【多线程,详细demo】Java多线程基础学习(二)
2023-09-14 09:05:03 时间
9. 线程安全/共享变量——同步
当多个线程用到同一个变量时,在修改值时存在同时修改的可能性,而此时该变量只能被赋值一次。这就会导致出现“线程安全”问题,这个被多个线程共用的变量称之为“共享变量”。
为了解决线程安全的问题,我们可以使用“同步”来控制线程访问。当一个线程在使用这个共享资源(不仅仅是变量,还可以是集合、对象等)的时候,其他线程就无法访问。
package threadStudy;
public class ThreadSynchronizedTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{
int i=0;
ObjA o = new ObjA(i);
TheThread theThread1 = new TheThread(o);
TheThread theThread2 = new TheThread(o);
theThread1.start();
theThread2.start();
}
static class TheThread extends Thread{
private ObjA objA;
public TheThread(ObjA objA){
this.objA = objA;
}
public void run(){
objA.method();
}
}
static class ObjA{
int i;
public ObjA(int i){
this.i = i;
}
synchronized public void method(){
for (int j=0;j<10;j++){
i++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": " + i);
try{
Thread.sleep(200);
}catch(InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
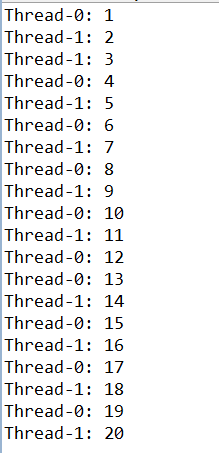
}以上述代码为例,如果加了关键字synchronized,则一个线程在使用共享资源o时,另一个线程必须等到前一个线程使用完,才能使用。
加synchronized的输出结果:

而不加synchronized的输出结果:
10. 容器类并发问题的同步解决方法
JDK中提供了并发容器,可以直接帮我们解决容器类出现的并发问题。它们大部分都存在java.util.concurrent这个包中,包括:ConcurrentHashmap,CopyOnWriteArrayList,ConcurrentLinkedQueue,BlockingQueue,ConcurrentSkipListMap。下面是使用ConcurrentHashmap解决Map容器并发问题的例子:
package threadStudy;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class ThreadConcurrencyCollectionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new HashTest.AddThread(0), "T0");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new HashTest.AddThread(1), "T1");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
class HashTest{
//static Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
static Map<String, String> map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<String, String>());
public static class AddThread extends Thread{
private int start;
public AddThread(int start){
this.start = start;
}
public void run(){
for (int i=start; i<10000; i+=2){
System.out.println(Integer.toString(i));
map.put(Integer.toString(i), Integer.toBinaryString(i));
}
}
}
}
相关文章
- Java并发性和多线程介绍
- [Java基础] java多线程关于消费者和生产者
- JAVA多线程售票问题
- java学习笔记14--多线程编程基础1
- java学习笔记15--多线程编程基础2
- java基础多线程之共享数据
- Java实现 蓝桥杯 算法提高 进攻策略加强(暴力)
- Java实现 LeetCode 190 颠倒二进制位
- java实现第三届蓝桥杯星期几
- java实现第五届蓝桥杯奇怪的分式
- Java实现第八届蓝桥杯外星日历
- Java实现 蓝桥杯 算法提高 7-1用宏求球的体积
- java核心知识点学习----多线程间的数据共享和对象独立,ThreadLocal详解
- java 多线程下载
- Java微服务篇1——SpringBoot
- Java多线程学习笔记 - 三、Thread类源码内的方法概览
- Java多线程学习笔记 - 十一、线程池
- 新手学JAVA(十)-多线程----线程的创建和启动
- 如何实现有返回值的多线程 JAVA多线程实现的三种方式
- Java 多线程 并发编程
- Java 多线程实现的四种方式
- 借助SimpleDateFormat来谈谈java里的多线程不安全
- Java多线程为什么使用while循环来调用wait方法
- 【华为OD机试 2023】快递投放问题(C++ Java JavaScript Python)
- Java多线程有哪几种实现方式? Java中的类如何保证线程安全? 请说明ThreadLocal的用法和适用场景
- 真实!美团到店-测试开发(已发offer),面经分享!(偏java测试开发)
- Java Thread 多线程 介绍
- JAVA---多线程篇

