python内置函数compile用法详解
Python 详解 函数 用法 内置 compile
2023-09-11 14:15:15 时间
python内置函数compile 可以将字符串编译成字节代码或者AST对象,字节代码对象可以被exec() 或 eval() 执行。
语法结构:
compile(source, filename, mode, flags=0, dont_inherit=False, optimize=- 1)参数解析:
- source 可以是字符串或者字节字符串,后者AST对象
- filename 是代码读取的文件名,source是从哪个文件里读取的,就用哪个文件的名称,如果不是从文件读取的source,则填写一个可辨识值,一般用''
- mode 编码模式,如果source是语句,则mode可以是exec,如果是单一表达式,则可以是eval,如果source是单个交互式语句,mode可以是single
- flags 和 dont_inherit 用来控制编译源码时的标志,一般情况下使用默认值
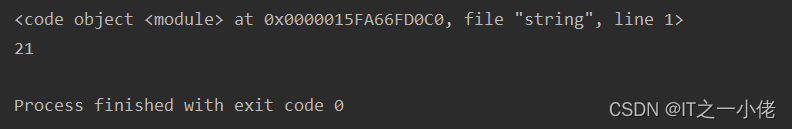
示例代码1:
aa = "3*5+6"
code = compile(aa, 'string', 'eval')
print(code)
print(eval(code))
运行结果:
示例代码2:
code_string = """
def func():
print('123456')
return '666'
func()
"""
code = compile(code_string, 'string', 'exec')
print(code)
print(exec(code))
运行结果:
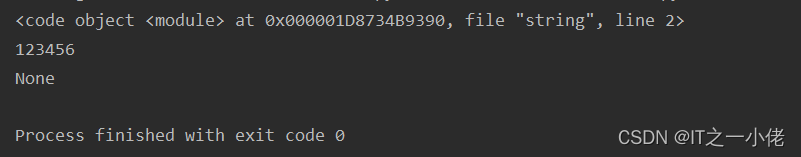
执行exec(code) 就如同执行了code_string所代表的代码,func函数会被调用,输出"123456"。
如果source只是一个表达式,那么mode应当使用eval,执行编译后的字节码也用eval;如果source是python语句,那么mode应当使用exec,执行编译后的字节码也要用exec。
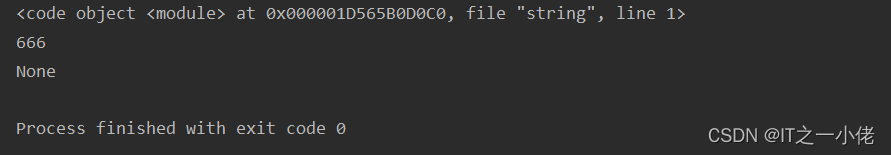
示例代码3:
import ast
code_string = ast.parse("print(666)")
code = compile(code_string, 'string', 'exec')
print(code)
print(exec(code))
运行结果:
相关文章
- Python单元测试框架 unittest详解
- 2023版python安装教程奉上,Python永久使用 超详细版,一看就会【小白友好】
- python内置函数bytearray用法详解
- python中any()函数用法详解
- python内置函数all()用法详解
- python中isinstance()函数用法详解
- python中链式调用方法详解
- python中getattr()函数用法详解
- python中repr()函数用法详解
- python中moviepy库的用法详解
- Python 函数调用父类详解
- 精通Python网络爬虫:核心技术、框架与项目实战.3.1 网络爬虫实现原理详解
- 源码编译vi过程中进行配置时报“checking if compile and link flags for Python are sane... no: PYTHON DISABLED”怎么办?
- Python基础必掌握的定义Python函数方法详解
- Python 教程之如何使用 matplotlib 在 python 中绘制数学函数
- Python学习---重点模块之shelve

