数据结构——线性表
数据结构 线性表
2023-09-11 14:22:32 时间
1.概述
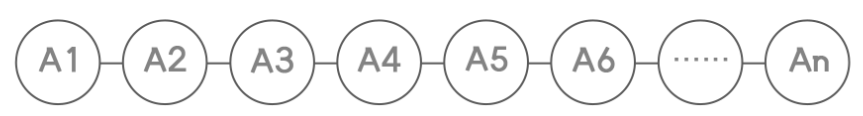
线性表: n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。
- 头结点:没有前驱元素的结点
- 尾结点:没有后驱元素的结点
前驱元素: A1在A2之前,A1就为A2的前驱元素
后驱元素: A2在A1之后,A2为A1的后驱元素
2.顺序表
2.1 顺序表的实现
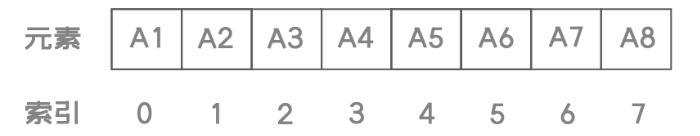
顺序表: 是在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表
- 特点:
存储单元地址连续(循序存储)
逻辑上相邻的数据元素在物理地址上也相邻
package linkedlist;
public class SequenceList<T>{
/*
属性部分
*/
//数组:存储数据
private T[] eles;
//记录元素个数(长度)
private int N;
//构造器:指定容量初始化表
public SequenceList(int capacity){
//eles = new T[capacity];给数组定义长度的写法不合法,使用Object数组强转:
eles = (T[])new Object[capacity];
N = 0;
}
/*
方法部分
*/
//获取顺序表长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//清空顺序表
public void clear(){
N = 0;
}
//判断顺序表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N == 0;
}
//获取指定位置元素
public T get(int i){
if (i < 0 || i >= N){
throw new RuntimeException("此处无元素!!");
}
return eles[i];
}
//向表中添加元素
public void insert(T t){
if (N == eles.length){
throw new RuntimeException("当前表已满");
}
eles[N++] = t;
}
//在指定位置添加元素
public void insert(int i,T t){
if (N == eles.length){
throw new RuntimeException("当前表已满");
}
if (i < 0 || i > N){
throw new RuntimeException("插入位置不合法!!");
}
//把i及之后的元素全部往后移动一位,空出i位置存储新元素
for (int index = N; index > i; index--) {
eles[index] = eles[index-1];
}
eles[i] = t;
//长度+1
N++;
}
//删除指定位置处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i){
if (i < 0 || i >= N){
throw new RuntimeException("此处无元素");
}
//记录下i处的元素
T temp = eles[i];
//将i位置后面的元素都往前移动一位
for (int index = i;index < N;index++){
eles[index] = eles[index+1];
}
//长度-1
N--;
return temp;
}
//查找元素第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
if (t == null){
throw new RuntimeException("查找的元素不合法");
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (eles[i] == t){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
2.2 实现foreach
实现Iterable接口,重写Iterator方法实现foreach循环
public class SequenceList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
......
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new SIterator();
}
private class SIterator implements Iterator{
private int cur;
public SIterator() {
//从0开始遍历
this.cur = 0;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return cur < N;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
return eles[cur++];
}
}
}
2.3 实现容量可变
容量伸缩性: 改变存储数据元素的数组的大小
- 添加元素:添加元素时,应该检查当前数组的大小是否能容纳新的元素,如果不能容纳,则需要创建新的容量更大的数组,创建一个原数组两倍长度的数组存储数据

- 移除元素:移除元素时,应该检查当前数组的大小是否太大,浪费空间。当元素个数不足数组长度的1/4时,创建一个原数组1/2长度的新数组存储数据
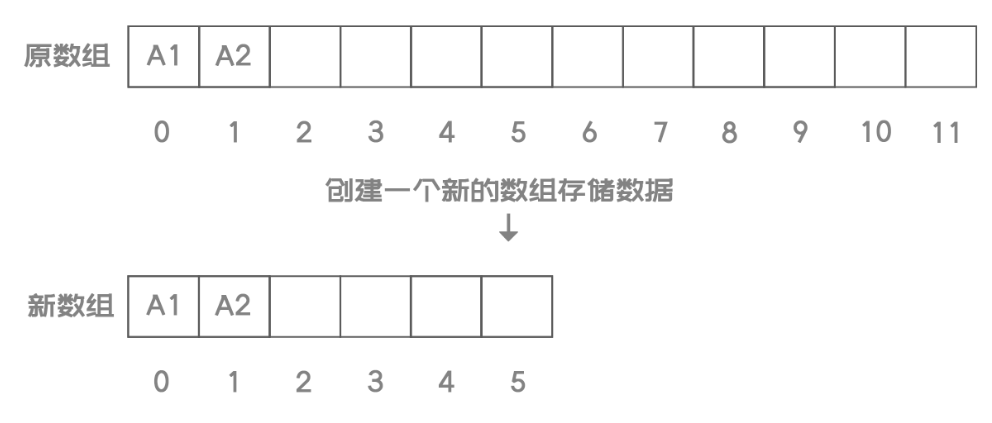
//改变容量
public void resize(int newCapacity){
//原数组数据
T[] temp = eles;
//创建新数组
eles = (T[]) new Object[newCapacity];
//将旧数组的元素拷贝到新数组
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
eles[i] = temp[i];
}
}
//查看顺序表容量
public int capacity(){
return eles.length;
}
综上可知:顺序表增删元素的方法的时间复杂度都为O(N),查询直接通过索引,时间复杂度为O(1)
3.链表
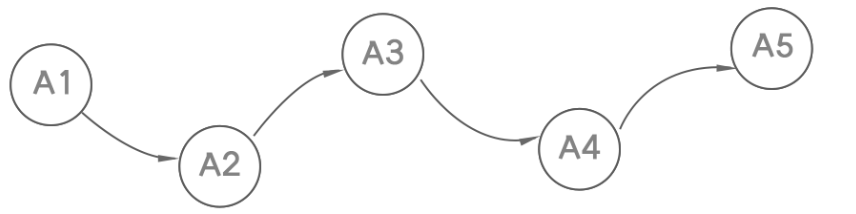
链表: 一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构
- 数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现
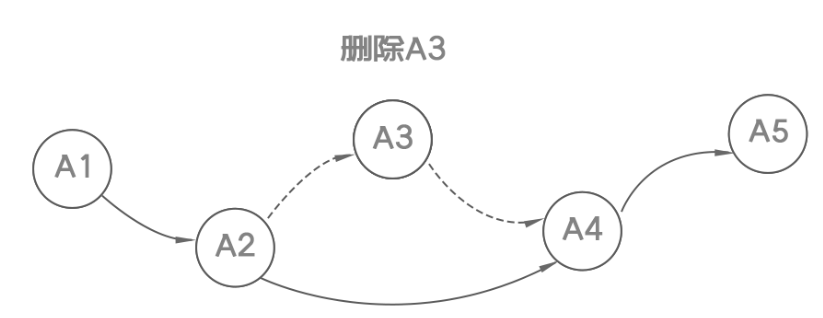
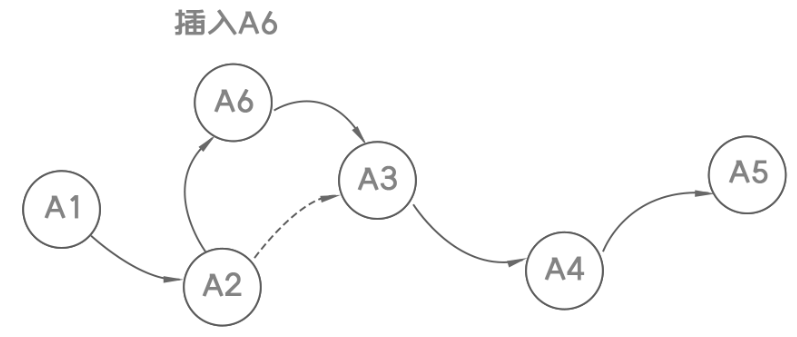
- 数据的增删实现图示:
3.1 单向链表的实现
单向链表: 头结点数据域不存数据,指针域指向下一个结点
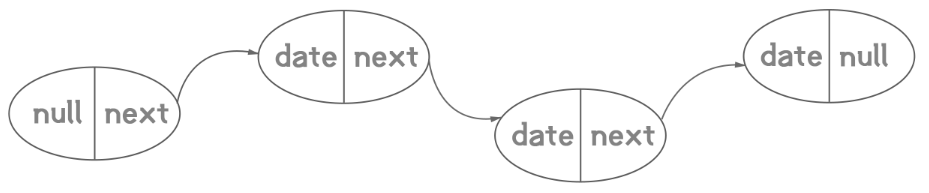
- 首先实现一个结点类(结点→组成链表的基本元素)
public class Node<T> {
//存储元素
public T item;
//指向下一个节点
public Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
- 实现链表
import java.util.Iterator;
public class LinkedList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
//记录头结点
private Node head;
//记录链表的长度
private int N;
public LinkedList(){
//初始化头结点
head = new Node(null,null);
N = 0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
head.next = null;
head.item = null;
N = 0;
}
//获取链表的长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
//获取指定位置i处的元素
public T get(int i){
if (i<0 || i>=N){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
Node n = head.next;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
n = n.next;
}
return (T) n.item;
}
//向链表中添加元素t
public void insert(T t){
//找到最后一个结点
Node n = head;
while (n.next!=null){
n = n.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node(t,null);
n.next = newNode;
//链表长度+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置i处,添加元素t
public void insert(int i,T t){
if (i < 0 || i >= N){
throw new RuntimeException("插入位置不合法!");
}
//找到指定的结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i-1; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//位置i的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//构建新的结点,让新结点指向位置i的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t,curr);
//让之前的结点指向新结点
pre.next = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
}
//删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回被删除的元素
public T remove(int i){
if (i < 0 || i >= N ){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法");
}
//寻找i之前的结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i-1; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//当前i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点,实现删除当前结点
pre.next = curr.next;
//长度-1
N--;
return (T) curr.item;
}
//查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n = head;
for (int i=0;n.next!=null;i++){
n = n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//结点类(内部类)
private class Node {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
//构造器
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
@Override
public Iterator iterator(){
return new LIterator();
}
private class LIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n;
public LIterator(){
this.n = head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next != null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
}
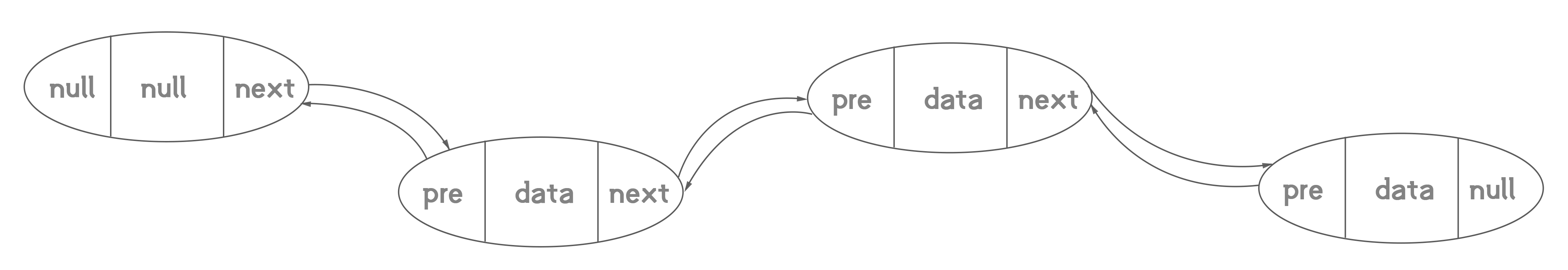
3.2 双向链表的实现
双向链表:
package linkedlist;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TwoWayLinkedList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
//结点类:
private class Node{
//存储数据
private T item;
//指向上一个结点
private Node pre;
//指向下一个结点
private Node next;
public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
}
//头结点
private Node head;
//尾结点
private Node last;
//链表长度
private int N;
//构造器
public TwoWayLinkedList(){
last = null;
head = new Node(null,null,null);
N = 0;
}
//获取长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
last = null;
head.next = last;
head.pre = null;
head.item = null;
N = 0;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N == 0;
}
//插入元素
public void insert(T t){
if (last == null){
last = new Node(t,head,null);
head.next = last;
}else {
Node oldLast = last;
Node node = new Node(t,oldLast,null);
oldLast.next = node;
last = node;
}
//长度+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置插入元素
public void insert(int i,T t){
if (i < 0 || i >= N){
throw new RuntimeException("插入位置不合法!!");
}
//找到位置i前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//位置i的元素
Node curr = pre.next;
//插入的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t,pre,curr);
//实现插入
curr.pre = newNode;
pre.next = newNode;
//长度+1
N++;
}
//删除指定位置处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i){
if (i < 0 || i>= N){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!!");
}
//寻找i位置前一个元素
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
//位置i的元素
Node curr = pre.next;
//实现删除
pre.next = curr.next;
curr.next.pre = pre;
//长度-1
N--;
return curr.item;
}
//获取指定位置元素
public T get(int i){
if (i < 0 || i>= N){
throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!!");
}
//寻找i处的结点
Node curr = head.next;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
return curr.item;
}
//找到元素第一次在链表出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n = head;
for (int i=0;n.next != null;i++){
n = n.next;
if (n.next.equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//获取第一个元素
public T getFirst(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
//获取最后一个元素
public T getLast(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new TIterator();
}
private class TIterator implements Iterator {
private Node n = head;
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next != null;
}
@Override
public T next() {
n = n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
}
综上可知:链表的增删方法的时间复杂度为O(N),但是相比顺序表,省去了整体元素移动这一操作,更加快捷。链表的查找时间复杂度为O(N),远远劣于顺序表。
相关文章
- 泛函编程(6)-数据结构-List基础
- 数据结构和算法-数据结构-线性结构-栈和队列
- 【学习总结】《大话数据结构》- 第8章-查找
- 小白学 Python 数据分析(3):Pandas (二)数据结构 Series
- 数据结构与算法之美-14 动态规划 [MD]
- 【学习总结】《大话数据结构》- 第2章-算法
- [数据结构] 选择排序
- 【数据结构笔记03】数据结构之线性表的链式表示和实现(双向链表、循环链表)
- C++数据结构--线性表的链式存储结构
- C++数据结构--线性表的顺序存储结构
- C++数据结构--异常类与顶层父类的实现
- 一个数据结构转换的问题
- 【数据结构基础】栈
- 【数据结构】测试2 线性表
- 《零基础入门数据结构与算法》专栏介绍
- 004-jdk-数据结构-ArrayList、LinkedList
- 数据结构 - 希尔排序(Shell's Sort) 具体解释 及 代码(C++)
- 数据结构(一)之线性表
- 【数据结构与算法】线性表--数组
- 【数据结构与算法】——第二章:线性表
- 【霍罗维兹数据结构】单链表 | 动态链接的栈和队列 | 多项式 - POLYNOMIALS | 一些链表的操作

