Netty网络编程第四卷
Netty网络编程第四卷
四. 优化与源码
1. 优化
1.1 扩展序列化算法
序列化,反序列化主要用在消息正文的转换上
- 序列化时,需要将 Java 对象变为要传输的数据(可以是 byte[],或 json 等,最终都需要变成 byte[])
- 反序列化时,需要将传入的正文数据还原成 Java 对象,便于处理
目前的代码仅支持 Java 自带的序列化,反序列化机制,核心代码如下
// 反序列化
byte[] body = new byte[bodyLength];
byteByf.readBytes(body);
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(body));
Message message = (Message) in.readObject();
message.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
// 序列化
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(message);
byte[] bytes = out.toByteArray();
为了支持更多序列化算法,抽象一个 Serializer 接口
public interface Serializer {
// 反序列化方法
<T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes);
// 序列化方法
<T> byte[] serialize(T object);
}
提供两个实现,我这里直接将实现加入了枚举类 Serializer.Algorithm 中
enum SerializerAlgorithm implements Serializer {
// Java 实现
Java {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
try {
ObjectInputStream in =
new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes));
Object object = in.readObject();
return (T) object;
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("SerializerAlgorithm.Java 反序列化错误", e);
}
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
new ObjectOutputStream(out).writeObject(object);
return out.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("SerializerAlgorithm.Java 序列化错误", e);
}
}
},
// Json 实现(引入了 Gson 依赖)
Json {
@Override
public <T> T deserialize(Class<T> clazz, byte[] bytes) {
return new Gson().fromJson(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8), clazz);
}
@Override
public <T> byte[] serialize(T object) {
return new Gson().toJson(object).getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
}
};
// 需要从协议的字节中得到是哪种序列化算法
public static SerializerAlgorithm getByInt(int type) {
SerializerAlgorithm[] array = SerializerAlgorithm.values();
if (type < 0 || type > array.length - 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("超过 SerializerAlgorithm 范围");
}
return array[type];
}
}
增加配置类和配置文件
public abstract class Config {
static Properties properties;
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static int getServerPort() {
String value = properties.getProperty("server.port");
if(value == null) {
return 8080;
} else {
return Integer.parseInt(value);
}
}
public static Serializer.Algorithm getSerializerAlgorithm() {
String value = properties.getProperty("serializer.algorithm");
if(value == null) {
return Serializer.Algorithm.Java;
} else {
return Serializer.Algorithm.valueOf(value);
}
}
}
配置文件
serializer.algorithm=Json
修改编解码器
/**
* 必须和 LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder 一起使用,确保接到的 ByteBuf 消息是完整的
*/
public class MessageCodecSharable extends MessageToMessageCodec<ByteBuf, Message> {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Message msg, List<Object> outList) throws Exception {
ByteBuf out = ctx.alloc().buffer();
// 1. 4 字节的魔数
out.writeBytes(new byte[]{1, 2, 3, 4});
// 2. 1 字节的版本,
out.writeByte(1);
// 3. 1 字节的序列化方式 jdk 0 , json 1
out.writeByte(Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().ordinal());
// 4. 1 字节的指令类型
out.writeByte(msg.getMessageType());
// 5. 4 个字节
out.writeInt(msg.getSequenceId());
// 无意义,对齐填充
out.writeByte(0xff);
// 6. 获取内容的字节数组
byte[] bytes = Config.getSerializerAlgorithm().serialize(msg);
// 7. 长度
out.writeInt(bytes.length);
// 8. 写入内容
out.writeBytes(bytes);
outList.add(out);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
int magicNum = in.readInt();
byte version = in.readByte();
byte serializerAlgorithm = in.readByte(); // 0 或 1
byte messageType = in.readByte(); // 0,1,2...
int sequenceId = in.readInt();
in.readByte();
int length = in.readInt();
byte[] bytes = new byte[length];
in.readBytes(bytes, 0, length);
// 找到反序列化算法
Serializer.Algorithm algorithm = Serializer.Algorithm.values()[serializerAlgorithm];
// 确定具体消息类型
Class<? extends Message> messageClass = Message.getMessageClass(messageType);
Message message = algorithm.deserialize(messageClass, bytes);
// log.debug("{}, {}, {}, {}, {}, {}", magicNum, version, serializerType, messageType, sequenceId, length);
// log.debug("{}", message);
out.add(message);
}
}
其中确定具体消息类型,可以根据 消息类型字节 获取到对应的 消息 class
@Data
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
/**
* 根据消息类型字节,获得对应的消息 class
* @param messageType 消息类型字节
* @return 消息 class
*/
public static Class<? extends Message> getMessageClass(int messageType) {
return messageClasses.get(messageType);
}
private int sequenceId;
private int messageType;
public abstract int getMessageType();
public static final int LoginRequestMessage = 0;
public static final int LoginResponseMessage = 1;
public static final int ChatRequestMessage = 2;
public static final int ChatResponseMessage = 3;
public static final int GroupCreateRequestMessage = 4;
public static final int GroupCreateResponseMessage = 5;
public static final int GroupJoinRequestMessage = 6;
public static final int GroupJoinResponseMessage = 7;
public static final int GroupQuitRequestMessage = 8;
public static final int GroupQuitResponseMessage = 9;
public static final int GroupChatRequestMessage = 10;
public static final int GroupChatResponseMessage = 11;
public static final int GroupMembersRequestMessage = 12;
public static final int GroupMembersResponseMessage = 13;
public static final int PingMessage = 14;
public static final int PongMessage = 15;
private static final Map<Integer, Class<? extends Message>> messageClasses = new HashMap<>();
static {
messageClasses.put(LoginRequestMessage, LoginRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(LoginResponseMessage, LoginResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(ChatRequestMessage, ChatRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(ChatResponseMessage, ChatResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupCreateRequestMessage, GroupCreateRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupCreateResponseMessage, GroupCreateResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupJoinRequestMessage, GroupJoinRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupJoinResponseMessage, GroupJoinResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupQuitRequestMessage, GroupQuitRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupQuitResponseMessage, GroupQuitResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupChatRequestMessage, GroupChatRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupChatResponseMessage, GroupChatResponseMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupMembersRequestMessage, GroupMembersRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(GroupMembersResponseMessage, GroupMembersResponseMessage.class);
}
}
1.2 参数调优
1)CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS
-
属于 SocketChannal 参数
-
用在客户端建立连接时,如果在指定毫秒内无法连接,会抛出 timeout 异常
-
SO_TIMEOUT 主要用在阻塞 IO,阻塞 IO 中 accept,read 等都是无限等待的,如果不希望永远阻塞,使用它调整超时时间
@Slf4j
public class TestConnectionTimeout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap()
.group(group)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 300)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new LoggingHandler());
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080);
future.sync().channel().closeFuture().sync(); // 断点1
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("timeout");
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
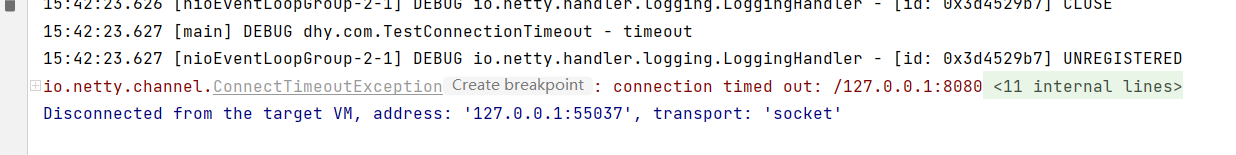
如果设置连接超时为5秒,并且连接不存在的主机,那么不到五秒就会抛出一个里连接拒绝异常:

另外源码部分 io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioChannel.AbstractNioUnsafe#connect
这里底层使用Promise在两个线程间做数据共享

@Override
public final void connect(
final SocketAddress remoteAddress, final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// ...
// Schedule connect timeout.
int connectTimeoutMillis = config().getConnectTimeoutMillis();
if (connectTimeoutMillis > 0) {
connectTimeoutFuture = eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ChannelPromise connectPromise = AbstractNioChannel.this.connectPromise;
ConnectTimeoutException cause =
new ConnectTimeoutException("connection timed out: " + remoteAddress); // 断点2
if (connectPromise != null && connectPromise.tryFailure(cause)) {
close(voidPromise());
}
}
}, connectTimeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// ...
}
- netty线程之间的通信采用的是promise
- netty的eventLoop对象可以执行定时任务
2)SO_BACKLOG
- 属于 ServerSocketChannal 参数
- 服务端的bind用来绑定端口,底层调用listen监听客户端连接
- 客户端的connect发送一次连接请求
- 还没有完成三次握手的连接信息会放入半连接队列
- 已经完成三次握手的连接信息会放入全连接队列

- 第一次握手,client 发送 SYN 到 server,状态修改为 SYN_SEND,server 收到,状态改变为 SYN_REVD,并将该请求放入 sync queue 队列
- 第二次握手,server 回复 SYN + ACK 给 client,client 收到,状态改变为 ESTABLISHED,并发送 ACK 给 server
- 第三次握手,server 收到 ACK,状态改变为 ESTABLISHED,将该请求从 sync queue 放入 accept queue
accept函数的调用是发生在三次握手之后,并且不是三次握手完成后,立马就可以拿到客户端连接请求,而是会从全连接队列中获取,这样可以防止同时大量连接进行,服务端处理不了的情况
其中
-
在 linux 2.2 之前,
backlog大小包括了两个队列的大小,在 2.2 之后,分别用下面两个参数来控制 -
sync queue- 半连接队列- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
syncookies启用的情况下,逻辑上没有最大值限制,这个设置便被忽略
- 大小通过 /proc/sys/net/ipv4/tcp_max_syn_backlog 指定,在
-
accept queue- 全连接队列- 其大小通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn 指定,在使用
listen函数时,内核会根据传入的backlog参数与系统参数,取二者的较小值 - 如果
accpet queue队列满了,server将发送一个拒绝连接的错误信息到client
- 其大小通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn 指定,在使用
netty 中
可以通过 option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 值) 来设置大小
源码查找netty中backlog设置位置:
- backlog参数是在ServerScoketChannel底层bind的时候作为参数传入的

这里我们只看netty的引用

我们追踪config对象,查看一下backlog的默认值

可以通过下面源码查看默认大小
public class DefaultServerSocketChannelConfig extends DefaultChannelConfig
implements ServerSocketChannelConfig {
private volatile int backlog = NetUtil.SOMAXCONN;
// ...
}

nio调试关键断点为:io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoop#processSelectedKey

oio 中更容易说明,不用 debug 模式
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(8888, 2);
Socket accept = ss.accept();
System.out.println(accept);
System.in.read();
}
}
客户端启动 4 个
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try {
Socket s = new Socket();
System.out.println(new Date()+" connecting...");
s.connect(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8888),1000);
System.out.println(new Date()+" connected...");
s.getOutputStream().write(1);
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(new Date()+" connecting timeout...");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
第 1,2,3 个客户端都打印,但除了第一个处于 accpet 外,其它两个都处于 accept queue 中
Tue Apr 21 20:30:28 CST 2020 connecting...
Tue Apr 21 20:30:28 CST 2020 connected...
第 4 个客户端连接时
Tue Apr 21 20:53:58 CST 2020 connecting...
Tue Apr 21 20:53:59 CST 2020 connecting timeout...
java.net.SocketTimeoutException: connect timed out
3)ulimit -n
- 属于操作系统参数
- 限制一个进程最大能够打开的文件描述符的数量
4)TCP_NODELAY
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- netty默认设置为false,表示开启nagal算法,nagal算法会导致黏包和消息发送不及时的现象,根据情况决定是否开启
5)SO_SNDBUF & SO_RCVBUF
- SO_SNDBUF 属于 SocketChannal 参数,操作系统发送窗口大小
- SO_RCVBUF 既可用于 SocketChannal 参数,也可以用于 Serv,erSocketChannal 参数(建议设置到 ServerSocketChannal 上),操作系统接收窗口大小
操作系统底层会动态调整,建议不改
6)ALLOCATOR
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- 用来分配 ByteBuf, ctx.alloc()
源码追踪默认实现
channelConfig是专门配置通过的相关信息的,找其默认实现

追踪默认ByteBuf配置
- ByteBufUtil找到最终的默认配置如下
static {
String allocType = SystemPropertyUtil.get(
"io.netty.allocator.type", PlatformDependent.isAndroid() ? "unpooled" : "pooled");
allocType = allocType.toLowerCase(Locale.US).trim();
ByteBufAllocator alloc;
if ("unpooled".equals(allocType)) {
alloc = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}", allocType);
} else if ("pooled".equals(allocType)) {
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: {}", allocType);
} else {
alloc = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT;
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.allocator.type: pooled (unknown: {})", allocType);
}
DEFAULT_ALLOCATOR = alloc;
THREAD_LOCAL_BUFFER_SIZE = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.threadLocalDirectBufferSize", 0);
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.threadLocalDirectBufferSize: {}", THREAD_LOCAL_BUFFER_SIZE);
MAX_CHAR_BUFFER_SIZE = SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.maxThreadLocalCharBufferSize", 16 * 1024);
logger.debug("-Dio.netty.maxThreadLocalCharBufferSize: {}", MAX_CHAR_BUFFER_SIZE);
}
通过下面的VM虚拟参数可以设置,应用启动默认采用池化类型还是非池化类型的缓冲区
-Dio.netty.allocator.type
追踪采用堆内存还是直接内存的默认实现

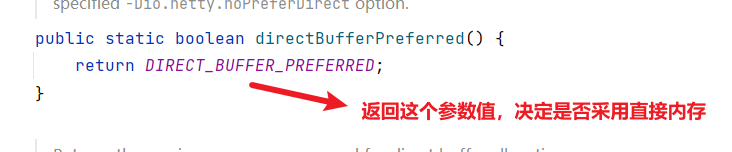
下面追踪这个参数的默认实现

-Dio.netty.noPreferDirect控制是直接内存还是堆内存
7)RCVBUF_ALLOCATOR
- 属于 SocketChannal 参数
- 控制 netty 接收缓冲区大小
- 负责入站数据的分配,决定入站缓冲区的大小(并可动态调整),
统一采用 direct 直接内存,具体池化还是非池化由 allocator 决定
netty对于IO读取的操作,统一采用直接内存,而非堆内存,下面源码走一波:
- AbstractNioByteChannel


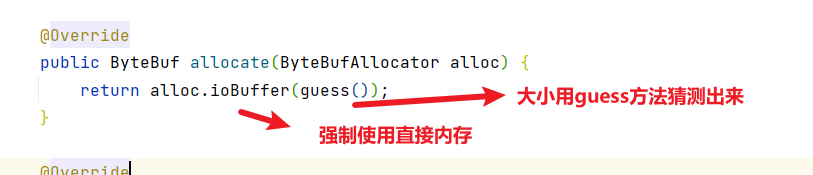
- guess方法会动态根据这几次的数据量对bytebuf的内存大小进行调整



1.3 RPC 框架
1)准备工作
这些代码可以认为是现成的,无需从头编写练习
为了简化起见,在原来聊天项目的基础上新增 Rpc 请求和响应消息
@Data
public abstract class Message implements Serializable {
// 省略旧的代码
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST = 101;
public static final int RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE = 102;
static {
// ...
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST, RpcRequestMessage.class);
messageClasses.put(RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE, RpcResponseMessage.class);
}
}
请求消息
@Getter
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class RpcRequestMessage extends Message {
/**
* 调用的接口全限定名,服务端根据它找到实现
*/
private String interfaceName;
/**
* 调用接口中的方法名
*/
private String methodName;
/**
* 方法返回类型
*/
private Class<?> returnType;
/**
* 方法参数类型数组
*/
private Class[] parameterTypes;
/**
* 方法参数值数组
*/
private Object[] parameterValue;
public RpcRequestMessage(int sequenceId, String interfaceName, String methodName, Class<?> returnType, Class[] parameterTypes, Object[] parameterValue) {
super.setSequenceId(sequenceId);
this.interfaceName = interfaceName;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.returnType = returnType;
this.parameterTypes = parameterTypes;
this.parameterValue = parameterValue;
}
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_REQUEST;
}
}
响应消息
@Data
@ToString(callSuper = true)
public class RpcResponseMessage extends Message {
/**
* 返回值
*/
private Object returnValue;
/**
* 异常值
*/
private Exception exceptionValue;
@Override
public int getMessageType() {
return RPC_MESSAGE_TYPE_RESPONSE;
}
}
服务器架子
@Slf4j
public class RpcServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
NioEventLoopGroup worker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
// rpc 请求消息处理器,待实现
RpcRequestMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcRequestMessageHandler();
try {
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
serverBootstrap.group(boss, worker);
serverBootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = serverBootstrap.bind(8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("server error", e);
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
worker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
客户端架子
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
// rpc 响应消息处理器,待实现
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务器端的 service 获取
public class ServicesFactory {
static Properties properties;
static Map<Class<?>, Object> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
static {
try (InputStream in = Config.class.getResourceAsStream("/application.properties")) {
properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
Set<String> names = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.endsWith("Service")) {
Class<?> interfaceClass = Class.forName(name);
Class<?> instanceClass = Class.forName(properties.getProperty(name));
map.put(interfaceClass, instanceClass.newInstance());
}
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
}
}
public static <T> T getService(Class<T> interfaceClass) {
return (T) map.get(interfaceClass);
}
}
相关配置 application.properties
serializer.algorithm=Json
cn.itcast.server.service.HelloService=cn.itcast.server.service.HelloServiceImpl
2)服务器 handler
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcRequestMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequestMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequestMessage message) {
RpcResponseMessage response = new RpcResponseMessage();
response.setSequenceId(message.getSequenceId());
try {
// 获取真正的实现对象
HelloService service = (HelloService)
ServicesFactory.getService(Class.forName(message.getInterfaceName()));
// 获取要调用的方法
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(message.getMethodName(), message.getParameterTypes());
// 调用方法
Object invoke = method.invoke(service, message.getParameterValue());
// 调用成功
response.setReturnValue(invoke);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 调用异常
response.setExceptionValue(e);
}
// 返回结果
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
3)客户端代码第一版
只发消息
@Slf4j
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
Channel channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
ChannelFuture future = channel.writeAndFlush(new RpcRequestMessage(
1,
"cn.itcast.server.service.HelloService",
"sayHello",
String.class,
new Class[]{String.class},
new Object[]{"张三"}
)).addListener(promise -> {
if (!promise.isSuccess()) {
Throwable cause = promise.cause();
log.error("error", cause);
}
});
channel.closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
4)客户端 handler 第一版
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
}
}
5)客户端代码 第二版
包括 channel 管理,代理,接收结果
@Slf4j
public class RpcClientManager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HelloService service = getProxyService(HelloService.class);
System.out.println(service.sayHello("zhangsan"));
// System.out.println(service.sayHello("lisi"));
// System.out.println(service.sayHello("wangwu"));
}
// 创建代理类
public static <T> T getProxyService(Class<T> serviceClass) {
ClassLoader loader = serviceClass.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = new Class[]{serviceClass};
// sayHello "张三"
Object o = Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, (proxy, method, args) -> {
// 1. 将方法调用转换为 消息对象
int sequenceId = SequenceIdGenerator.nextId();
RpcRequestMessage msg = new RpcRequestMessage(
sequenceId,
serviceClass.getName(),
method.getName(),
method.getReturnType(),
method.getParameterTypes(),
args
);
// 2. 将消息对象发送出去
getChannel().writeAndFlush(msg);
// 3. 准备一个空 Promise 对象,来接收结果 指定 promise 对象异步接收结果线程
DefaultPromise<Object> promise = new DefaultPromise<>(getChannel().eventLoop());
RpcResponseMessageHandler.PROMISES.put(sequenceId, promise);
// promise.addListener(future -> {
// // 线程
// });
// 4. 等待 promise 结果
promise.await();
if(promise.isSuccess()) {
// 调用正常
return promise.getNow();
} else {
// 调用失败
throw new RuntimeException(promise.cause());
}
});
return (T) o;
}
private static Channel channel = null;
private static final Object LOCK = new Object();
// 获取唯一的 channel 对象
public static Channel getChannel() {
if (channel != null) {
return channel;
}
synchronized (LOCK) { // t2
if (channel != null) { // t1
return channel;
}
initChannel();
return channel;
}
}
// 初始化 channel 方法
private static void initChannel() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
LoggingHandler LOGGING_HANDLER = new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.DEBUG);
MessageCodecSharable MESSAGE_CODEC = new MessageCodecSharable();
RpcResponseMessageHandler RPC_HANDLER = new RpcResponseMessageHandler();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProcotolFrameDecoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast(LOGGING_HANDLER);
ch.pipeline().addLast(MESSAGE_CODEC);
ch.pipeline().addLast(RPC_HANDLER);
}
});
try {
channel = bootstrap.connect("localhost", 8080).sync().channel();
channel.closeFuture().addListener(future -> {
group.shutdownGracefully();
});
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("client error", e);
}
}
}
6)客户端 handler 第二版
@Slf4j
@ChannelHandler.Sharable
public class RpcResponseMessageHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponseMessage> {
// 序号 用来接收结果的 promise 对象
public static final Map<Integer, Promise<Object>> PROMISES = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponseMessage msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("{}", msg);
// 拿到空的 promise
Promise<Object> promise = PROMISES.remove(msg.getSequenceId());
if (promise != null) {
Object returnValue = msg.getReturnValue();
Exception exceptionValue = msg.getExceptionValue();
if(exceptionValue != null) {
promise.setFailure(exceptionValue);
} else {
promise.setSuccess(returnValue);
}
}
}
}
思路整理

具体执行流程

2.所以我们客户端需要构建和服务器端能接收的通用请求
我们本地写和服务器端一样的接口 然后用代理模式 发送请求给服务器端 服务器端返回结果响应

这里我对注册中心没有进行实现,包括负载均衡也是
还有一个重点是,这里没有设置心跳机制,是一个缺陷,可能会出现客户端假死的情况

当然这里考虑到功能的需要,客户端需要手动通过EnableRpcMain注解开启rpc远程调用服务,为什么服务端不需要加?
- 只有客户端开启了该服务,客户端采用通过代理对象调用方法,发送请求到服务端,然后阻塞等待结果
- 服务器这边只有客户端发送请求过来,才会去执行对应的方法,然后返回方法结果
gitee仓库rpc框架源码链接
2. 源码分析
2.1 启动剖析
我们就来看看 netty 中对下面的代码是怎样进行处理的
下面是nio时期的基本步骤,包括netty在nio不同时期做的一些事件的简要概述:
//1 netty 中使用 NioEventLoopGroup (简称 nio boss 线程)来封装线程和 selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//2 创建 NioServerSocketChannel,同时会初始化它关联的 handler,以及为原生 ssc 存储 config
//这里NioServerSocketChannel继承至ServerSocketChannel
NioServerSocketChannel attachment = new NioServerSocketChannel();
//3 创建 NioServerSocketChannel 时,创建了 java 原生的 ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//4 启动 nio boss 线程执行接下来的操作
//5 注册(仅关联 selector 和 NioServerSocketChannel),未关注事件
SelectionKey selectionKey = serverSocketChannel.register(selector, 0, attachment);
//6 head -> 初始化器 -> ServerBootstrapAcceptor -> tail,初始化器是一次性的,只为添加 acceptor
//7 绑定端口
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
//8 触发 channel active 事件,在 head 中关注 op_accept 事件
selectionKey.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
入口 io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#bind


关键代码 io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind
doBind()方法做的工作比较多,下面我先对方法进行拆分讲解,在对局部进行深入分析

private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 1. 执行初始化和注册 regFuture 会由 initAndRegister 设置其是否完成,从而回调 3.2 处代码
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
// 2. 因为是 initAndRegister 异步执行,需要分两种情况来看,调试时也需要通过 suspend 断点类型加以区分
// 2.1 如果已经完成
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
// 3.1 立刻调用 doBind0
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
}
// 2.2 还没有完成
else {
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
// 3.2 回调 doBind0
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// 处理异常...
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
promise.registered();
// 3. 由注册线程去执行 doBind0
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
关键代码 io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister




到此为止,ServerSocketChannel创建完毕

init方法探究



一会在初始化器被调用的时候,再进行深入分析,下面来看register部分


eventLoop本质是一个线程池,线程池中的线程都是懒加载的,只有用到的时候才会创建,从register0方法开始,注册的一些工作就都由nio线程完成了,而不是主线程

下面进入register0方法,线程切换发生在这里



doregister方法结束,回到register0方法体内部

探究initChannel方法


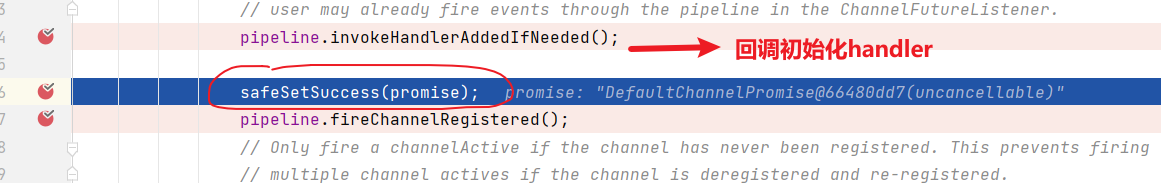
下面执行的这行代码,大概可以猜出,是通知事件完成的信息,可能会唤醒或者通过监听器机制回调其他接口,那么这里会去唤醒或者回调什么呢?
- 让我们回到最开始的doBind()方法中

这里就是通过同一个promise对象,完成回调


doBind0方法调用链比较长,我们只看最终的调用方法



绑定完端口,通道基本就绪,下一步就是唤醒干活的处理器了


默认通道上面有三个handler,是head--->accpetor--->tail处理器,上面会依次触发每个handler的active事件

初始时,active事件的触发主要是在head处理器中完成,下面我们来追踪一下


继续往下追踪,看看头处理都干了啥

read方法调用链很长,我们直接追踪到最终的调用方法


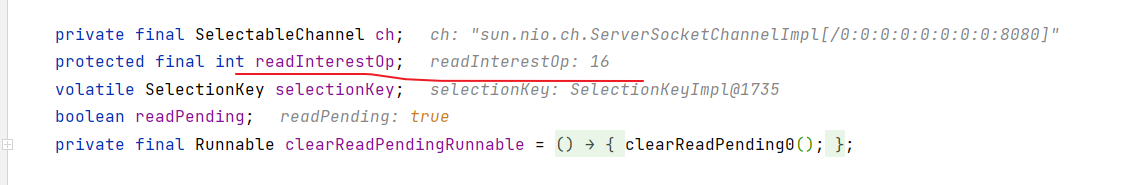
头处理器这里注册的是accept事件,不是读事件,不要被名字误导

到此为止,netty启动创建channel,绑定选择器,绑定端口,注册accept事件的流程就走完了
下面使用代码演示最后一遍流程
入口 io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#bind
关键代码 io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind
private ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) {
// 1. 执行初始化和注册 regFuture 会由 initAndRegister 设置其是否完成,从而回调 3.2 处代码
final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister();
final Channel channel = regFuture.channel();
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
return regFuture;
}
// 2. 因为是 initAndRegister 异步执行,需要分两种情况来看,调试时也需要通过 suspend 断点类型加以区分
// 2.1 如果已经完成
if (regFuture.isDone()) {
ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise();
// 3.1 立刻调用 doBind0
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
return promise;
}
// 2.2 还没有完成
else {
final PendingRegistrationPromise promise = new PendingRegistrationPromise(channel);
// 3.2 回调 doBind0
regFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (cause != null) {
// 处理异常...
promise.setFailure(cause);
} else {
promise.registered();
// 3. 由注册线程去执行 doBind0
doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise);
}
}
});
return promise;
}
}
关键代码 io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#initAndRegister
final ChannelFuture initAndRegister() {
Channel channel = null;
try {
channel = channelFactory.newChannel();
// 1.1 初始化 - 做的事就是添加一个初始化器 ChannelInitializer
init(channel);
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 处理异常...
return new DefaultChannelPromise(new FailedChannel(), GlobalEventExecutor.INSTANCE).setFailure(t);
}
// 1.2 注册 - 做的事就是将原生 channel 注册到 selector 上
ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel);
if (regFuture.cause() != null) {
// 处理异常...
}
return regFuture;
}
关键代码 io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap#init
// 这里 channel 实际上是 NioServerSocketChannel
void init(Channel channel) throws Exception {
final Map<ChannelOption<?>, Object> options = options0();
synchronized (options) {
setChannelOptions(channel, options, logger);
}
final Map<AttributeKey<?>, Object> attrs = attrs0();
synchronized (attrs) {
for (Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object> e: attrs.entrySet()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
AttributeKey<Object> key = (AttributeKey<Object>) e.getKey();
channel.attr(key).set(e.getValue());
}
}
ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline();
final EventLoopGroup currentChildGroup = childGroup;
final ChannelHandler currentChildHandler = childHandler;
final Entry<ChannelOption<?>, Object>[] currentChildOptions;
final Entry<AttributeKey<?>, Object>[] currentChildAttrs;
synchronized (childOptions) {
currentChildOptions = childOptions.entrySet().toArray(newOptionArray(0));
}
synchronized (childAttrs) {
currentChildAttrs = childAttrs.entrySet().toArray(newAttrArray(0));
}
// 为 NioServerSocketChannel 添加初始化器
p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception {
final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
ChannelHandler handler = config.handler();
if (handler != null) {
pipeline.addLast(handler);
}
// 初始化器的职责是将 ServerBootstrapAcceptor 加入至 NioServerSocketChannel
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor(
ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs));
}
});
}
});
}
关键代码 io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#register
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
// 一些检查,略...
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
// 首次执行 execute 方法时,会启动 nio 线程,之后注册等操作在 nio 线程上执行
// 因为只有一个 NioServerSocketChannel 因此,也只会有一个 boss nio 线程
// 这行代码完成的事实是 main -> nio boss 线程的切换
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 日志记录...
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#register0
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
// 1.2.1 原生的 nio channel 绑定到 selector 上,注意此时没有注册 selector 关注事件,附件为 NioServerSocketChannel
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// 1.2.2 执行 NioServerSocketChannel 初始化器的 initChannel
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
// 回调 3.2 io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind0
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// 对应 server socket channel 还未绑定,isActive 为 false
if (isActive()) {
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
关键代码 io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer#initChannel
private boolean initChannel(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
if (initMap.add(ctx)) { // Guard against re-entrance.
try {
// 1.2.2.1 执行初始化
initChannel((C) ctx.channel());
} catch (Throwable cause) {
exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
} finally {
// 1.2.2.2 移除初始化器
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline();
if (pipeline.context(this) != null) {
pipeline.remove(this);
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
关键代码 io.netty.bootstrap.AbstractBootstrap#doBind0
// 3.1 或 3.2 执行 doBind0
private static void doBind0(
final ChannelFuture regFuture, final Channel channel,
final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
channel.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (regFuture.isSuccess()) {
channel.bind(localAddress, promise).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} else {
promise.setFailure(regFuture.cause());
}
}
});
}
关键代码 io.netty.channel.AbstractChannel.AbstractUnsafe#bind
public final void bind(final SocketAddress localAddress, final ChannelPromise promise) {
assertEventLoop();
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
if (Boolean.TRUE.equals(config().getOption(ChannelOption.SO_BROADCAST)) &&
localAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress &&
!((InetSocketAddress) localAddress).getAddress().isAnyLocalAddress() &&
!PlatformDependent.isWindows() && !PlatformDependent.maybeSuperUser()) {
// 记录日志...
}
boolean wasActive = isActive();
try {
// 3.3 执行端口绑定
doBind(localAddress);
} catch (Throwable t) {
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
closeIfClosed();
return;
}
if (!wasActive && isActive()) {
invokeLater(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 3.4 触发 active 事件
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
}
});
}
safeSetSuccess(promise);
}
3.3 关键代码 io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel#doBind
protected void doBind(SocketAddress localAddress) throws Exception {
if (PlatformDependent.javaVersion() >= 7) {
javaChannel().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
} else {
javaChannel().socket().bind(localAddress, config.getBacklog());
}
}
3.4 关键代码 io.netty.channel.DefaultChannelPipeline.HeadContext#channelActive
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
ctx.fireChannelActive();
// 触发 read (NioServerSocketChannel 上的 read 不是读取数据,只是为了触发 channel 的事件注册)
readIfIsAutoRead();
}
关键代码 io.netty.channel.nio.AbstractNioChannel#doBeginRead
protected void doBeginRead() throws Exception {
// Channel.read() or ChannelHandlerContext.read() was called
final SelectionKey selectionKey = this.selectionKey;
if (!selectionKey.isValid()) {
return;
}
readPending = true;
final int interestOps = selectionKey.interestOps();
// readInterestOp 取值是 16,在 NioServerSocketChannel 创建时初始化好,代表关注 accept 事件
if ((interestOps & readInterestOp) == 0) {
selectionKey.interestOps(interestOps | readInterestOp);
}
}
下面会对EventLoop的整体架构进行分析,更多详情请关注本专栏netty网络编程第五卷
相关文章
- 网络编程:socket 编程
- socket网络编程——UDP编程流程「建议收藏」
- 使用tcpdump抓包分析网络请求_抓包报文分析
- 【网络编程开发系列】一种网络编程中的另类内存泄漏(RT-Thread技术论坛优秀文章)
- java高级编程——网络编程(解析网页中的内容)
- [Information Sciences | 论文简读] DA-Net:用于多变量时间序列分类的双注意力网络
- 云数据中心网络现状:100G捕蝉,800G在后
- 网络工程师:什么是机架服务器?
- 【Android 应用开发】Android 网络编程 API笔记 - java.net 包相关 接口 api
- IOS网络编程—(数据请求+slider)将网络上的大文件下载到本地,并打印其进度详解手机开发
- 网络编程基础详解编程语言
- Linux网络编程:套接字文件(linux套接字文件)
- Linux多线程网络编程:实现更高效率(linux多线程网络编程)
- 探索Linux网络技术的新奇世界(Linux网络技术)
- HalloApp应用上架:由两位前WhatsApp资深员工创办 主打私人社交网络
- 驾驭Linux网络多线程编程之道(linux网络多线程编程)
- Linux C语言网络编程技巧分享(linuxc的网络编程)
- Linux虚拟机网络问题:无法上网(linux虚拟机上不了网)
- 黑客通过树莓派设备攻入 NASA 网络
- Dropbox是一个提供同步本地文件的网络存储在线应用,支持在多台电脑多种操作中自动同步,并可当作大容量的网络硬盘使用。
- Linux下查看网络负载的简易方法(linux 查看网络负载)
- Linux实现虚拟交换机,构建稳健网络(linux虚拟交换机)
- Linux网络编程:深入浅出指南(linux网络编程目录)
- Linux网络编程之LWIP协议栈(linuxlwip)
- Oracle MDNSD服务一次性建设稳定可靠的网络环境(oracle mdnsd)
- android网络编程之android连接网络的简单示例代码


