[转] 公司使用SpringMVC的RESTful接口的坑
原文出处:https://tech.imdada.cn/2015/12/23/springmvc-restful-optimize/
这边文章的根源可以理解成Spring是何如路径解析的
背景:在公司还没有服务化的时候,在整个DB层上架构了一个系统作为数据访问层(封装业务系统对数据层的调用,实现对数据库的分库分表,实现对数据的缓存)对外提供的是RESTful接口
RESTful:
@RequestMapping(path = "/list/cityId/{cityId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getJsonByCityId(@PathVariable Integer cityId)
客户端请求: GET /list/cityId/1
非RESTful
@RequestMapping(path = "/list/cityId", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody public String getJsonByCityId(@RequestParam Integer cityId)
客户端请求: GET /list/cityId?cityId=1
在接口越来越多的情况下,系统的性能在降低
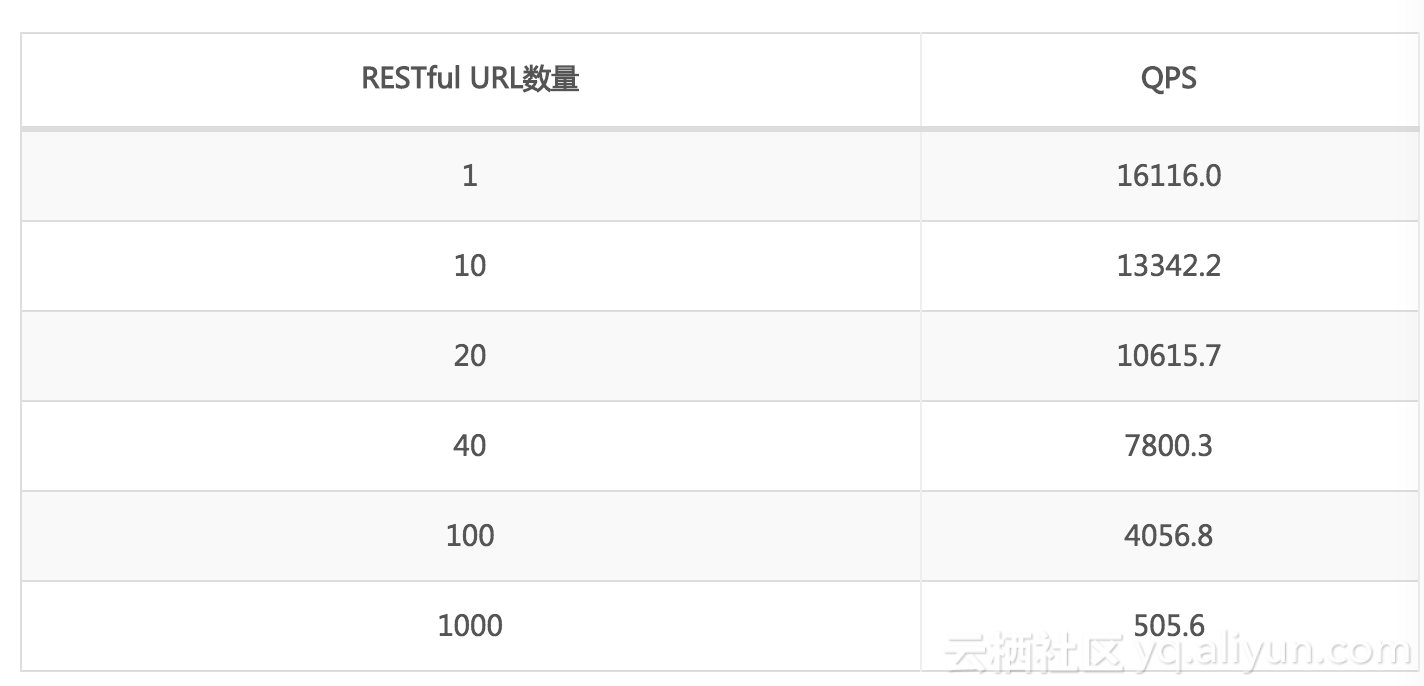
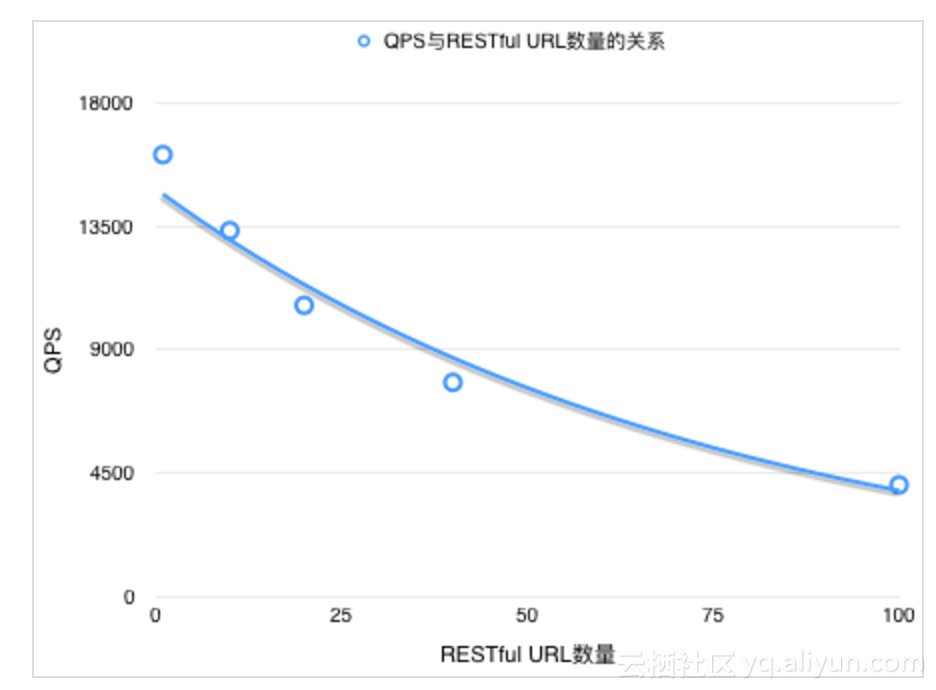
从结果上可以看出,URL的数量越多,SpringMVC的性能越差,查看源码,依然从DispatcherServlet#doDispatch方法入手
(1)AbstractHandlerMapping #getHandler
(2)AbstractHandlerMethodMapping #getHandlerInternal
(3)AbstractHandlerMethodMapping #lookupHandlerMethod
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List Match matches = new ArrayList Match
// 通过lookupPath获取匹配到的path
List T directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
// 非restful的接口,会匹配到并且添加到matches
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
// restful的接口,会匹配所有的URL (这就是根源所在,数量越多,性能越差)
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator Match comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
// 选取排序后的第一个作为最近排序条件
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
// 前两个匹配条件排序一样抛出异常
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path " +
request.getRequestURL() + ": {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
SpringMVC首先对HTTP请求中的path与已注册的RequestMappingInfo(经解析的@RequestMapping)中的path进行一个完全匹配来查找对应的HandlerMethod,即处理该请求的方法,这个匹配就是一个Map#get方法。若找不到则会遍历所有的RequestMappingInfo进行查找。这个查找是不会提前停止的,直到遍历完全部的RequestMappingInfo
springMVC的匹配逻辑:
在遍历的过程中,SpringMVC首先会根据@RequestMapping的headers,params,produces,consumes,methods与实际的HttpServletRequest中的信息对比,剔除一些明显不合格的RequestMapping,如果以上信息都能匹配上,那么就会对path进行正则匹配,进行打分
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null || params == null || headers == null || consumes == null || produces == null) {
return null;
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, patterns,methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom.getCondition());
}
Comparator comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request))
String match = getMatchingPattern(pattern, lookupPath);
path的匹配首先会把url按照“/”分割,然后对于每一部分都会使用到正则表达式,即使该字符串是定长的静态的。所以该匹配逻辑的性能可能会很差
至于解决方案,公司的文章里面有写到,我正好趁这次机会把原理重新熟悉了一遍
SpringBoot2.x系列教程12--SpringBoot中构建RESTful风格的API接口 在前面的章节中,壹哥 给大家介绍了在前后端不分离的开发模式中,SpringBoot是如何处理静态资源的。但是现在真正的企业开发中,前后端分离才是比较流行的开发模式。而在这种开发模式中,前端团队负责UI界面,后端团队负责实现Web接口和核心业务逻辑,两个团队之间密切配合,共同完成项目开发。 前端需要调用后端的Web接口,而后端团队也需要把数据以合适的格式传递给前端,现在主流的数据载体是用JSON格式。另外因为Web接口是后端团队开发的,前端团队并不知道这个Web接口的定义和使用规则,所以现在比较流行基于RESTful风格的Web接口设计,这样设计出来的Web接口就都遵循着一定的规范,前端
基于多数据源零代码同时生成多个数据库CRUD增删改查RESTful API接口——MySql,PostgreSql,Oracle,Microsoft SQL Server 利用spring boot多数据源功能,可以同时支持不同类型数据库mysql,oracle,postsql,sql server等,以及相同类型数据库不同的schema。零代码同时生成不同类型数据库增删改查RESTful api,且支持同一接口中跨库数据访问二次开发。在同一个Java程序中,通过多数据源功能,不需要一行代码,我们就可以得到不同数据库的基本crud功能,包括API和UI。
vue-admin-chart实现管理后台登陆页面,axios请求restful接口,Composition API风格 vue-admin-chart管理后台登陆界面是基于Vue3.2 vue-cli5 vue-router4 ElementPlus2.2 Pinia2.0状态管理存储 axios网络请求等搭建,采用TS(TypeScript)脚本语言,以Composition api风格编写,采用axios请求远程Restful API接口调试。
无需编程,基于微软mssql数据库零代码生成CRUD增删改查RESTful API接口 通过之前一篇文章 无需编程,基于甲骨文oracle数据库零代码生成CRUD增删改查RESTful API接口 的介绍,引入了FreeMarker模版引擎,通过配置模版实现创建和修改物理表结构SQL语句,并且通过配置oracle数据库SQL模版,基于oracle数据库,零代码实现crud增删改查。本文采用同样的方式,很容易就可以支持微软SQL Server数据库。
相关文章
- SpringMVC源码解析之ServletInvocableHandlerMethod
- 菜鸟学习Spring——SpringMVC注解版前台向后台传值的两种方式
- SpringMVC的AJAX请求报406错误
- SpringMVC传递参数和获取参数以及返回数据
- SpringMvc项目加载顺序及上下文小结
- maven+springMVC+mybatis+easyUI管理用户增删改查
- SpringMVC——redirect重定向跳转传值
- SpringMVC响应Ajax请求(@Responsebody注解返回页面)
- 【SpringMVC】SpringMVC系列7之POJO 对象绑定请求参数值
- JSP-Servlet-SpringMVC
- Spring SpringMVC SpringBoot SpringCloud概念、关系及区别
- springmvc 例
- SpringMVC系列(十二)自定义拦截器
- springMVC如何访问静态文件

