Spring学习笔记(一)---Bean生命周期(源码浅析)
一、学习内容
1.Bean的定义
2.Bean的作用域
3.Bean的生命周期
4.总结
二、具体内容
2.1 Bean的定义
<beans…/>元素是Spring配置文件的根元素,<bean…/>元素是<beans…/>元素的子元素,<beans…/>元素可以包含多个<bean…/>子元素,每个<bean…/>元素可以定义一个Bean实例,每一个Bean对应Spring容器里的一个Java实例定义Bean时通常需要指定两个属性。
-
Id:确定该Bean的唯一标识符,容器对Bean管理、访问、以及该Bean的依赖关系,都通过该属性完成。Bean的id属性在Spring容器中是唯一的。
-
Class:指定该Bean的具体实现类。注意这里不能是接口。通常情况下,Spring会直接使用new关键字创建该Bean的实例,因此,这里必须提供Bean实现类的类名。
Spring容器集中管理Bean的实例化,Bean 实例可以通过 BeanFactory 的getBean(Stringbeanid) 方法得到。BeanFactory 是一个工厂,程序只需要获取BeanFactory 引用,即可获得 Spring 容器管理全部实例的引用。程序不需要与具体实例的实现过程耦合。大部分 JavaEE 应用里,应用在启动时,会自动创建 Spring 容器,组件之间直接以依赖注入的方式耦合,甚至无须主动访问 Spring 容器本身。
2.2 bean的作用域
| bean的作用域 | 释义 |
|---|---|
| singleton | 单例,指一个Bean容器中只存在一份 |
| prototype | 每次请求(每次使用)创建新的实例,destroy方法不生效 |
| request | 每次http请求创建一个实例且仅在当前request内有效 |
| session | 同上,每次http请求创建,当前session内有效 |
| global session | 基于portlet的web中有效(portlet定义了global session),如果是在web中,同session |
如果我们不指定 Bean 的作用域,则 Spring 会默认使用 singleton 作用域。
- Java 在创建 Java 实例时,需要进行内存申请。销毁实例时,需要完成垃圾回收。这些工作都会导致系统开销的增加。因此,prototype 作用域 Bean 的创建、销毁代价会比较大。而 singleton 作用域的 Bean 实例一旦创建成功,可以重复使用。因此,除非必要,否则尽量避免将 Bean 的作用域设置为 prototype。
例子:singleton与prototype
定义BeanScope类
package com.imooc.bean;
public class BeanScope {
public void say(){
System.out.println("BeanScope say:" + this.hashCode()); // 当前对象的hashCode
}
}
配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd ">
<bean id="beanScope" class="com.imooc.bean.BeanScope" scope="singleton"></bean>
</beans>
定义测试类TestBeanScope
package com.imooc.test.bean;
@RunWith(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class TestBeanScope {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Test
public void testBeanScope(){
context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"spring-beanscope.xml");
BeanScope beanScope1 = (BeanScope) context.getBean("beanScope");
beanScope1.say(); // 定义两个实例对象,hashCode一样
BeanScope beanScope2 = (BeanScope) context.getBean("beanScope");
beanScope2.say();
}
}
运行结果
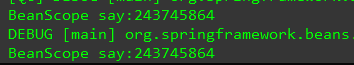
当我们把配置文件中的scope改为prototype改了之后
<bean id="beanScope" class="com.imooc.bean.BeanScope" scope="prototype"></bean>
运行的结果如下:
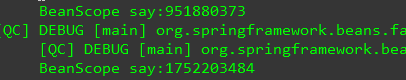
可以明显看到两个实例的hashCode不一样.
对于request作用域而言,先看如下Bean实例定义:
对于每次HTTP请求,Spring容器都会根据login Bean定义创建一个全新的LoginAction Bean实例,且该loginAction Bean实例仅在当前HTTP Request内有效。对于session作用域相同。只不过有效范围不同而已。
request和session作用域只在web应用中才会有效,并且必须在Web应用中增加额外配置才会生效。为了能够让request和session两个作用域生效,必须将HTTP请求对象绑定到该请求提供的服务线程上,这使得具有request和session作用的Bean实例能够在后面的调用链中被访问到。
因此我们可以采用两种配置方式:采用Listener配置或者采用Filter配置,在web.xml中。
Listener配置:
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
Filter配置
<filter>
<filter-name>requestContextFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.RequestContextFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>requestContextFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
一旦在web.xml中增加上面两种配置中的一种,程序就可以在Spring配置文件中使用request或者session作用域了。如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd">
<!-- 指定使用request作用域 -->
<bean id="p" class="com.imooc.ioc.bean.Person" scope="request"/>
</beans>
上面的配置文件配置了一个实现类Person的Bean,指定它的作用域为request。这样Spring容器会为每次的HttP请求生成一个Person的实例,当该请求响应结束时,该实例也会被注销。
2.3 Bean的生命周期
- 定义
- 初始化
- 使用
- 销毁
例子:Bean的初始化和销毁
- 配置init-method destroy-method
- 初始化和销毁可以实现org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean接口覆盖afterPropertiesSet方法和实现
org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean接口,覆盖destroy方法
使用第二种方式:配置文件定义
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd ">
<bean id="beanLifecycle" class="com.imooc.lifecycle.BeanLifecycle">
</bean>
</beans>
定义类BeanLifecycle
package com.imooc.lifecycle;
public class BeanLifecycle implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean{
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Bean destroy.");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Bean afterPropertiesSet.");
}
}
定义测试类
package com.imooc.test.lifecycle;
@RunWith(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class TestBeanLifecycle {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Test
public void testBeanLifeCycle(){
context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"spring-lifecycle.xml");
context.getBean("beanLifecycle"); //直接获取beanLifecycle
}
}
结果输出了初始化和销毁的语句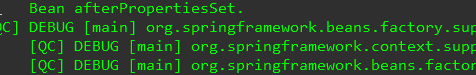
同时使用了这几种方式初始化和销毁Bean的时候,先后的顺序是
-*接口
-* * 配置文件中自定义<init-method=" “>
<destroy-method=” ">
其中default-init-method default-destroy-method 会被覆盖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-init-method="defaultInit" default-destroy-method="default-Destroy">
<bean id="beanLifecycle" class="com.imooc.lifecycle.BeanLifecycle">
</bean>
</beans>
Bean生命周期的详细过程(画的有点丑,呵呵)
了解一下此过程帮助理解Bean 由出生到牺牲,是我们更好地使用Bean。

Bean实例生命周期的执行过程如下:
- Spring对bean进行实例化,默认bean是单例;
- Spring对bean进行依赖注入;
- 如果bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,spring将bean的id传给setBeanName()方法;
- 如果bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,spring将调用setBeanFactory方法,将BeanFactory实例传进来;
- 如果bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,它的setApplicationContext()方法将被调用,将应用上下文的引用传入到bean中;
- 如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,它的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法将被调用
- 如果bean实现了InitializingBean接口,spring将调用它的afterPropertiesSet接口方法,类似的如果bean使用了init-method属性声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用;
- 如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,它的postProcessAfterInitialization接口方法将被调用;
- 此时bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了,他们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁;
- 若bean实现了DisposableBean接口,spring将调用它的distroy()接口方法。同样的,如果bean使用了destroy-method属性声明了销毁方法,则该方法被调用;
3总结
1.Bean的作用域最常用的是单例;
2.理解Bean的生命周期,面试会问到;
相关文章
- spring项目(springmvc)(多模块/单模块)maven打包引入第三方jar方式,使用scope:system配置systemPath编译,不用添加到本地仓库!
- Spring基础-10-源码分析
- ssm(Spring+Spring mvc+mybatis)——saveDept.jsp
- Spring Boot启动时数据库初始化spring.datasource(转)
- 带着问题学 Spring MVC 源码: 一、概述
- [Java Spring] Spring Expression Language
- Spring AOP源码分析(七)ProxyFactoryBean介绍
- [Spring学习笔记 3 ] spring 注解详解,完全注解,常用注解
- spring调用memcached client for java
- spring boot:给接口增加签名验证(spring boot 2.3.1)
- Spring Bean的获取与实例化
- 关于spring-cloud-starter-oauth2源码跟踪笔记
- Spring读源码系列06----容器扩展功能--上
- Spring读源码系列02----默认标签解析过程
- 不一样的视角来学习Spring源码之AOP---中
- Spring MVC注解Controller源码流程解析--定位HandlerMethod
- spring-session源码解读-2
- @Value的使用 《Spring源码解析》java笔记
- 整理spring + mysql + redis + 测试 的配置格式 和源码
- 毕业设计 Spring Boot的网课在线点播管理系统(含源码+论文)
- 毕设项目 Spring Boot大学生兼职发布管理系统(含源码+论文)
- spring常用注解
- SpringBoot(Spring、SpringMVC)集成Mybatis操作Mysql数据库
- Spring MVC密码处理
- spring mongodb 复制集配置(实现读写分离)
- Spring Cloud Alibaba微服务第7章之负载均衡Ribbon
- Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis(开发必备技能)04、mybatis自动生成mapper_dao_model(包含工具与视频讲解) 纯绿色版本、配套使用视频,100%运行成功

