人脸识别-Loss-2018:ArcFace【对CosFace的改进】【ArcFace:直接在角度空间(angular space)中最大化分类界限;CosFace是在余弦空间中最大化分类界限】
论文:ArcFace: Additive Angular Margin Loss for Deep Face Recognition
代码:https://github.com/deepinsight/insightface
本文提出了新的监督值: c o s ( θ + m ) cos(θ+m) cos(θ+m),在进行权重和特征归一化的基础上最大化角度空间的决策边界。
ArcFace,Insight face,又名Additive Angular Margin Loss,是人脸识别领域2019年前最好的结果
源码及文档见:https://gitee.com/swjtugx/classmate
一、概述
1、网络结构优化---->损失函数优化
特征提取通常可以认为是人脸识别最关键的步骤,我们希望提取到的特征更偏向于该人脸"独有"的特征。
我们的网络和模型承担着提取特征的重任,优秀的网络和训练策略使模型更加健壮。
在ResNet在2015年被提出后,越来越多优秀的网络基于ResNet进行优化更新也已取得卓越的成就,而在网络结构进一步升级优化有困难的情况下,研究者逐步将目光转向损失函数。
关于Loss对于网络的影响,最直观的就是训练中通过计算Loss反传梯度来实现对模型参数的更新。因此 不同的Loss可以使模型更加侧重于学习到数据某一方面的特性,并在之后能够更好地提取到这一"独有”的 特征,Loss对于网络优化有导向性的作用。
文章 ArcFace:Additive Angular Margin Loss for Deep Face Recognition 的作者提出了Additive Angular Margin Loss。在继SoftmaxLoss、Center Loss、A-Softmax Loss、Cosine Margin Loss之后有好的表现。
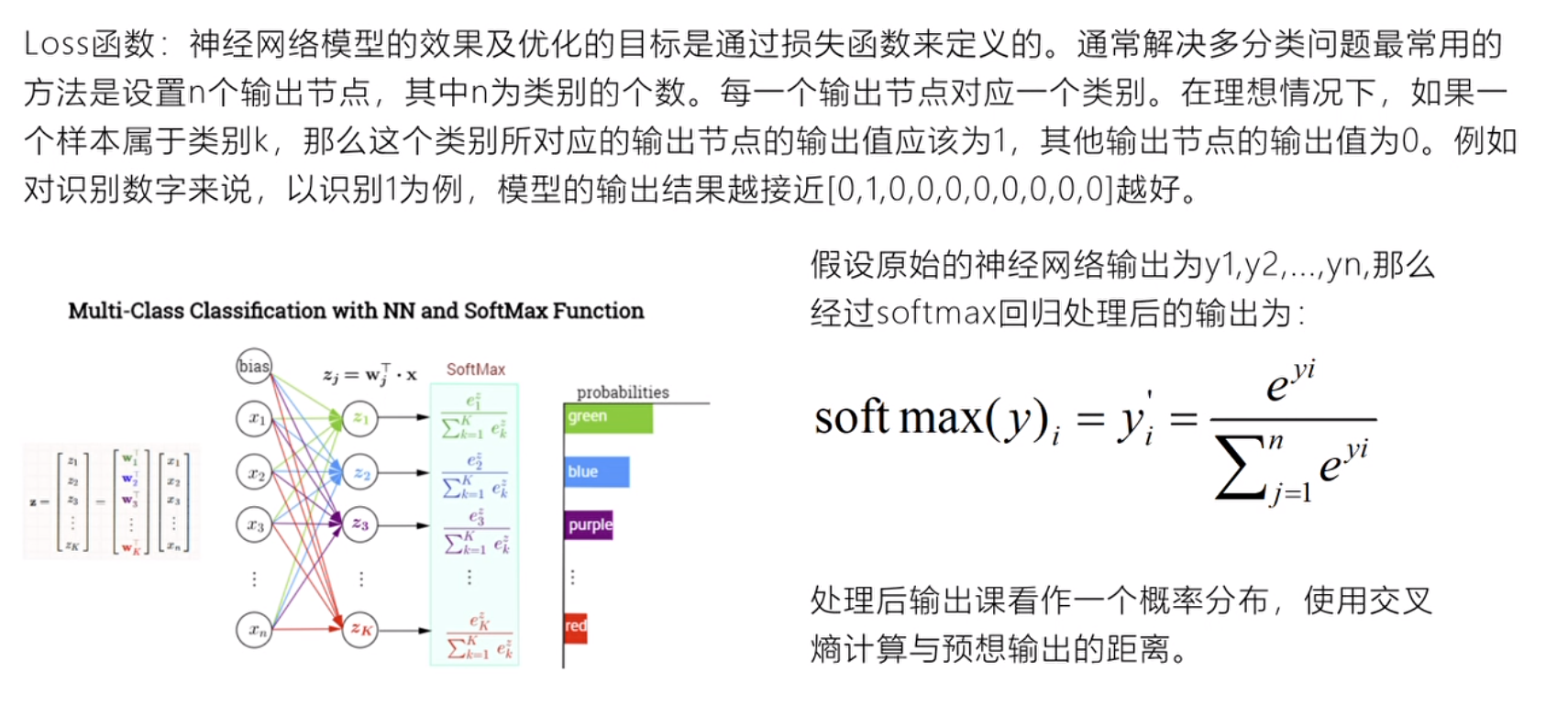
1、简介
目前已经有大量的基于深度学习的人脸识别模型,这些模型主要有三方面的不同:
- 训练数据的规模不同:
- 目前常用的人脸识别数据集VGG-Face,VGG-Face2,CAISA-WebFace,UMDFaces,MS-Celeb-1M,MegaFace,图像的规模从几千到数十万不等。
- 虽然MS-Celeb-1M,MegaFace收集的大量人员的人脸图像,但是他们存在标注噪声和长尾效应。作为对比,谷歌的私有人脸数据集包含数百万人员的照片,FRVT比赛的冠军依图科技,用于18亿规模的私有数据集。
- 因为数据集的规模不同,工业界人脸识别产品的性能要好于学术界。由于数据集规模不同,很多深度学习模型的效果无法完全复现。
- 网络结构及相关参数设置不同:
- 如果使用大的网络(ResNet和Inception-Resnet),效果就要比小网络(VGGNet和Google Inception V1)要好。
- 不同的应用场景需要考虑的产品性能不同,移动式设备上根据关注识别效率,安保场景下更加关注识别精度。
- 损失函数不同:
- 基于欧式间隔的损失: center loss,Range loss,Marginal loss在类别数很多时占用GPU过多,contrastive loss,triplet loss构建样本对需要很强的策略性;
- 基于角度间隔和余弦间隔的损失:L-softmax提出了 c o s ( m θ ) cos(mθ) cos(mθ) 实现了在角度空间内进行识别,SphereFace(A-Softmax)在其基础上加上了权重归一化,AM-Softmax提出了 c o s ( θ ) − m cos(θ)−m cos(θ)−m 在余弦空间内进行识别,取得了当下最先进的识别结果。
- 相比于欧式空间间隔,角度空间间隔和余弦空间间隔在超平面上增加了判别限制,符合人脸分布在超平面上这一先验知识。
作者认为,数据 > 网络 > 损失 由高到低的影响识别效果。
使用深度卷积神经网络 (DCNN) 进行大规模人脸识别的特征学习中,主要挑战之一在于 设计适当的损失函数以增强判别能力。
Center Loss 会惩罚欧式空间中深层特征及其对应的类中心之间的距离,以实现 类内紧凑性 (intra-class compactness)。
SphereFace 假定 最后一个全连接层中的线性变换矩阵 可用作角度空间 (angular space) 中类中心的表示,并以乘法方式惩罚深度特征及其相应权重 (weights) 之间的角度 (angles)。
近期,一种流行的研究方向是将 margins 纳入已建立的损失函数中,以最大程度地提高人脸类别可分性 (face class separability)。
本文提出了一个 加性角度边距损失 (Additive Angular Margin Loss, ArcFace),以获取用于人脸识别的高判别度特征 (highly discriminative features)。
由于所提出的 ArcFace 与 超球面上的测地距离 (geodesic distance on the hypersphere) 精确对应,故其具有明晰的几何解释。大量实验表明,ArcFace 始终优于 SOTA,且容易实现,计算开销可忽略不计。
一、Large Margin Cosine Loss (LMCL)【CosFace】
Large Margin Cosine Loss (LMCL):
L
L
M
C
=
−
1
N
∑
i
=
1
N
log
e
s
⋅
[
cos
(
θ
y
i
,
i
)
−
m
]
e
s
⋅
[
cos
(
θ
y
i
,
i
)
−
m
]
+
∑
j
=
1
,
j
≠
y
i
c
e
s
⋅
cos
(
θ
j
,
i
)
(4)
\begin{aligned}{{L}_{LMC}}=-\frac{1}{N}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{N}{\log \frac{{{e}^{s· [\cos ({{\theta }_{y_i,i} })-m]}}}{{{e}^{s·[\cos ({{\theta }_{y_i,i}})-m]}}+\sum\nolimits_{j=1,j\ne yi}^{c}{{{e}^{s· \cos {{(\theta }_{j},i)}}}}}} \tag4 \end{aligned}
LLMC=−N1i=1∑Nloges⋅[cos(θyi,i)−m]+∑j=1,j=yices⋅cos(θj,i)es⋅[cos(θyi,i)−m](4)
二、Additive Angular Margin Loss(ArcFace)
ArchFace中是直接在角度空间(angular space)中最大化分类界限,而CosineFace是在余弦空间中最大化分类界限,这也是为什么这篇文章叫ArcFace的原因,因为arc含义和angular一样。
L A r c = − 1 N ∑ i = 1 N l o g e s [ c o s ( θ y i , i + m ) ] e s [ c o s ( θ y i , i + m ) ] + ∑ j ≠ y i e s c o s ( θ j , i ) \begin{aligned}L_{Arc}=-\frac{1}{N}\sum\limits_{i=1}^{N}log\frac{e^{s[cos(\theta_{y_i,i}+m)]}}{e^{s[cos(\theta_{y_i,i}+m)]}+\sum_{j\neq y_i}e^{s\ cos(\theta_j,i)}} \end{aligned} LArc=−N1i=1∑Nloges[cos(θyi,i+m)]+∑j=yies cos(θj,i)es[cos(θyi,i+m)]
约束条件有:
- W = W ∗ ∣ ∣ W ∗ ∣ ∣ W=\cfrac{W^*}{||W^*||} W=∣∣W∗∣∣W∗
- x = x ∗ ∣ ∣ x ∗ ∣ ∣ x=\cfrac{x^*}{||x^*||} x=∣∣x∗∣∣x∗
- c o s ( θ j , i ) = W j T x i cos(θ_j,i)=W_j^Tx_i cos(θj,i)=WjTxi
其中:
- N N N:训练样本数,
- x i x_i xi:与 y i y_i yi 的 ground-truth类对应的第 i i i 个特征向量;
- W j W_j Wj: W j W_j Wj 是第 j j j 类的权重向量;
- θ j θ_j θj: W j W_j Wj 与 x i x_i xi的夹角;
可以看到和CosFace非常类似,只是将 m m m 作为角度加上去了,这样就强行拉大了同类之间的角度,使得神经网络更努力地将同类收得更紧。
三、Softmax、SphereFace、CosFace、ArcFace对比(二分类场景)

- p i p_i pi:样本 x i x_i xi被正确分类的概率;
- N N N:训练样本数量;
- C C C:分类数量;
四、ArcFace Loss代码实现
伪代码实现步骤:
- 对 x x x 进行归一化
- 对 W W W 进行归一化
- 计算 W T ⋅ x W^T·x WT⋅x 得到预测向量 y y y
- 从 y y y 中挑出与ground truth对应的值
- 计算其反余弦得到角度
- 角度加上 m m m
- 得到挑出从 y y y 中挑出与ground truth对应的值所在位置的独热码
- 将 c o s ( θ + m ) cos(\theta+m) cos(θ+m) 通过独热码放回原来的位置
- 对所有值乘上固定值 s s s
1、代码01

2、代码02
# ArcFace
class ArcMarginProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin arc distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
s: norm of input feature
m: margin
cos(theta + m)
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, s=30.0, m=0.50, easy_margin=False):
super(ArcMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.s = s
self.m = m
# Parameter 的用途:
# 将一个不可训练的类型Tensor转换成可以训练的类型parameter
# 并将这个parameter绑定到这个module里面
# net.parameter()中就有这个绑定的parameter,所以在参数优化的时候可以进行优化的
# https://www.jianshu.com/p/d8b77cc02410
# 初始化权重
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.easy_margin = easy_margin
self.cos_m = math.cos(m)
self.sin_m = math.sin(m)
self.th = math.cos(math.pi - m)
self.mm = math.sin(math.pi - m) * m
def forward(self, input, label):
# --------------------------- cos(theta) & phi(theta) ---------------------------
# torch.nn.functional.linear(input, weight, bias=None)
# y=x*W^T+b
cosine = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
sine = torch.sqrt(1.0 - torch.pow(cosine, 2))
# cos(a+b)=cos(a)*cos(b)-size(a)*sin(b)
phi = cosine * self.cos_m - sine * self.sin_m
if self.easy_margin:
# torch.where(condition, x, y) → Tensor
# condition (ByteTensor) – When True (nonzero), yield x, otherwise yield y
# x (Tensor) – values selected at indices where condition is True
# y (Tensor) – values selected at indices where condition is False
# return:
# A tensor of shape equal to the broadcasted shape of condition, x, y
# cosine>0 means two class is similar, thus use the phi which make it
phi = torch.where(cosine > 0, phi, cosine)
else:
phi = torch.where(cosine > self.th, phi, cosine - self.mm)
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
# one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), requires_grad=True, device='cuda')
# 将cos(\theta + m)更新到tensor相应的位置中
one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), device='cuda')
# scatter_(dim, index, src)
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
# -------------torch.where(out_i = {x_i if condition_i else y_i) -------------
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine)
# you can use torch.where if your torch.__version__ is 0.4
output *= self.s
# print(output)
return output
3、代码03
# ! /usr/bin/python
# -*- encoding: utf-8 -*-
# ArcFace
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math
from torch.nn import Parameter
class ArcMarginProduct(nn.Module):
r"""Implement of large margin arc distance: :
Args:
in_features: size of each input sample
out_features: size of each output sample
s: norm of input feature
m: margin
cos(theta + m)<===> cos(θ + m)
"""
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features, s=30.0, m=0.50, easy_margin=False):
super(ArcMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features
self.out_features = out_features
self.s = s
self.m = m
# Parameter 的用途:
# 将一个不可训练的类型Tensor转换成可以训练的类型parameter
# 并将这个parameter绑定到这个module里面
# net.parameter()中就有这个绑定的parameter,所以在参数优化的时候可以进行优化的
# https://www.jianshu.com/p/d8b77cc02410
# 初始化权重
self.weight = Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_features, in_features))
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.easy_margin = easy_margin
self.cos_m = math.cos(m)
self.sin_m = math.sin(m)
# make the function cos(θ+m) monotonic decreasing while θ in [0°,180°]
self.th = math.cos(math.pi - m)
self.mm = math.sin(math.pi - m) * m
def forward(self, input, label):
# --------------------------- cos(θ) & phi(θ) ---------------------------
# torch.nn.functional.linear(input, weight, bias=None)
# y=x*W^T+b
cosine = F.linear(F.normalize(input), F.normalize(self.weight))
sine = torch.sqrt(1.0 - torch.pow(cosine, 2))
# cos(a+b)=cos(a)*cos(b)-sin(a)*sin(b)
phi = cosine * self.cos_m - sine * self.sin_m
if self.easy_margin:
# torch.where(condition, x, y) → Tensor
# condition (ByteTensor) – When True (nonzero), yield x, otherwise yield y
# x (Tensor) – values selected at indices where condition is True
# y (Tensor) – values selected at indices where condition is False
# return:
# A tensor of shape equal to the broadcasted shape of condition, x, y
# cosine>0 means two class is similar, thus use the phi which make it
phi = torch.where(cosine > 0, phi, cosine)
else:
phi = torch.where(cosine > self.th, phi, cosine - self.mm)
# --------------------------- convert label to one-hot ---------------------------
# one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), requires_grad=True, device='cuda')
# 将cos(θ + m)更新到tensor相应的位置中
one_hot = torch.zeros(cosine.size(), device='cuda')
# scatter_(dim, index, src)
one_hot.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
# -------------torch.where(out_i = {x_i if condition_i else y_i) -------------
output = (one_hot * phi) + ((1.0 - one_hot) * cosine)
# you can use torch.where if your torch.__version__ is 0.4
output *= self.s
# print(output)
return output
4、代码04
luckycallor/InsightFace-tensorflow
def calculate_arcface_logits(embds, weights, labels, class_num, s, m):
embds = tf.nn.l2_normalize(embds, axis=1, name='normed_embd')
weights = tf.nn.l2_normalize(weights, axis=0)
cos_m = math.cos(m)
sin_m = math.sin(m)
mm = sin_m * m
threshold = math.cos(math.pi - m)
cos_t = tf.matmul(embds, weights, name='cos_t')
cos_t2 = tf.square(cos_t, name='cos_2')
sin_t2 = tf.subtract(1., cos_t2, name='sin_2')
sin_t = tf.sqrt(sin_t2, name='sin_t')
cos_mt = s * tf.subtract(tf.multiply(cos_t, cos_m), tf.multiply(sin_t, sin_m), name='cos_mt')
cond_v = cos_t - threshold
cond = tf.cast(tf.nn.relu(cond_v, name='if_else'), dtype=tf.bool)
keep_val = s*(cos_t - mm)
cos_mt_temp = tf.where(cond, cos_mt, keep_val)
mask = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=class_num, name='one_hot_mask')
inv_mask = tf.subtract(1., mask, name='inverse_mask')
s_cos_t = tf.multiply(s, cos_t, name='scalar_cos_t')
output = tf.add(tf.multiply(s_cos_t, inv_mask), tf.multiply(cos_mt_temp, mask), name='arcface_logits')
return output
5、代码05
class ArcMarginProduct(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_features=128, out_features=200, s=32.0, m=0.50, easy_margin=False, gpunum=0): # in_features=128 对应context?
super(ArcMarginProduct, self).__init__()
self.in_features = in_features # 384
self.out_features = out_features # 4 (类别数量)
self.s = s # 参数s,30
self.m = m # 参数m, 0.5
self.gpunum = gpunum
self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(out_features, in_features)) # shape = [(类别数⽬, 128)]
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.weight)
self.easy_margin = easy_margin
def forward(self, X, label): # X: torch.Size([32, 384]); label: torch.Size([32])
assert self.s > 0.0
assert 0 <= self.m <= π/2 # 0 <= m <= 1.57
cos_m = cos(self.m) # cos_m = cos(0.5) = 0.8775825618903728
sin_m = sin(self.m) # sin_m = sin(0.5) = 0.479425538604203
mm = sin(π - self.m) * self.m # sin(π-m)*m = sin(m) * m =sin(0.5)*0.5 = 0.23971276930210156
# threshold: 这个阈值避免 theta+m >= π 【make the function cos(theta+m) monotonic decreasing while theta in [0°,180°]】
threshold = cos(π - self.m) # cos(π - m) = -cos(m) 【π - m = 2.64弧度; self.threshold = -0.8775825618903726】
X = F.normalize(X) # torch.Size([32, 384])
weight = F.normalize(self.weight) # torch.Size([4, 384])
cos_θ = F.linear(X, weight) # cosθ torch.Size([32, 4])
sin_θ = torch.sqrt(1.0 - torch.pow(cos_θ, 2)) # torch.Size([32, 4])
cos_θm = cos_θ * cos_m - sin_θ * sin_m # cos_θm = cos(θ+m)=cosθ*cosm-sinθ*sinm 【torch.Size([32, 4])】
if self.easy_margin: # 将0作为阈值,得到超过阈值的索引
condition = cos_θ > 0
cos_θm = torch.where(condition, cos_θm, cos_θ)
else: # 将负数作为阈值
condition = cos_θ > threshold
keep_val = cos_θ - mm
cos_θm = torch.where(condition, cos_θm, keep_val)
one_hot_mask = torch.zeros(cos_θ.size(), device=f'cuda:{self.gpunum}')
one_hot_mask.scatter_(1, label.view(-1, 1).long(), 1)
inversed_mask = 1.0 - one_hot_mask
output = (cos_θm * one_hot_mask) + (cos_θ * inversed_mask) # arcface_logits
output = self.s * output
return output
在论文中,作者实际计算 cos(θ+ m) \text{cos(θ+ m)} cos(θ+ m) 用的是下⾯这个公式:
cos(θ+ m)=cosθcosm-sinθsinm \text{cos(θ+ m)=cosθcosm-sinθsinm} cos(θ+ m)=cosθcosm-sinθsinm
所以,关键是怎么算?
下⾯的⼀坨代码都是为了计算这个式⼦,之所以这么复杂,是因为 cos(theta + m) \text{cos(theta + m)} cos(theta + m) 并非是单调的。
我们知道,在L-softmax,A-softmax中, 作者为了解决cos函数不单调的时候,提出了使⽤
(
−
1
)
m
c
o
s
θ
m
−
2
k
(−1)^mcosθm − 2k
(−1)mcosθm−2k
这个函数来代替原始的cos函数,就是保证在训练过程中,保证函数⼀直保持在递减的区间,这样算法才是有效的。这⾥arcface在实现中 也进⾏了处理,只不过不是使⽤上⾯的函数⽽已。
作者在计算的时候,使⽤了⼀个叫做“threshold”的变量来进⾏约束。这块内容推敲⼀下还是可以理解的。
因为在原始的输出 c o s θ cosθ cosθ 中, θ θ θ 的取值范围为 [ 0 , π ] [0,π] [0,π],那么如果直接对 θ θ θ 加上 m m m,则可能会超过 π π π,那么这时候函数就不单调了,所以要在保证 cos(θ+ m) \text{cos(θ+ m)} cos(θ+ m)⼯作在 [ 0 , π ] [0,π] [0,π] 范围内。这时候的限制条件就变成了 0 ≤ θ + m ≤ π 0≤θ+ m≤π 0≤θ+m≤π,即: − m ≤ θ ≤ π − m -m≤θ≤π-m −m≤θ≤π−m。
因为cos函数是递减函数,那么对于cos函数来说,就是要求 c o s θ ≥ c o s ( π − m ) cosθ≥cos(π-m) cosθ≥cos(π−m),即代码中的:cos_theta > self.threshold
参考资料:
Bilibili:计算机视觉 - 人脸识别 - VGGFace2 & ArcFace (FG2018, CVPR2019)
Bilibili【人脸识别】ArcFace/Insight face模型及代码讲解
arcface代码,arcface sdk
【机器学习】详解 ArcFace
人脸识别损失函数简介与Pytorch实现:ArcFace、SphereFace、CosFace
解析人脸识别中cosface和arcface(insightface)的损失函数以及源码
【机器学习】详解 ArcFace
arcface的前世今生
ArcFace-人脸识别
解析ArcFace源码
知乎:ArcFace论文解析
GitHub:InsightFace-tensorflow
【人脸识别】MTCNN + Arcface全流程详解 Pytorch代码 损失函数发展
相关文章
- Angular CLI 使用教程指南参考
- angular依赖注入的理解(转)
- Angular 英雄示例教程
- angular基本入门教程
- Angular 复习与进阶系列 – Component 组件 の Template Binding Syntax
- Angular 学习笔记 (cdk focus monitor 和一些 focus tabindex 的基础)
- Asp.net core Identity + identity server + angular 学习笔记 (第四篇)
- Asp.net core Identity + identity server + angular 学习笔记 (第二篇)
- Angular 学习笔记 (Material Datepicker)
- angular.module()参数问题
- 【6】 angular 路由基础知识_在路由时传递数据_重定向路由_子路由_辅助路由_路由守卫
- YY游戏云的angular js实践总结

