Android ListView + ArrayAdapter、SimpleAdapter、BaseAdapter实现列表
2023-09-14 09:04:24 时间
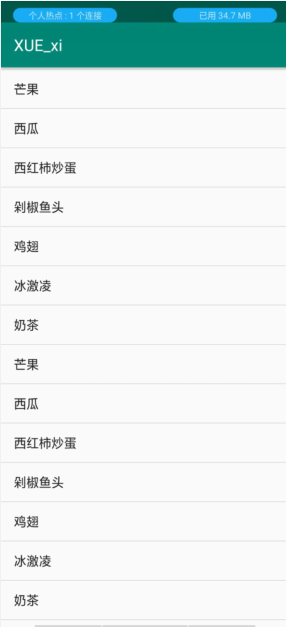
效果图:
ListView 与 ArrayAdapter 之间的配合:
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/ls_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"></ListView>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.ls_view);
// 创造数据源
String[] data = {"冰激凌","奶茶","芒果","西瓜","西红柿炒蛋","剁椒鱼头","鸡翅","冰激凌","奶茶","芒果","西瓜","西红柿炒蛋","剁椒鱼头","鸡翅","冰激凌","奶茶","芒果","西瓜","西红柿炒蛋","剁椒鱼头","鸡翅"};
/**
* 创建ArrayAdapter 适配器 — 把数据源放入适配器中
* 第一个参数是: context
* 第二个参数是: 每一条数据显示的布局item,这里用系统默认的就行
* 第三个参数是: 放入刚刚创建好的数据源
*/
ArrayAdapter adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1,data);
listView.setAdapter(adapter); // 再让列表与适配器产生联系
}
}
ListView 与 SimpleAdapter 之间的配合:

activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv_list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></ListView>
</LinearLayout>
ly_item.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img_view"
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:text="你好"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:text="你好"></TextView>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
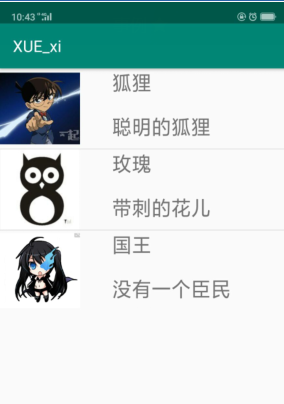
private String[] name = {"狐狸","玫瑰","国王"}; // 名字
private String[] info = {"聪明的狐狸","带刺的花儿","没有一个臣民"}; // 介绍
private int[] image = {R.mipmap.ic_one,R.mipmap.ic_two,R.mipmap.ic_three}; // 每一个item对应的图标
List<Map<String,Object>> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 创建 数据源 list
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// 给数据源装配数据
for (int i=0;i<name.length;i++){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); // 在创建一个map集合
map.put("image",image[i]);
map.put("name",name[i]);
map.put("info",info[i]);
list.add(map); // 将每一组map对象的值,加入到list集合中
}
/**
* 创建 SimpleAdapter 适配器
* 第一个参数: context
* 第二个参数: 放入数据源
* 第三个参数: 每一个item的布局
* 第四个参数: 创建map的键对象,并放入相应的值,因为要从数据源中识别对应值,每一个键对象对应着一个值对象
* 第五个参数: 创建一个int对象,放入item布局中 每一个控件对应的id,这个id与刚才的键对象位置要对应
*/
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this,list,R.layout.ly_item,new String[]{"image","name","info"},new int[]{R.id.img_view,R.id.tv_name,R.id.tv_info});
// 得到listView 对象
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.lv_list);
// 让listview 与 SimpleAdapter 适配器产生联系
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
ListView 与 BaseAdapter 之间的配合【推荐】:
activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lv_list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"></ListView>
</LinearLayout>
ly_item.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/img_view"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:text="你好"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_info"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="40dp"
android:textSize="25dp"
android:text="你好"></TextView>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
MainActivity.java:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.lv_list);
List<CostBean> costBeanList = new ArrayList<>(); //创建封装好的bean对象
// 装配数据源
costBeanList.add(new CostBean(R.mipmap.ic_one,"狐狸","聪明的狐狸"));
costBeanList.add(new CostBean(R.mipmap.ic_two,"玫瑰","带刺的花儿"));
costBeanList.add(new CostBean(R.mipmap.ic_three,"国王","没有一个臣民"));
// 因为 MyAdapter 继承了 BaseAdapter,所以这里直接让 listView 与 Myadapter产生联系
listView.setAdapter(new MyAdapter(this,costBeanList));
}
}
CostBean.java:
**
* CostBean —— 封装数据源
*/
public class CostBean {
private int imgId;
private String name;
private String info;
public CostBean(int imgId, String name, String info) {
this.imgId = imgId;
this.name = name;
this.info = info;
}
public int getImgId() {
return imgId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
MyAdapter.java:
**
* BaseAdapter —— 适配器管理数据源
*/
public class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private List<CostBean> costBeanList;
private LayoutInflater inflater;
// 通过构造方法关联数据源与适配器
public MyAdapter(Context context,List<CostBean> costBeanList) {
this.costBeanList = costBeanList;
// context:要使用当前的Adapter的界面对象mInflater:布局 装载器对象
this.inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return costBeanList.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return costBeanList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder holder;
//第一次创建view即可,以免给程序带来太多负担
if (convertView == null){
holder = new ViewHolder();
// 由于我们只需要将XML转化为View,并不涉及到具体的布局,所以第二个参数通常设置为null
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.ly_item,null);
holder.imageView = convertView.findViewById(R.id.img_view);
holder.title = convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_name);
holder.content = convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_info);
//这句话的意思就是,让convertView与holder产生关联,通过set保存在Tag中
convertView.setTag(holder);
}else{
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
//通过getTag,取出上面绑定的holder,以免多次绑定,造成资源浪费
}
//设置控件的数据,可以理解为从封装的数据中取出一个一个对应的值
CostBean costBean = costBeanList.get(position);
holder.imageView.setImageResource(costBean.getImgId());
holder.title.setText(costBean.getName());
holder.content.setText(costBean.getInfo());
return convertView;
}
class ViewHolder{
public ImageView imageView;
public TextView title;
public TextView content;
}
}
相关文章
- 深入 Android 系统 - Android 的 JNI
- android scaleanimation动画,【Android动画九章】-RotateAnimation(旋转动画)和ScaleAnimation(尺寸动画)…[通俗易懂]
- Android telephony_android获取真实时间
- 加密狗android,Android系统加密狗的设计与实现
- android 混淆不起作用,Android代码混淆的写法总结
- android 混淆规则作用,Android代码混淆详解
- android 读取本地数据库db文件(Android sqlite)
- Android layout属性之gravity和layout_gravity「建议收藏」
- Android listview 实现列表多选
- android短信验证码方案,Android之短信验证码
- 【Android布局】在程序中设置android gravity 和 android layout Gravity属性
- Android angle_android 界面悬停
- android登录注册跳转的代码_Android开发代码
- Android触摸事件_android设置按钮点击事件
- android两级分类列表且子列表item不同布局实现
- 【Android从零单排系列六】《Android视图控件——TextView》
- Yolov5 Android tf-lite方式集成
- 【Android 文件管理】分区存储 ( 分区存储机制 和 文件索引数据 )
- 【Android 插件化】“ 插桩式 “ 插件化框架 ( 注入上下文的使用 )
- 【Android 屏幕适配】异形屏适配 ② ( 需要异形屏适配情况 | 需要异形屏适配的 Android 系统版本 | 刘海屏状态判定 | 异形屏适配调试 - 华为云调试 )
- 【Android Gradle 插件】组件化中的 Gradle 构建脚本实现 ⑤ ( 优化 Gradle 构建脚本 | 构建脚本结构 | 闭包定义及用法 | 依赖配置 | android 块配置 )
- android Universal Image Loader for Android 说明文档 (1)详解手机开发
- android JNI学习详解手机开发
- 使用Android实现连接MySQL数据库:实现快速数据交互与管理(android连接mysql数据库)
- Android系统基于Linux内核,实现移动设备突破极限。(android linux内核)
- Android列表实现(1)_数组列表实例介绍
- android二级listview列表实现代码
- android支持的语言列表(汇总)
- Android中AsyncTask的用法实例分享
- android开发教程之wifi开发示例

