会话跟踪技术-session和cookie
会话(Session)跟踪是Web程序中常用的技术,用来跟踪用户的整个会话。常用的会话跟踪技术是Cookie与Session。
Cookie通过在客户端记录信息确定用户身份,Session通过在服务器端记录信息确定用户身份。
Cookie对象与HttpSession对象简介
但是在有些时候我们是需要服务端能够记录客户端浏览器的访问状态的,如获取当前客户端浏览器的访问服务端的次数时就需要会话状态的维持。在Servlet中提供了Cookie对象与HttpSession对象用于维护客户端与服务端的会话状态的维持。二者不同的是Cookie是通Cookie对象与HttpSession对象的作用是维护客户端浏览器与服务端的会话状态的两个对象。由于HTTP协议是一个无状态的协议,所以服务端并不会记录当前客户端浏览器的访问状态,过客户端浏览器实现会话的维持,而HttpSession是通过服务端来实现会话状态的维持。
如何记录用户状态信息原理,举例:会员卡,银行卡
用户记录用户状态的技术
一 Cookie的使用
Cookie是一种保存少量信息至浏览器的一种技术,第一请求时,服务器可以响应给浏览器一些Cookie信息,第二次请求,浏览器会携带之前的cookie发送给服务器,通过这种机制可以实现在浏览器端保留一些用户信息.为服务端获取用户状态获得依据
1 Cookie对象的特点
Ø Cookie使用字符串存储数据
Ø Cookie使用Key与Value结构存储数据
Ø 单个Cookie存储数据大小限制在4097个字节
Ø Cookie存储的数据中不支持中文,Servlet4.0中支持
Ø Cookie是与域名绑定所以不支持跨一级域名访问
Ø Cookie对象保存在客户端浏览器内存上或系统磁盘中
Ø Cookie分为持久化Cookie(保存在磁盘上)与状态Cookie(保存在内存上)
Ø 浏览器在保存同一域名所返回Cookie的数量是有限的。不同浏览器支持的数量不同,
Chrome浏览器为50个
Ø 浏览器每次请求时都会把与当前访问的域名相关的Cookie在请求中提交到服务端。
2 Cookie对象的创建
Cookie cookie = new Cookie("key","value")
通过new关键字创建Cookie对象
response.addCookie(cookie)
通过HttpServletResponse对象将Cookie写回给客户端浏览器。
3 Cookie中数据的获取
通过HttpServletRequest对象获取Cookie,返回Cookie数组。
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies()
4 Cookie不支持中文解决方案
在Servlet4.0版本之前的Cookie中是不支持中文存储的,如果存储的数据中含有中文,代码会直接出现异常。我们可以通过对含有中文的数据重新进行编码来解决该问题。在Servlet4.0中的Cookie是支持中文存储的。
可以使用对中文进行转码处理
URLEncoder.encode("content","code")
将内容按照指定的编码方式做URL编码处理。
URLDecoder.decode("content","code")
将内容按照指定的编码方式做URL解码处理。
5 Cookie持久化和状态Cookie
状态Cookie:浏览器会缓存Cookie对象。浏览器关闭后Cookie对象销毁。
持久化Cookie:浏览器会对Cookie做持久化处理,基于文件形式保存在系统的指定目录中。在Windows10系统中为了安全问题不会显示Cookie中的内容。
当Cookie对象创建后默认为状态Cookie。可以使用Cookie对象下的cookie.setMaxAge(60)方法设置失效时间,单位为秒。一旦设置了失效时间,那么该Cookie为持久化Cookie,浏览器会将Cookie对象持久化到磁盘中。当失效时间到达后文件删除。
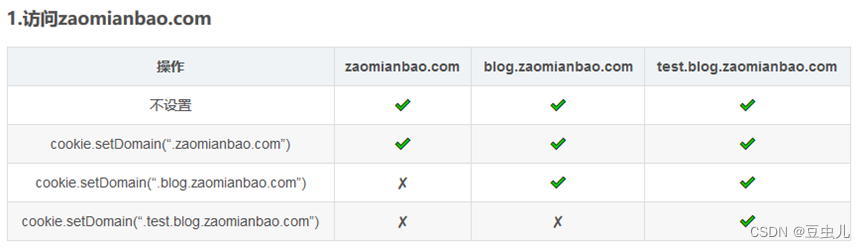
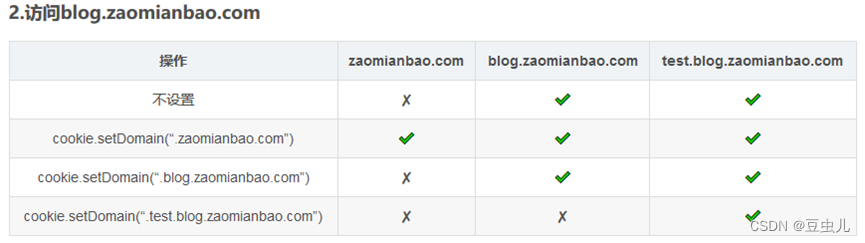
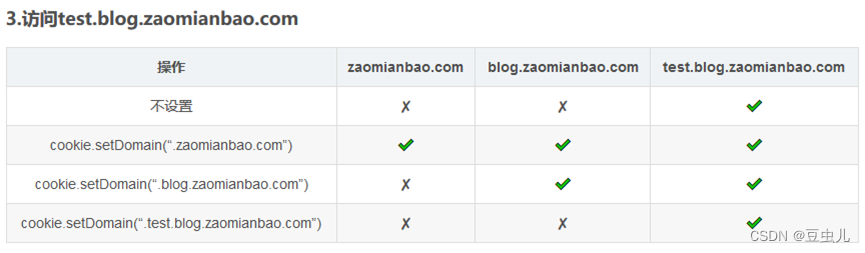
6 Cookie跨域问题
域名分类:
域名分为顶级域、顶级域名(一级域名)、二级域名。
域名等级的区别:
一级域名比二级域名更高级,二级域名是依附于一级域名之下的附属分区域名,即二级域名是一级域名的细化分级。例如:baidu.com 为一级域名,news.baidu.com为二级域名。
Cookie不支持一级域名的跨域,支持二级域名的跨域。
测试代码
1向浏览器响应Cookie
package com.mashibing.test;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servlet1.do")
public class Servlet1 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 通过响应对象,向浏览器响应一些Cookie
Cookie c1=new Cookie("age","10");// 状态Cookie 重启即清除
Cookie c2=new Cookie("gender", "男");//持久化Cookie 让浏览器保留1分钟
//c2.setMaxAge(60);// 秒钟 持久化Cookie 让浏览器保留1分钟
resp.addCookie(c1);
resp.addCookie(c2);
}
}
2读取请求中的Cookie
package com.mashibing.test;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.xml.ws.WebEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servlet2.do")
public class Servlet2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 读取请求中的Cookie
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
//cookies不为null
if(null != cookies){
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
System.out.println(cookie.getName()+"="+cookie.getValue());
}
}
}
}案例:通过Cookie判断用户是否访问过当前Servlet
需求:当客户端浏览器第一次访问Servlet时返回“您好,欢迎您第一次访问!”,第二次访问时返回“欢迎您回来!”
package com.mashibing.test;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servlet3.do")
public class Servlet3 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 如果是第一访问当前Servlet.向浏览器响应一个cookie ("servlet3","1")
// 如果是多次访问,就再次数上+1
Cookie[] cookies = req.getCookies();
boolean flag =false ;
if(null !=cookies){
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
String cookieName = cookie.getName();
if(cookieName.equals("servlet3")){
// 创建Cookie次数+1
Integer value = Integer.parseInt(cookie.getValue())+1;
Cookie c=new Cookie("servlet3", String.valueOf(value));
resp.addCookie(c);
System.out.println("欢迎您第"+value+"访问");
flag=true;
}
}
}
if(!flag){
System.out.println("欢迎您第一次访问");
Cookie c=new Cookie("servlet3", "1");
resp.addCookie(c);
}
}
}
Cookie对象总结
Cookie对于存储内容是基于明文的方式存储的,所以安全性很低。不要在Cookie中存放敏感数据。在数据存储时,虽然在Servlet4.0中Cookie支持中文,但是建议对Cookie中存放的内容做编码处理,也可提高安全性。
二 Session的使用
HttpSession对象
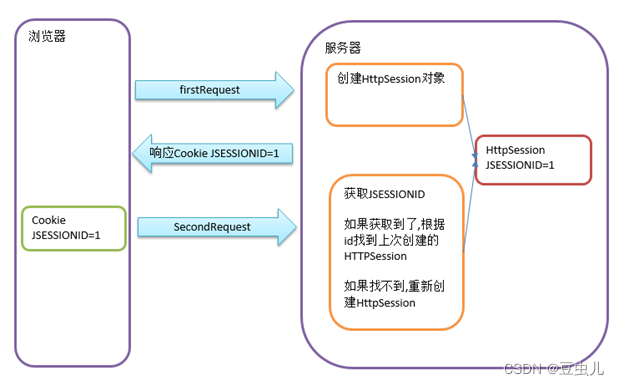
HttpSession是一种保存少量信息至服务器端的一种技术,第一请求时,服务器会创建HttpSession,我们可以在HttpSession对象中保存一些关于用户的状态信息,并将HttpSession的JSESSIONID以Cookie形式响应给浏览器 ,第二次请求,浏览器会携带之前的JSESSIONID的Cookie,发送给服务器,服务器根据JSESSIONID获取对应的HttpSession对象.通过这种技术可以解决HTTP协议本身无法记录用户状态情况.
HttpSession对象的特点
- HttpSession保存在服务端
- HttpSession可以存储任何类型的数据
- HttpSession使用Key与Value结构存储数据 value是Object类型
- HttpSession存储数据大小无限制
HttpSession对象的创建
HttpSession对象的创建是通过request.getSession()方法来创建的。客户端浏览器在请求服务端资源时,如果在请求中没有JSESSIONID,getSession()方法将会为这个客户端浏览器创建一个新的HttpSession对象,并为这个HttpSession对象生成一个JSESSIONID,在响应中通过Cookie写回给客户端浏览器,如果在请求中包含了JSESSIONID,getSession()方法则根据这个ID返回与这个客户端浏览器对应的HttpSession对象。
getSession()方法还有一个重载方法getSession(true|false)。当参数为true时与getSession()方法作用相同。当参数为false时则只去根据SessionID查找是否有与这个客户端浏览器对应的HttpSession,如果有则返回,如果没有SessionID则不会创建新的HttpSession对象。
HttpSession中数据的获取
session.setAttribute("key",value)
将数据存储到HttpSession对象中
Object value = session.getAttribute("key")
根据key获取HttpSession中的数据,返回Object
Enumeration<String> attributeNames = session.getAttributeNames()
获取HttpSession中所有的key,返回枚举类型
session.removeAttribute("key")
根据key删除HttpSession中的数据
String id = session.getId()
根据获取当前HttpSession的SessionID,返回字符串类型
HttpSession的销毁方式
HttpSession的销毁方式有两种:
- Ø 通过web.xml文件指定超时时间(最大不活动时间)
- Ø 通过HttpSession对象中的invalidate()方法销毁当前HttpSession对象
我们可以在web.xml文件中指定HttpSession的超时时间,当到达指定的超时时间后,容器就会销该HttpSession对象,单位为分钟。该时间对整个web项目中的所有HttpSession对象有效。时间的计算方式是根据最后一次请求时间作为起始时间。如果有哪个客户端浏览器对应的HttpSession的失效时间已到,那么与该客户端浏览器对应的HttpSession对象就会被销毁。其他客户端浏览器对应的HttpSession对象会继续保存不会被销毁。
<session-config>
<session-timeout>1</session-timeout>
</session-config>
我们也可以在Tomcat的web.xml文件中配置HttpSession的销毁时间。如果在Tomcat的web.xml文件中配置了HttpSession的超时时间对应的是Tomcat中所有的Web项目都有效。相当于配置了全局的HttpSession超时时间。如果我们在Web项目中配置了超时时间,那么会以Web项目中的超时时间为准。

invalidate()方法是HttpSession对象中所提供的用于销毁当前HttpSession的方法。我们通过调用该方法可以销毁当前HttpSession对象。
HttpSession生命周期
在HttpSession对象生命周期中没有固定的创建时间与销毁时间。何时创建取决于我们什么时候第一次调用了getSession()或getSession(true)的方法。HttpSession对象的销毁时间取决于超时时间的到达以及调用了invalidate()方法。如果没有超时或者没有调用invalidate()方法,那么HttpSession会一直存储。默认超时时间为30分钟(Tomcat的web.xml文件配置的时间就是默认超时时间)。
HttpSession对象总结
HttpSession与Cookie的区别:
- Ø cookie数据存放在客户的浏览器或系统的文件中,而HttpSession中的数据存放在服务器中。
- Ø cookie不安全,而HttpSession是安全的。
- Ø 单个cookie保存的数据不能超过4K,很多浏览器都限制一个域名保存cookie的数量。而HttpSession没有容量以及数量的限制。
HttpSession的使用建议
HttpSession对象是保存在服务端的,所以安全性较高。我们可以在HttpSession对象中存储数据,但是由于HttpSession对象的生命周期不固定,所以不建议存放业务数据。一般情况下我们只是存放用户登录信息。
测试代码
Servlet1 创建并向HttpSession中存放数据
package com.mashibing.test;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servlet1.do")
public class Servlet1 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获得HttpSession对象 是一种保存更多数据在服务器端的一种技术
// 一般保存当前登录 的用户
// 用户的权限
// 用户的其他信息 ... ...
/*
* getSession方法执行内容
* 从request中尝试获取JSESSIONID的Cookie
*
* A如果获取失败,
* 认为上次会话已经结束,在这里要开启新的会话,创建一个新的HttpSession并返回
* 将新的HttpSession对象的JSESSIONID以Cookie的形式放在Response对象,响应给浏览器
*
* B如果获取成功
* 根据JSESSIONID在服务器内找对应HttpSession对象
* 1) 找到了,返回找到的HttpSession
* 2) 没找到,创建新的HTTPSession并将SESSIONID以Cookie的形式放在Response对象,响应给浏览器
*
* */
HttpSession httpSession=req.getSession();
// 向HttpSession中存放一些数据
httpSession.setAttribute("username", "msb");
httpSession.setAttribute("password", "1234");
httpSession.setAttribute("level", "A");
//httpSession.invalidate();// 手动设置HTTPSession不可用 退出登录
}
}
Servlet2 获得并取出HTTPSession中的数据
package com.mashibing.test;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/servlet2.do")
public class Servlet2 extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取HTTPSession
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 尝试从HTTPSession中获取数据
String username = (String)session.getAttribute("username");
String password = (String)session.getAttribute("password");
String level = (String)session.getAttribute("level");
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(level);
// 获取Session对象的其他信息
System.out.println("创建时间:"+session.getCreationTime());
System.out.println("最后一次访问时间:"+session.getLastAccessedTime());
System.out.println("最大不活动时间:"+session.getMaxInactiveInterval());
}
}
案例:通过HttpSession判断用户是否登录
需求:实现登录一次即可,在一次会话内,可以反复多次访问WEB-INF/ welcome.html,如果没有登录过,跳转到登录页,登录成功后,可以访问
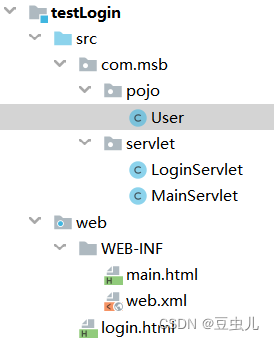
组件介绍:
login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form method="get" action="loginServlet.do">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username" ><br/>
密码:<input type="password" name="password" ><br/>
<input type="submit" >
</form>
</body>
</html>
登录成功之后可以访问的资源
main.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
this is main page
</body>
</html>
LoginServlet
用来校验登录的,登录成功将用户信息存户HttpSession,否则回到登录页
package com.msb.servlet;
import com.msb.pojo.User;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/loginServlet.do")
public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取用户名和密码
String username = req.getParameter("username");
String password = req.getParameter("password");
// 如果用户名和密码为 msb 1234
if("msb".equals(username) && "1234".equals(password)){
// 将用户信息放在HTTPSession中
User user =new User(null, null, "msb", "1234");
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.setAttribute("user", user);
// 登录成功 跳转至 main.html
resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath()+"/mainServlet.do");
}else{
// 登录失败 回到login.html
resp.sendRedirect(req.getContextPath()+"/login.html");
}
}
}
MainServlet
用来向main.html中跳转的,同时验证登录,登录过,可以直接跳转,否则回到登录页
package com.msb.servlet;
import com.msb.pojo.User;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.logging.Handler;
/**
* @Author: Ma HaiYang
* @Description: MircoMessage:Mark_7001
*/
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/mainServlet.do")
public class MainServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//跳转至main.html
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
User user = (User)session.getAttribute("user");
if(null != user){
// 判断如果登录过 允许跳转 HTTPSession中如果有登陆过的信息
req.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/main.html").forward(req,resp);
}else{
// 如果没有登录过 回到登录去登录 HTTPSession中如果有登陆过的信息
resp.sendRedirect("login.html");
}
}
}
User
用来存储一个用户的信息的实体类对象
public class User implements Serializable {
private Integer uid;
private String realname;
private String username;
private String pasword;相关文章
- 技术分享连载(五十七)
- UWA学堂专栏推荐:创业团队的技术管理
- JavaEE基础(04):会话跟踪技术,Session和Cookie详解
- js_html_input中autocomplete="off"在chrom中失效的解决办法 使用JS模拟锚点跳转 js如何获取url参数 C#模拟httpwebrequest请求_向服务器模拟cookie发送 实习期学到的技术(一) LinqPad的变量比较功能 ASP.NET EF 使用LinqPad 快速学习Linq
- 基于投影仪的定位技术
- 微服务技术系列教程(34) - SpringCloud-使用RabbitMQ实现消息驱动
- 传统企业,如何构建性能测试技术体系
- 微信红包【技术篇】——如何在服务有损的情况下保证用户体验
- Hadoop创始人Doug Cutting谈未来大数据的技术
- 干货 | 东南大学教授漆桂林:知识图谱中的推理技术进展及应用
- 技术栈待整理
- 「SAP 技术」SAP MM 给合同的ITEM上传附件以及附件查询
- Cookie技术
- 中移物联技术总监肖青:中移物联网eSIM相关进展介绍
- ChatGPT vs Bard 背后的技术
- YAML 技术研究
- 安晓辉:程序员在公司没事干时候,做什么好?(产品上想多一点,设计上想多一点,技术上做深一点、做宽一点,思维框架上学多一点)
- 惠普公司推出新的数据中心动态冷却技术
- 游戏盾的三次技术演进
- XSS攻击技术详解
- 【历史上的今天】3 月 27 日:《华尔街日报》技术专栏作家出生;AMD 推出 K5 处理器;匈牙利数理逻辑的奠基人诞生
- 新技术带来新活力 南通物联网产业蓬勃发展

