基于Android的“哲学家就餐问题”防死锁的设计与实现
1问题描述
如图1.1,有5个哲学家围着一个大圆桌就餐。哲学家和筷子都按逆时针顺序编号,每个哲学家的编号与他左边的筷子的编号一致。
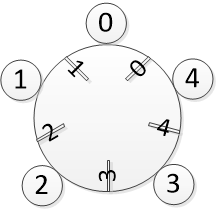
规定如下:
(1)哲学家之间不相互交流;
(2)哲学家只做两件事:吃饭或思考;
(3)每个哲学家只能拿其邻近的左右两支筷子;
(4)哲学家不能抢占别人已经拿起的筷子;
(5)哲学家在拿到两支筷子之前,不会放下手中的筷子;
(6)哲学家只有拿到两支筷子才开始就餐,然后又放下两支筷子;
当所有哲学家都拿起了左边的筷子时,将出现他们都在等待其右边的哲学家放下左边的筷子,这样一直等待下去,就会造成所有哲学家都吃不了饭,这种状态称为“死锁”。本文要解决的问题是,如何避免死锁,使所有哲学家都能愉快地吃饭。
2算法描述
基于Android的哲学家就餐问题源代码下载
2.1主类与布局
2.1.1主类
MainActivity.java
package com.philosohper;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static Button clear,start_stop,m1,m2,m3,m4;//清除、开始|暂停、方法1、方法2、方法3、方法4按钮
private static ScrollView scrollView;//滚动视图
private static TextView status;//输出的哲学家状态信息文本框
public static StringBuilder str;//输出的哲学家状态信息字符串
private Philosopher_manager philosopher_manager;//哲学家管理者
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
getWindow().setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN, WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);//设置全屏
init_view();
philosopher_manager=new Philosopher_manager();
}
private void init_view(){//初始化UI界面
clear= (Button) findViewById(R.id.clear);
start_stop= (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_stop);
m1= (Button) findViewById(R.id.m1);
m2= (Button) findViewById(R.id.m2);
m3= (Button) findViewById(R.id.m3);
m4= (Button) findViewById(R.id.m4);
scrollView= (ScrollView) findViewById(R.id.scrollView);
status= (TextView) findViewById(R.id.status);
str=new StringBuilder();
clear.setOnClickListener(cl);
start_stop.setOnClickListener(cl);
m1.setOnClickListener(cl);
m2.setOnClickListener(cl);
m3.setOnClickListener(cl);
m4.setOnClickListener(cl);
}
private View.OnClickListener cl =new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.clear:
clear();//清空显示
break;
case R.id.start_stop:
start_stop();//开始|暂停
break;
case R.id.m1:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"最多拿起4个",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
if(Philosopher.method==1) break;
philosopher_manager.set_methord(1);//设置防死锁方法1
break;
case R.id.m2:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"一次拿2个",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
if(Philosopher.method==2) break;
philosopher_manager.set_methord(2);//设置防死锁方法2
break;
case R.id.m3:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"偶先左,奇先右",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
if(Philosopher.method==3) break;
philosopher_manager.set_methord(3);//设置防死锁方法3
break;
case R.id.m4:
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"先拿小编号",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
if(Philosopher.method==4) break;
philosopher_manager.set_methord(4);//设置防死锁方法4
break;
}
}
};
public static void clear(){//清空显示
str.delete(0,str.length());
status.setText(str);
}
private void start_stop(){//开始|暂停
if (philosopher_manager.is_start){
philosopher_manager.is_start=false;
start_stop.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.start);
}else {
philosopher_manager.is_start=true;
start_stop.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.stop);
}
}
public static Handler handler=new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (str.length()>10000){
str.delete(0,2000);//只留10000的缓存
}
status.setText(str);
scrollView.fullScroll(ScrollView.FOCUS_DOWN);//滚动到底部
}
};
public static void send_message(String s,int method){//发送消息
if (method==Philosopher.method){//过滤掉切换方法以前消息
str.append(s);
handler.sendEmptyMessage(method);
}
}
}
2.1.2布局
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.philosohper.MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:padding="10dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/clear"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:background="@drawable/clear"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/start_stop"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:background="@drawable/start"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="390dp"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:background="#f3efef">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/status"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</ScrollView>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="center"
android:padding="10dp">
<Button
android:id="@+id/m1"
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:layout_margin="7dp"
android:background="@drawable/m1"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/m2"
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:layout_margin="7dp"
android:background="@drawable/m2"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/m3"
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:layout_margin="7dp"
android:background="@drawable/m3"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/m4"
android:layout_width="70dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:layout_margin="7dp"
android:background="@drawable/m4"/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
界面效果如下:
2.2哲学家管理者类、哲学家类、筷子类
2.2.1哲学家管理者类
Philosopher_manager.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Philosopher_manager {
private Philosopher[] philosopher;
public static boolean is_start;//开始|暂停
Philosopher_manager(){
philosopher=new Philosopher[Chopsticks.N];
create();
is_start=false;
}
private void create(){//创建哲学家线程
is_start=false;
Chopsticks.init();
for (int i=0;i<Chopsticks.N;i++){
philosopher[i]=new Philosopher(i);
philosopher[i].start();
}
}
public void set_methord(int methord){//设置避免死锁方法
Philosopher.method=methord;
for (int i=0;i<Chopsticks.N;i++){
philosopher[i].exist=false;
}
boolean flag=is_start;
is_start=true;//让所有哲学家线程运行至结束
if (is_all_died()) {
create();
}
MainActivity.clear();//清楚显示
is_start=flag;
}
private boolean is_all_died(){//判断所有哲学家线程是否运行结束
while(philosopher[0].isAlive()){
Chopsticks.init();
sleep();
}
while(philosopher[1].isAlive()){
Chopsticks.init();
sleep();
}
while(philosopher[2].isAlive()){
Chopsticks.init();
sleep();
}
while(philosopher[3].isAlive()){
Chopsticks.init();
sleep();
}
return true;
}
private void sleep(){
try {
Thread.sleep(80);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.2.2哲学家类
Philosopher.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Philosopher extends Thread{//哲学家类
private Method1 method1;
private Method2 method2;
private Method3 method3;
private Method4 method4;
public static int method=1;//所有哲学家使用的防死锁方法
public boolean exist=true;//标记线程是否存活
Philosopher(int num){//num为哲学家编号
method1=new Method1(num);
method2=new Method2(num);
method3=new Method3(num);
method4=new Method4(num);
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(exist){
switch (method){
case 1:
method1.run();
break;
case 2:
method2.run();
break;
case 3:
method3.run();
break;
case 4:
method4.run();
break;
}
}
}
}
2.2.3筷子类
Chopsticks.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Chopsticks {//筷子对象,规定:0号筷子在0号哲学家的左边,哲学家和筷子都按逆时针编号
public static final int N=5;
public static int[] chopsticks;
public static void init(){
chopsticks=new int[N];
for (int i=0;i<N;i++){
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]=1;//1表示筷子资源个数
}
}
public synchronized static int count(){//计算当前已被占用的筷子个数
int s=0;
for (int i=0;i<N;i++){
if (Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]<1){
s++;
}
}
return s;
}
}
2.3避免死锁的方案
本文采用4种方法避免死锁:最多允许4个哲学家拿起筷子、哲学家一次拿两支筷子、偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的筷子奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子、所有哲学家先拿小编号的筷子。
2.3.1最多允许4个哲学家拿起筷子
Method1.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Method1{//最多允许4个哲学家拿起筷子
protected int num;//哲学家编号
protected int left,right;//num号哲学家左边、右边的筷子编号
protected final int wait_time=400;//等待时间
protected int method;//防止死锁的方法代号
protected boolean exit=true;
Method1(int num) {
this.num=num;
left=num;//num号哲学家左边的筷子编号
right=(num+1)%Chopsticks.N;//num号哲学家右边的筷子编号
method=1;
}
protected void run() {//最多允许4个哲学家拿起筷子
think();//哲学家在思考
P(left);
P(right);
eat();//哲学家在吃放
V(left);
V(right);
}
protected synchronized void P(int i) {//P原语,申请筷子资源
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
while(Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]<=0||Chopsticks.count()>=Chopsticks.N-1&&i==left){//如果已经有4个人拿起了筷子,不允许手里没筷子的人拿筷子
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]--;
if (i==num){
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家拿起了左边的" + i + "号筷子\n",method);
}else{
MainActivity.send_message(""+num+"号哲学家拿起了右边的"+i+"号筷子\n",method);
}
}
protected synchronized void V(int i){//V原语,释放筷子资源
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]++;
if (i==num){
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家放下了左手的" + i + "号筷子\n",method);
}
else{
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家放下了右手的" + i + "号筷子\n",method);
}
}
protected synchronized void think(){//哲学家在思考
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家在思考\n", method);
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
protected synchronized void eat(){//哲学家在吃放
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家握着左边" + left + "号和右边" + right + "号筷子在吃饭\n",method);
block_thread();//哲学家就餐一会儿
}
protected void wait_start(){//等待游戏开始
while(!Philosopher_manager.is_start){
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
}
protected void block_thread(){//阻塞线程
try {
Thread.sleep(wait_time);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.3.2哲学家一次拿两支筷子
Method2.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Method2 extends Method1 {//哲学家一次拿两支筷子
Method2(int num) {
super(num);
method=2;
}
protected void run() {//哲学家一次拿两支筷子
think();//哲学家在思考
P(left,right);
eat();//哲学家在吃放
V(left, right);
}
protected synchronized void P(int i,int j) {//P原语,申请筷子资源
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
while(Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]<=0||Chopsticks.chopsticks[j]<=0){
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]--;
Chopsticks.chopsticks[j]--;
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家拿起了左边的" + i + "号和右边的" + j + "号筷子\n",method);
}
protected synchronized void V(int i,int j){//V原语,释放筷子资源
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]++;
Chopsticks.chopsticks[j]++;
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家放下了左手的" + i + "号和右手的" + j + "号筷子\n",method);
}
}
2.3.3偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的筷子,奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子
Method3.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Method3 extends Method1 {//偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的快在,奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子
Method3(int num){
super(num);
method=3;
}
@Override
protected void run() {//偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的筷子,奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子
if (num%2==0){//偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的筷子
think();//哲学家在思考
P(left);
P(right);
eat();//哲学家在吃放
V(left);
V(right);
}else {//奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子
think();//哲学家在思考
P(right);
P(left);
eat();//哲学家在吃放
V(left);
V(right);
}
}
protected synchronized void P(int i) {//P原语,申请筷子资源
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
while(Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]<=0){
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]--;
if (i==num){
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家拿起了左边的" + i + "号筷子\n", method);
}
else{
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家拿起了右边的" + i + "号筷子\n",method);
}
}
protected synchronized void eat(){//哲学家在吃放
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
if (num%2==0){
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家握着左边" + left + "号和右边" + right + "号筷子在吃饭\n",method);
}
else{
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家握着右边" + right + "号和左边" + left + "号筷子在吃饭\n",method);
}
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
}
2.3.4所有哲学家先拿小编号的筷子
Method4.java
package com.philosohper;
public class Method4 extends Method1 {//所有哲学家先拿小编号的筷子
Method4(int num) {
super(num);
method=4;
}
protected void run() {//所有哲学家先拿小编号的筷子
if (num<Chopsticks.N-1){//0~N-2号哲学家先拿左边的小编号筷子
think();//哲学家在思考
P(left);
P(right);
eat();//哲学家在吃放
V(left);
V(right);
}else {//N-1号哲学家先拿右边的小编号筷子
think();//哲学家在思考
P(right);
P(left);
eat();//哲学家在吃放
V(left);
V(right);
}
}
protected synchronized void P(int i) {//P原语,申请筷子资源
wait_start();//等待游戏开始
while(Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]<=0){
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
Chopsticks.chopsticks[i]--;
if (i==num){
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家拿起了左边的" + i + "号筷子\n", method);
}else{
MainActivity.send_message("" + num + "号哲学家拿起了右边的" + i + "号筷子\n", method);
}
}
protected synchronized void eat(){//哲学家在吃放
if (num<Chopsticks.N-1){
MainActivity.send_message(""+num+"号哲学家握着左边"+left+"号和右边"+right+"号筷子在吃饭\n",method);
}else{
MainActivity.send_message(""+num+"号哲学家握着右边"+right+"号和左边"+left+"号筷子在吃饭\n",method);
}
block_thread();//阻塞线程
}
}
3运行结果
3.1最多允许4个哲学家拿起筷子
3.2哲学家一次拿两支筷子

3.3偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的筷子,奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子

3.4所有哲学家先拿小编号的筷子

4 拓展延伸
实际上,有很多种防死锁的方法,不仅仅局限于以上四种。下面从3个角度讨论:限制最大持筷子的哲学家数、限制哲学家拿筷子动作、限制哲学家拿筷子顺序。
4.1限制最大持筷子的哲学家数
方法一中,限制最多只允许4个哲学家同时持有筷子,我们也可以限制最多只允许3个哲学家同时持有筷子。当然,还可以限制最多只允许1个哲学家同时持有筷子,即哲学家排队就餐。
4.2限制哲学家拿筷子动作
方法二中,限制哲学家一次拿两支筷子。
4.3限制哲学家拿筷子顺序
当哲学家一次只能拿一支筷子时,只要不是所有哲学家都按相同的循序拿起筷子,就可以避免死锁。比如:方法四中,所有哲学家都先拿小编号的筷子,实际上就是0-3号哲学家先拿左边的筷子,4号哲学家先拿右边的筷子。我们也可以定义:1-4号哲学家先拿左边的筷子,0号哲学家先拿右边的筷子。再比如:方法三中,偶数编号的哲学家先拿左边的筷子,奇数编号的哲学家先拿右边的筷子,实际上就是0、2、4号哲学家先拿左边的筷子,1、3号哲学家先拿右边的筷子。我们也可以定义0、1、2号哲学家先拿左边的筷子,3、4号哲学家先拿右边的筷子。
综合以上三大类防死锁策略,我们也可以综合起来使用,比如:限制最多只允许4个哲学家同时持有筷子,0号哲学家一次只能拿2支筷子,1、2号哲学家先拿左边的筷子,3、4号哲学家先拿右边的筷子。
相关文章
- Android系统自带的android.util.Base64的实现源码
- Android实战简易教程-第二十三枪(基于Baas的用户注冊和登录模块实现!)
- Android RecyclerView实现侧滑删除
- Android开发工程师文集-Android知识点讲解
- Android开发工程师文集-1 小时学会各种Drawable
- Android 用Animation-list实现逐帧动画
- 基于Android实现音乐APP【100010380】
- 基于android实现航空订票系统【100010286】
- 基于Android实现短视频APP【100010136】
- Android中自定义checkbox样式
- Android ActionBar详解(二):ActionBar实现Tabs标签以及下拉导航 .
- Android提高第九篇之GridView和SQLite实现分页表格
- android UI进阶之用ViewPager实现欢迎引导页面
- Android 串口通信基于licheedev、rxjava、eventbus敏捷实现
- Android Studio升级或更新项目,经常造访的“Could not find com.android.tools.build :gradle: x.x.x”的原因分析
- Android 实现EditText不可编辑
- Android系统启动流程(三)解析SystemServer进程启动过程
- LoadRunner+Android模所器实现抓包并调试本地服务端
- Android实战简易教程-第二十五枪(基于Baas的数据表查询下拉刷新和上拉载入实现!)
- Android - 小的特点 - 使用最新版本ShareSDK手册分享(分享自己定义的接口)
- Android编译项目发生 String index out of range: -1 解决办法

