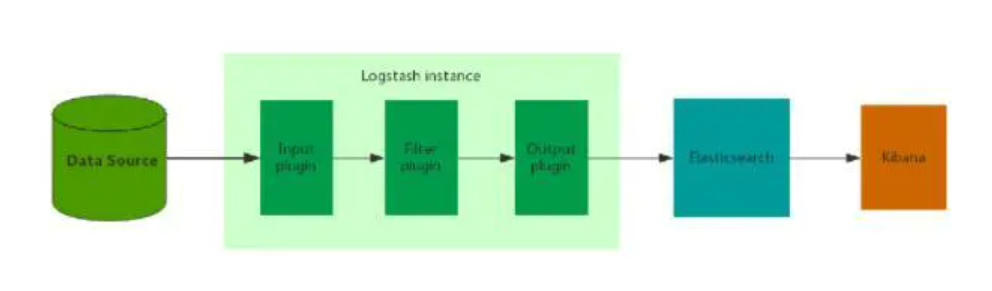
日志搜集部分的logstash可以部署在多台机器上 当然 也可以采用其他日志收集工具 比如Filebeat rsyslog fluent等。这种架构每个环节都有单点故障的可能 而且没有分流的功能 一旦出现数据量激增的情况可能中间的某个组件就挂了。
生产环境中会在上述架构的基础上增加一些高可用的特性 示例如下
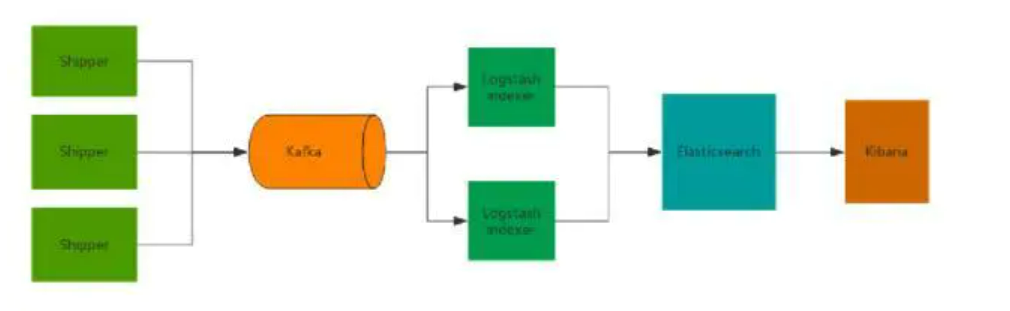
这里首先注意到的是增加了一个消息队列来削峰填谷 在收集数据完之后 这里还用logstash做了数据过滤 格式转换等数据处理工作 可选 elasticsearch采用集群的方式部署 图中未体现出来 。
Kubernetes Logging Architecture
在k8s官网中 对于日志处理的理论部分说的还是挺详细的。总结如下
在k8s日志收集方案中 大致可以分为三个级别 第一级别是pod中程序产生的应用日志 第二个级别是node级别的系统日志 第三个级别是集群级别的日志收集方案。
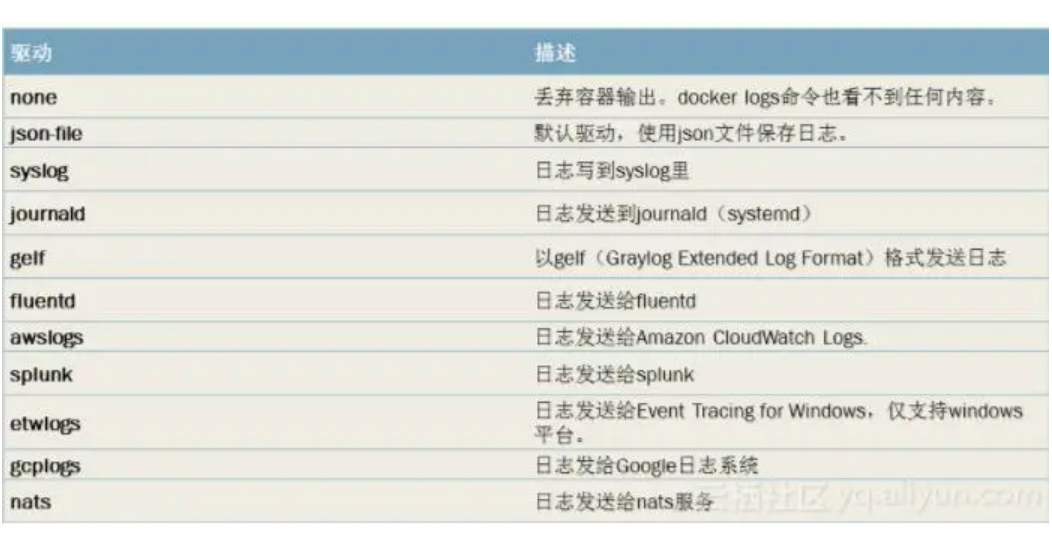
首先是pod级别的日志 默认指定程序输出到标准输出 然后就可以通过kubectl logs获取到日志。node级别的日志收集方案 首先要考虑的就是容器中程序产生的日志 这部分日志可以通过容器配置中的log-driver来对日志进行日志管理。其他程序的日志可以指定日志输出路径 比如/var/log 。值得注意的是 这个级别的解决方案需要一个logrotate组件来对日志文件进行管理。常用的log-driver如下
集群级别的日志解决方案 这种情况下就要使用ELK Stack了 同时还要考虑容器漂移问题。对于日志收集部分 有三种日志收集方案
使用节点日志agent:也就是在node级别进行日志收集。一般使用DaemonSet部署在每个node中。这种方式优点是耗费资源少 因为只需部署在节点 且对应用无侵入。缺点是只适合容器内应用日志必须都是标准输出。
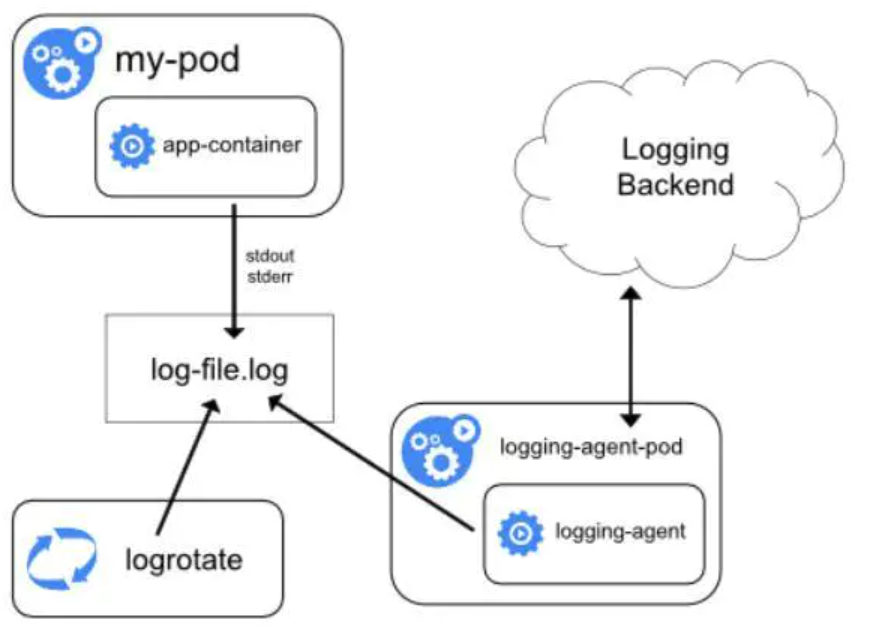
使用sidecar container作为容器日志agent 也就是在pod中跟随应用容器起一个日志处理容器 有两种形式 一种是直接将应用容器的日志收集并输出到标准输出 叫做Streaming sidecar container 如下图
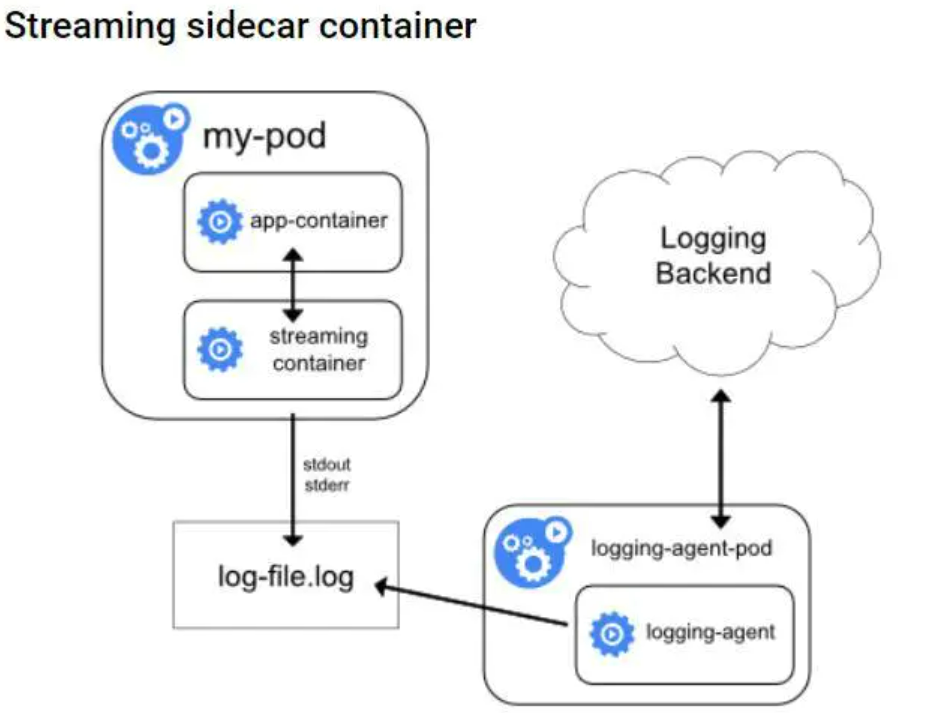
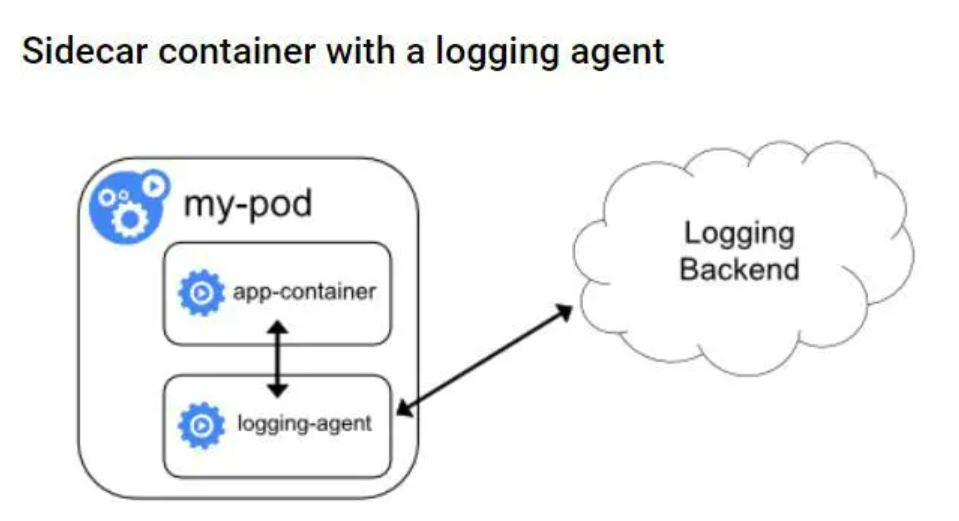
还有一种是将应用容器日志直接输出到日志收集后端 也就是每一个pod中都起一个日志收集agent 比如logstash或fluebtd 。如下图 这种方式的优点是可以收集多种形式的日志(比如文件 socket等) 缺点是耗费资源较多 每个pod都要起一个日志收集容器 相对来说 Streaming sidecar container的形式比较折中 既能收集多种形式的容器 耗费资源也没有太多 因为起的日志处理容器仅仅是将多种形式的日志输出到标准输出而已。
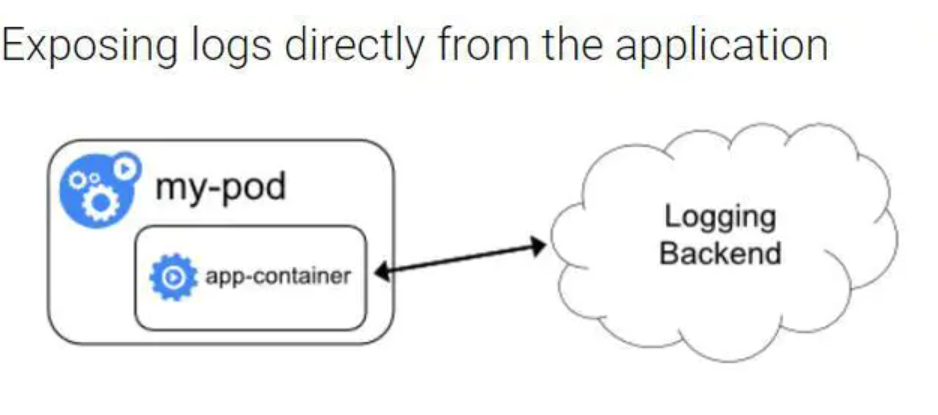
在应用容器中直接将日志推到存储后端。
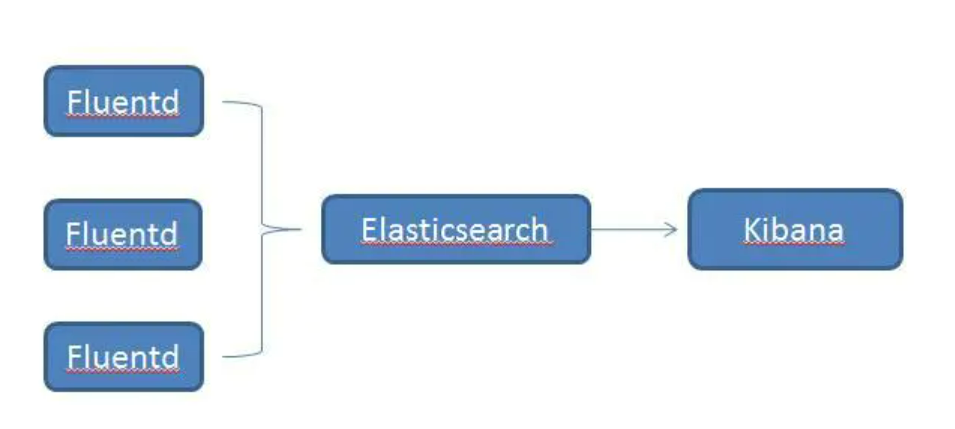
EFK 实践
接下来是具体实践 以k8s项目的addon中的EFK为例 因为版本不同 我这边的k8s是1.7.3,而github中的是1.8,所以yaml文件做了一些更改 主要是api-version的改变。
首先说明一下该实践的大体架构 每个节点以daemonset的形式跑一个fluentd 收集节点日志 收集的数据存储到ES中 最终通过Kibana可视化。这种部署方式只能收集容器应用日志输出到标准输出。而且 因为没有对ES加验证 且存储方式不是持久存储 所以不能在生产环境中使用。
部署Elasticsearch
在部署ES之前 首先看一下docker 的log-driver配置 修改为json-file,默认的可能是journald。fluentd要读取/var/log/containers/目录下的log日志 这些日志是从/var/lib/docker/containers/${CONTAINER_ID}/${CONTAINER_ID}-json.log链接过来的 如果log-driver是journald 就会读取不到:
vim /etc/sysconfig/docker
OPTIONS --selinux-enabled --log-driver json-file --signature-verification false
........
部署es-statefulset es-statefulset.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
rules:
- apiGroups:
-
resources:
- services
- namespaces
- endpoints
verbs:
- get
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: kube-system
name: elasticsearch-logging
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
apiGroup:
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: elasticsearch-logging
apiGroup:
---
# Elasticsearch deployment itself
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
version: v5.6.4
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
serviceName: elasticsearch-logging
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
version: v5.6.4
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
version: v5.6.4
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
spec:
serviceAccountName: elasticsearch-logging
containers:
- image: registry.cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/zhangchen-aisino/elasticsearch:v5.6.4
name: elasticsearch-logging
resources:
# need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: db
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9300
name: transport
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- name: elasticsearch-logging
mountPath: /data
env:
- name: NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
# Elasticsearch requires vm.max_map_count to be at least 262144.
# If your OS already sets up this number to a higher value, feel free
# to remove this init container.
volumes:
- name: elasticsearch-logging
emptyDir: {}
# Elasticsearch requires vm.max_map_count to be at least 262144.
# If your OS already sets up this number to a higher value, feel free
# to remove this init container.
initContainers:
- image: alpine:3.6
command: [ /sbin/sysctl , -w , vm.max_map_count 262144 ]
name: elasticsearch-logging-init
securityContext:
privileged: true
部署es-service:es-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
kubernetes.io/name: Elasticsearch
spec:
ports:
- port: 9200
protocol: TCP
targetPort: db
selector:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
部署Fluentd
部署fluentd配置文件
kind: ConfigMap
apiVersion: v1
data:
containers.input.conf: |-
source
type tail
path /var/log/containers/*.log
pos_file /var/log/es-containers.log.pos
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%NZ
tag kubernetes.*
read_from_head true
format multi_format
pattern
format json
time_key time
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%NZ
/pattern
pattern
format /^(? time . ) (? stream stdout|stderr) [^ ]* (? log .*)$/
time_format %Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%N%:z
/pattern
/source
system.input.conf: |-
# Example:
# 2015-12-21 23:17:22,066 [salt.state ][INFO ] Completed state [net.ipv4.ip_forward] at time 23:17:22.066081
source
type tail
format /^(? time [^ ]* [^ ,]*)[^\[]*\[[^\]]*\]\[(? severity [^ \]]*) *\] (? message .*)$/
time_format %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
path /var/log/salt/minion
pos_file /var/log/es-salt.pos
tag salt
/source
# Example:
# Dec 21 23:17:22 gke-foo-1-1-4b5cbd14-node-4eoj startupscript: Finished running startup script /var/run/google.startup.script
source
type tail
format syslog
path /var/log/startupscript.log
pos_file /var/log/es-startupscript.log.pos
tag startupscript
/source
# Examples:
# time 2016-02-04T06:51:03.053580605Z level info msg GET /containers/json
# time 2016-02-04T07:53:57.505612354Z level error msg HTTP Error err No such image: -f statusCode 404
source
type tail
format /^time (? time [^)]*) level (? severity [^ ]*) msg (? message [^ ]*) ( err (? error [^ ]*) )?( statusCode ($ status_code \d ))?/
path /var/log/docker.log
pos_file /var/log/es-docker.log.pos
tag docker
/source
# Example:
# 2016/02/04 06:52:38 filePurge: successfully removed file /var/etcd/data/member/wal/00000000000006d0-00000000010a23d1.wal
source
type tail
# Not parsing this, because it doesn t have anything particularly useful to
# parse out of it (like severities).
format none
path /var/log/etcd.log
pos_file /var/log/es-etcd.log.pos
tag etcd
/source
# Multi-line parsing is required for all the kube logs because very large log
# statements, such as those that include entire object bodies, get split into
# multiple lines by glog.
# Example:
# I0204 07:32:30.020537 3368 server.go:1048] POST /stats/container/: (13.972191ms) 200 [[Go-http-client/1.1] 10.244.1.3:40537]
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/kubelet.log
pos_file /var/log/es-kubelet.log.pos
tag kubelet
/source
# Example:
# I1118 21:26:53.975789 6 proxier.go:1096] Port nodePort for kube-system/default-http-backend:http (:31429/tcp) was open before and is still needed
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/kube-proxy.log
pos_file /var/log/es-kube-proxy.log.pos
tag kube-proxy
/source
# Example:
# I0204 07:00:19.604280 5 handlers.go:131] GET /api/v1/nodes: (1.624207ms) 200 [[kube-controller-manager/v1.1.3 (linux/amd64) kubernetes/6a81b50] 127.0.0.1:38266]
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/kube-apiserver.log
pos_file /var/log/es-kube-apiserver.log.pos
tag kube-apiserver
/source
# Example:
# I0204 06:55:31.872680 5 servicecontroller.go:277] LB already exists and doesn t need update for service kube-system/kube-ui
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/kube-controller-manager.log
pos_file /var/log/es-kube-controller-manager.log.pos
tag kube-controller-manager
/source
# Example:
# W0204 06:49:18.239674 7 reflector.go:245] pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:193: watch of *api.Service ended with: 401: The event in requested index is outdated and cleared (the requested history has been cleared [2578313/2577886]) [2579312]
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/kube-scheduler.log
pos_file /var/log/es-kube-scheduler.log.pos
tag kube-scheduler
/source
# Example:
# I1104 10:36:20.242766 5 rescheduler.go:73] Running Rescheduler
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/rescheduler.log
pos_file /var/log/es-rescheduler.log.pos
tag rescheduler
/source
# Example:
# I0603 15:31:05.793605 6 cluster_manager.go:230] Reading config from path /etc/gce.conf
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/glbc.log
pos_file /var/log/es-glbc.log.pos
tag glbc
/source
# Example:
# I0603 15:31:05.793605 6 cluster_manager.go:230] Reading config from path /etc/gce.conf
source
type tail
format multiline
multiline_flush_interval 5s
format_firstline /^\w\d{4}/
format1 /^(? severity \w)(? time \d{4} [^\s]*)\s (? pid \d )\s (? source [^ \]] )\] (? message .*)/
time_format %m%d %H:%M:%S.%N
path /var/log/cluster-autoscaler.log
pos_file /var/log/es-cluster-autoscaler.log.pos
tag cluster-autoscaler
/source
# Logs from systemd-journal for interesting services.
source
type systemd
filters [{ _SYSTEMD_UNIT : docker.service }]
pos_file /var/log/gcp-journald-docker.pos
read_from_head true
tag docker
/source
source
type systemd
filters [{ _SYSTEMD_UNIT : kubelet.service }]
pos_file /var/log/gcp-journald-kubelet.pos
read_from_head true
tag kubelet
/source
source
type systemd
filters [{ _SYSTEMD_UNIT : node-problem-detector.service }]
pos_file /var/log/gcp-journald-node-problem-detector.pos
read_from_head true
tag node-problem-detector
/source
forward.input.conf: |-
# Takes the messages sent over TCP
source
type forward
/source
monitoring.conf: |-
# Prometheus Exporter Plugin
# input plugin that exports metrics
source
type prometheus
/source
source
type monitor_agent
/source
# input plugin that collects metrics from MonitorAgent
source
type prometheus_monitor
labels
host ${hostname}
/labels
/source
# input plugin that collects metrics for output plugin
source
type prometheus_output_monitor
labels
host ${hostname}
/labels
/source
# input plugin that collects metrics for in_tail plugin
source
type prometheus_tail_monitor
labels
host ${hostname}
/labels
/source
output.conf: |-
# Enriches records with Kubernetes metadata
filter kubernetes.**
type kubernetes_metadata
/filter
match **
type elasticsearch
log_level info
include_tag_key true
host elasticsearch-logging
port 9200
logstash_format true
# Set the chunk limits.
buffer_chunk_limit 2M
buffer_queue_limit 8
flush_interval 5s
# Never wait longer than 5 minutes between retries.
max_retry_wait 30
# Disable the limit on the number of retries (retry forever).
disable_retry_limit
# Use multiple threads for processing.
num_threads 2
/match
metadata:
name: fluentd-es-config-v0.1.1
namespace: kube-system
labels:
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
在部署fluentd-daemonset之前 先要给k8s node 添加label beta.kubernetes.io/fluentd-ds-ready: “true” 因为fluentd-daemonset是根据这个label进行node selector。可以通过kubectl label 命令添加:
kubectl label node/node1 beta.kubernetes.io/fluentd-ds-ready: true
然后部署fluentd-daemonsetfluentd-es-ds.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: fluentd-es
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-es
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: fluentd-es
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-es
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
rules:
- apiGroups:
-
resources:
- namespaces
- pods
verbs:
- get
- watch
- list
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: fluentd-es
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-es
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: fluentd-es
namespace: kube-system
apiGroup:
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: fluentd-es
apiGroup:
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: fluentd-es-v2.0.2
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-es
version: v2.0.2
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: fluentd-es
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
version: v2.0.2
# This annotation ensures that fluentd does not get evicted if the node
# supports critical pod annotation based priority scheme.
# Note that this does not guarantee admission on the nodes (#40573).
annotations:
scheduler.alpha.kubernetes.io/critical-pod:
spec:
serviceAccountName: fluentd-es
containers:
- name: fluentd-es
image: registry.cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/zhangchen-aisino/fluentd-elasticsearch:v2.0.2
env:
- name: FLUENTD_ARGS
value: --no-supervisor -q
resources:
limits:
memory: 500Mi
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 200Mi
volumeMounts:
- name: varlog
mountPath: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
readOnly: true
- name: libsystemddir
mountPath: /host/lib
readOnly: true
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/fluent/config.d
nodeSelector:
beta.kubernetes.io/fluentd-ds-ready: true
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: varlog
hostPath:
path: /var/log
- name: varlibdockercontainers
hostPath:
path: /var/lib/docker/containers
# It is needed to copy systemd library to decompress journals
- name: libsystemddir
hostPath:
path: /usr/lib64
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: fluentd-es-config-v0.1.1
部署 Kibana
部署kibana-deployment kibana-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: kibana-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: kibana-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: kibana-logging
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kibana-logging
spec:
containers:
- name: kibana-logging
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:5.6.4
resources:
# need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_URL
value: http://elasticsearch-logging:9200
- name: SERVER_BASEPATH
value: /api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kibana-logging
- name: XPACK_MONITORING_ENABLED
value: false
- name: XPACK_SECURITY_ENABLED
value: false
ports:
- containerPort: 5601
name: ui
protocol: TCP
部署kibana-service kibana-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: kibana-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: kibana-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
kubernetes.io/name: Kibana
spec:
ports:
- port: 5601
protocol: TCP
targetPort: ui
selector:
k8s-app: kibana-logging
等到所有 pod都running之后 执行kubectl proxy 命令
kubectl proxy --address 172.16.21.250 --port 8086 --accept-hosts ^*$
在doscovery中 创建index,便可以看到ES中的日志数据了。
问题汇总
kibana使用Nodeport之后 本以为可以直接使用Nodeport连接 但是会报404 status 错误 在搜索之后 大概明白一点 如果启动参数中添加了server.basePath 那么一般是需要在前端做一个反向代理来重定向。在kibana的yaml文件中删除SERVER_BASEPATH该环境变量后 可以正常访问。
之后 尝试将ES的数据存储放到ceph中 yaml文件老写不对 最终尝试成功 文件如下
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
---
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
rules:
- apiGroups:
-
resources:
- services
- namespaces
- endpoints
verbs:
- get
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
namespace: kube-system
name: elasticsearch-logging
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
apiGroup:
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: elasticsearch-logging
apiGroup:
---
# Elasticsearch deployment itself
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
namespace: kube-system
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
version: v5.6.4
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
addonmanager.kubernetes.io/mode: Reconcile
spec:
serviceName: elasticsearch-logging
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
version: v5.6.4
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: elasticsearch-logging
version: v5.6.4
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: true
spec:
serviceAccountName: elasticsearch-logging
containers:
- image: registry.cn-qingdao.aliyuncs.com/zhangchen-aisino/elasticsearch:v5.6.4
name: elasticsearch-logging
resources:
# need more cpu upon initialization, therefore burstable class
limits:
cpu: 1000m
requests:
cpu: 100m
ports:
- containerPort: 9200
name: db
protocol: TCP
- containerPort: 9300
name: transport
protocol: TCP
volumeMounts:
- name: elasticsearch-logging
mountPath: /data
env:
- name: NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
#volumes:
#- name: elasticsearch-logging
#emptyDir: {}
# Elasticsearch requires vm.max_map_count to be at least 262144.
# If your OS already sets up this number to a higher value, feel free
# to remove this init container.
initContainers:
- image: alpine:3.6
command: [ /sbin/sysctl , -w , vm.max_map_count 262144 ]
name: elasticsearch-logging-init
securityContext:
privileged: true
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: elasticsearch-logging
annotations:
volume.beta.kubernetes.io/storage-class: ceph-web
spec:
accessModes: [ ReadWriteOnce ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 50Gi
iLogtail社区版使用入门 - K8s环境采集业务日志到SLS 本文介绍建立集中式日志采集分析系统的常用架构,并使用iLogtail社区版采集K8s环境业务日志到SLS,完成构建可观测平台的第一步。 iLogtail已经完整开源,期望同众多开发者一起将iLogtail打造成世界一流的可观测数据采集器。
iLogtail社区版使用入门 - 使用DaemonSet模式采集K8s容器日志 本文介绍K8s的日志架构,并通过利用K8s提供的基础能力完成数据驱动应用架构的第一步,使用iLogtail将日志统一采集写入Kafka。 iLogtail已经完整开源,期望同众多开发者一起将iLogtail打造成世界一流的可观测数据采集器。
Kubernetes容器平台建设中,F5解决方案好不好? 近年来,随着OpenStack、Kubernetes等云技术的兴起,应用系统的微服务化、快速迭代对资源的弹性伸缩能力提出了更高的要求。基于多年在负载均衡领域的经验,Kubernetes容器平台建设中,F5解决方案好不好? F5推出了Kubernetes容器服务解决方案 前不久,民生银行在Kubernetes容器平台建设中,探索使用了一种灵活的软件F5解决方案,在利用F5传统优势的同时,也满足了容器应用的高灵活性要求。
Kubernetes 监控一站式解决方案:阿里云 Prometheus 免费公测 近日刚刚发布免费公测的阿里云Prometheus(免费试用页面)提供了无缝对接Kubernetes集群的一站式、全托管监控解决方案,让用户可以方便灵活的一键配置对一个或多个阿里云Kubernetes集群的监控。
Rook:基于Ceph的Kubernetes存储解决方案 Rook是一款运行在Kubernetes集群中的存储服务编排工具,在0.8版本中,Rook已经变成Beta发行版,如果还没有尝试过Rook,可以现在尝鲜。Rook是什么,为什么很重要?Ceph运行在Kubernetes集群中很久了,为什么要有这么大的变动?如果以前玩过Ceph集群,肯定深知维护Ceph集群的复杂性,Rook就是为此而生,使用Kubernetes分布式平台简化大量针对Ceph存储的操作和维护工作。
相关文章
- 使用Kubernetes的挑战和应对技巧
- Kubernetes笔记:深入kubernetes---日志和监控( Prometheus、Helm、PrometheusOperator、Grafana)
- 6个工具帮助你在Windows上轻松运行Kubernetes
- kubespray v2.21.0 部署 kubernetes v1.24.0 集群
- Kubernetes ImagePolicyWebhook与ValidatingAdmissionWebhook【2】Image_Policy.go源码解析
- Kubernetes【日志】日志架构介绍
- Kubernetes CKS 2021【7】---Cluster Setup - Verify Platform
- docker/kubernetes国内源/镜像源解决方式
- Kubernetes集群开启Firewall
- Kubernetes教程之探索 Kubernetes 容器的艺术与科学
- kubernetes应用部署原理
- Kubernetes管理:看看EBay的蜜汁配方
- kubernetes介绍
- CentOS7 使用二进制部署 Kubernetes 1.15-1.17集群(均通用,已经尝试,细心)

