PostgreSQL 在路上的特性 - 远离触发器, 拥抱内置分区
之前分享过阿里云RDS PG支持分区表的文章
https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/113
今天要给大家带来另一个好消息,
PostgreSQL 社区版本终于要有集成的分区表特性了,再也不用为写分区触发器烦恼了。
(很多人认为PG现有的分区表用法是"惨无人道"的(除了管理不方便,性能也是个问题),就像是一粒老鼠屎,坏了一锅汤。社区终于要把老鼠屎请出去了。)
如果你不care性能,可以看看我以前写的一个通用的分区表触发器函数,一个函数打天下
http://blog.163.com/digoal@126/blog/static/16387704020128772037884/
内置分区表的讨论和patch详见
https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/flat/55D3093C.5010800@lab.ntt.co.jp#55D3093C.5010800@lab.ntt.co.jp
https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Table_partitioning
基本已成型,9.6有合进来的可能。
相比触发器的方法,内置分区直接使用插入更新删除接口处理,节省了parser和optimize的过程,比触发器转成SQL更高效。
src/backend/access/heap/heapam.c * heap_insert - insert tuple into a relation * heap_delete - delete a tuple from a relation * heap_update - replace a tuple in a relation with another tuple
创建分区主表
-- create partitioned table and child partitions at once.
CREATE TABLE parent (...)
PARTITION BY [ RANGE | LIST ]( key ) [ opclass ] -- 默认使用分区列的btree默认opclass, 也可以自定义
PARTITION child
VALUES LESS THAN { ... | MAXVALUE } -- for RANGE
| VALUES [ IN ]( { ... | DEFAULT } ) -- for LIST
[ WITH ( ... ) ] [ TABLESPACE tbs ]
[, ...]
) ] ;
-- add a partition key to a table.
ALTER TABLE parent PARTITION BY [ RANGE | LIST ]( key ) [ opclass ] [ (...) ] ;
添加分区子表
-- create a new partition on a partitioned table. CREATE PARTITION child ON parent VALUES ... ; -- add a table as a partition. ALTER TABLE parent ATTACH PARTITION child VALUES ... ; -- Remove a partition as a normal table. ALTER TABLE parent DETACH PARTITION child ;分区表描述
分区主表 postgres=# \d+ test Unlogged partitioned table "public.test" Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description ----------+-----------------------------+-----------+----------+--------------+------------- id | integer | | plain | | info | text | | extended | | crt_time | timestamp without time zone | | plain | | Partition Key: PARTITION BY RANGE (id) postgres=# \d+ test0 Unlogged table "public.test0" Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description ----------+-----------------------------+-----------+----------+--------------+------------- id | integer | | plain | | info | text | | extended | | crt_time | timestamp without time zone | | plain | | Partition Of: test FOR VALUES START (0) END (1000)分区表元数据
分区主表
postgres=# select * from pg_partitioned; partedrelid | partstrat | partnatts | partattrs | partclass | partexprs -------------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+----------- 16405 | r | 1 | 1 | 1978 | (1 row) postgres=# select * from pg_class where relkind =P; relname | relnamespace | reltype | reloftype | relowner | relam | relfilenode | reltablespace | relpages | reltuples | relallvisible | reltoastrelid | relhasindex | relisshared | relpersistence | relkind | relnatts | relchecks | relhaso ids | relhaspkey | relhasrules | relhastriggers | relhassubclass | relrowsecurity | relforcerowsecurity | relispopulated | relreplident | relfrozenxid | relminmxid | relacl | reloptions ---------+--------------+---------+-----------+----------+-------+-------------+---------------+----------+-----------+---------------+---------------+-------------+-------------+----------------+---------+----------+-----------+-------- ----+------------+-------------+----------------+----------------+----------------+---------------------+----------------+--------------+--------------+------------+--------+------------ test | 2200 | 16407 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 16405 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16408 | f | f | u | P | 3 | 0 | f | f | f | f | t | f | f | t | d | 0 | 0 | | (1 row)
分区子表
记录了每个子表的分区规则,是不是和pg_rewrite很像呢
postgres=# select * from pg_partition;
partrelid | partbound
-----------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
16411 | {PARTITIONRANGE :lowerinc true :lower ({CONST :consttype 23 :consttypmod -1 :constcollid 0 :constlen 4 :constbyval true :constisnull false :location 64 :constvalue 4 [ 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ]}) :upperinc false :upper ({CONST :cons
ttype 23 :consttypmod -1 :constcollid 0 :constlen 4 :constbyval true :constisnull false :location 72 :constvalue 4 [ -24 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 ]})}
......
16567 | {PARTITIONRANGE :lowerinc true :lower ({CONST :consttype 23 :consttypmod -1 :constcollid 0 :constlen 4 :constbyval true :constisnull false :location 65 :constvalue 4 [ -56 50 0 0 0 0 0 0 ]}) :upperinc false :upper ({CONST :c
onsttype 23 :consttypmod -1 :constcollid 0 :constlen 4 :constbyval true :constisnull false :location 77 :constvalue 4 [ -80 54 0 0 0 0 0 0 ]})}
(14 rows)
通过记录找出对应范围分区的代码,可以看到它这里用了二分查找来提高范围分区表的分区定位效率
+/* + * range_partition_for_tuple + * Search the range partition for a range key (values) + * Returns -1 if none found. +static int +range_partition_for_tuple(PartitionKey key, PartitionDesc pdesc, Datum *values) + Assert(pdesc- nparts + return range_partition_bsearch(key, pdesc, values); + * range_partition_bsearch + * Workhorse of range_partition_for_tuple +static int +range_partition_bsearch(PartitionKey key, PartitionDesc pdesc, + Datum *values) + int low, high; + /* Good ol bsearch */ + low = 0; + high = pdesc- nparts - 1; + while (low = high) + int idx = (low + high) / 2; + if (pdesc- rangeuppers[idx]- infinite) + if (rightof(key, values, pdesc- rangelowers[idx])) + return idx; + break; + else if (leftof(key, values, pdesc- rangeuppers[idx])) + if (pdesc- rangelowers[idx]- infinite) + return idx; + if (rightof(key, values, pdesc- rangelowers[idx])) + return idx; + high = idx - 1; + continue; + low = idx + 1; + return -1; +}
查找list 分区
+/* + * list_partition_for_tuple + * Find the list partition for a tuple + * Returns -1 if none found. +static int +list_partition_for_tuple(PartitionKey key, PartitionDesc pdesc, + Datum value, bool isnull) + int i; + Assert(pdesc- nparts + for (i = 0; i pdesc- nparts; i++) + int j; + if (isnull) + if (pdesc- lists[i]- contains_null) + return i; + continue; + for (j = 0; j pdesc- lists[i]- nvalues; j++) + int32 cmpval; + cmpval = DatumGetInt32(FunctionCall2Coll( key- partsupfunc[0], + key- tcinfo- typcoll[0], + pdesc- lists[i]- values[j], + value)); + if (!cmpval) + return i; + return -1; +}
插入直接使用的是heap_insert接口,而不是rewrite。
+ heap_insert(resultRelInfo- ri_RelationDesc, + tuple, mycid, hi_options, bistate);
(ps: 触发器的分区查找算法有优化的空间,这里没有使用二分查找。因此最后一个分区的性能落差不至于这么大。)
COPY 500W记录的性能对比。 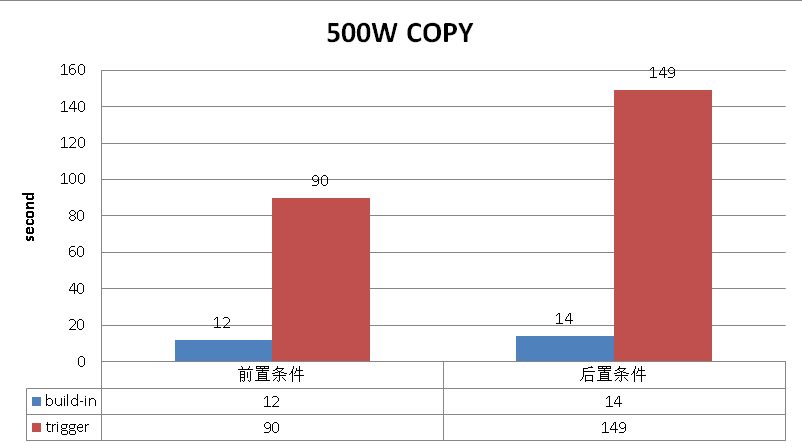
使用PostgreSQL 9.6 beta1的源码,用最近的patch.
wget https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/attachment/44614/0001-Add-syntax-to-specify-partition-key-v6.patch wget https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/attachment/44615/0002-Add-a-IGNORE-dependency-type-v6.patch wget https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/attachment/44616/0003-Infrastructure-for-creation-of-partitioned-tables-v6.patch wget https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/attachment/44617/0004-Add-syntax-to-create-partitions-v6.patch wget https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/attachment/44618/0005-Infrastructure-for-partition-metadata-storage-and-ma-v6.patch wget https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/attachment/44619/0006-Introduce-tuple-routing-for-partitioned-tables-v6.patch wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/source/v9.6beta1/postgresql-9.6beta1.tar.bz2 tar -jxvf postgresql-9.6beta1.tar.bz2 cd postgresql-9.6beta1/ patch -p1 ../0001-Add-syntax-to-specify-partition-key-v6.patch patch -p1 ../0002-Add-a-IGNORE-dependency-type-v6.patch patch -p1 ../0003-Infrastructure-for-creation-of-partitioned-tables-v6.patch patch -p1 ../0004-Add-syntax-to-create-partitions-v6.patch patch -p1 ../0005-Infrastructure-for-partition-metadata-storage-and-ma-v6.patch patch -p1 ../0006-Introduce-tuple-routing-for-partitioned-tables-v6.patch
安装和测试
./configure --prefix=/home/digoal/pgsql9.6 gmake world -j 32 gmake install-world -j 32 vi ~/env9.6.sh export PS1="$USER@`/bin/hostname -s`- " export PGPORT=1922 export PGDATA=/home/digoal/pgdata9.6 export LANG=en_US.utf8 export PGHOME=/home/digoal/pgsql9.6 export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$PGHOME/lib:/lib64:/usr/lib64:/usr/local/lib64:/lib:/usr/lib:/usr/local/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH export DATE=`date +"%Y%m%d%H%M"` export PATH=$PGHOME/bin:$PATH:. export MANPATH=$PGHOME/share/man:$MANPATH export PGHOST=$PGDATA export PGUSER=postgres export PGDATABASE=postgres alias rm=rm -i alias ll=ls -lh unalias vi . ~/env9.6.sh initdb -D $PGDATA -E SQL_ASCII -U postgres --locale=C vi $PGDATA/postgresql.conf listen_addresses = 0.0.0.0 # what IP address(es) to listen on; port = 1922 # (change requires restart) max_connections = 100 # (change requires restart) unix_socket_directories = . # comma-separated list of directories unix_socket_permissions = 0700 # begin with 0 to use octal notation shared_buffers = 128MB # min 128kB dynamic_shared_memory_type = posix # the default is the first option log_destination = csvlog # Valid values are combinations of logging_collector = on # Enable capturing of stderr and csvlog log_directory = pg_log # directory where log files are written, log_truncate_on_rotation = on # If on, an existing log file with the log_timezone = PRC datestyle = iso, mdy timezone = PRC lc_messages = C # locale for system error message lc_monetary = C # locale for monetary formatting lc_numeric = C # locale for number formatting lc_time = C # locale for time formatting default_text_search_config = pg_catalog.english pg_ctl start 创建分区表 CREATE unlogged TABLE test(id int, info text, crt_time timestamp) PARTITION BY RANGE (id); create unlogged table test0 partition of test for values start (0) end (1000); create unlogged table test1 partition of test for values start (1000) end (2000); create unlogged table test2 partition of test for values start (2000) end (3000); create unlogged table test3 partition of test for values start (3000) end (4000); create unlogged table test4 partition of test for values start (4000) end (5000); create unlogged table test5 partition of test for values start (5000) end (6000); create unlogged table test6 partition of test for values start (6000) end (7000); create unlogged table test7 partition of test for values start (7000) end (8000); create unlogged table test8 partition of test for values start (8000) end (9000); create unlogged table test9 partition of test for values start (9000) end (10000); create unlogged table test10 partition of test for values start (10000) end (11000); create unlogged table test11 partition of test for values start (11000) end (12000); create unlogged table test12 partition of test for values start (12000) end (13000); create unlogged table test13 partition of test for values start (13000) end (14000); 使用触发器的方法创建分区表 一坨坨的代码来了 create unlogged table t(id int, info text, crt_time timestamp); create unlogged table t0 (like t including all) inherits(t);; create unlogged table t1 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t2 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t3 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t4 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t5 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t6 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t7 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t8 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t9 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t10 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t11 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t12 (like t including all) inherits(t); create unlogged table t13 (like t including all) inherits(t); alter table t0 add constraint ck1 check (id =0 and id 1000); alter table t1 add constraint ck1 check (id =1000 and id 2000); alter table t2 add constraint ck1 check (id =2000 and id 3000); alter table t3 add constraint ck1 check (id =3000 and id 4000); alter table t4 add constraint ck1 check (id =4000 and id 5000); alter table t5 add constraint ck1 check (id =5000 and id 6000); alter table t6 add constraint ck1 check (id =6000 and id 7000); alter table t7 add constraint ck1 check (id =7000 and id 8000); alter table t8 add constraint ck1 check (id =8000 and id 9000); alter table t9 add constraint ck1 check (id =9000 and id 10000); alter table t10 add constraint ck1 check (id =10000 and id 11000); alter table t11 add constraint ck1 check (id =11000 and id 12000); alter table t12 add constraint ck1 check (id =12000 and id 13000); alter table t13 add constraint ck1 check (id =13000 and id 14000); postgres=# create or replace function ins() returns trigger as declare begin if 0 = new.id and new.id 1000 then insert into t0 values (new.*); elsif 1000 = new.id and new.id 2000 then insert into t1 values (new.*); elsif 2000 = new.id and new.id 3000 then insert into t2 values (new.*); elsif 3000 = new.id and new.id 4000 then insert into t3 values (new.*); elsif 4000 = new.id and new.id 5000 then insert into t4 values (new.*); elsif 5000 = new.id and new.id 6000 then insert into t5 values (new.*); elsif 6000 = new.id and new.id 7000 then insert into t6 values (new.*); elsif 7000 = new.id and new.id 8000 then insert into t7 values (new.*); elsif 8000 = new.id and new.id 9000 then insert into t8 values (new.*); elsif 9000 = new.id and new.id 10000 then insert into t9 values (new.*); elsif 10000 = new.id and new.id 11000 then insert into t10 values (new.*); elsif 11000 = new.id and new.id 12000 then insert into t11 values (new.*); elsif 12000 = new.id and new.id 13000 then insert into t12 values (new.*); elsif 13000 = new.id and new.id 14000 then insert into t13 values (new.*); else raise partition key value overflow; end if; return null; language plpgsql strict; postgres=# create trigger tg1 before insert on t for each row execute procedure ins(); 测试传统的方法和内置分区表的方法进行测试 cat t.sql insert into t values (0,t,now()); insert into t values (1000,t,now()); insert into t values (2000,t,now()); insert into t values (3000,t,now()); insert into t values (4000,t,now()); insert into t values (5000,t,now()); insert into t values (6000,t,now()); insert into t values (7000,t,now()); insert into t values (8000,t,now()); insert into t values (9000,t,now()); insert into t values (10000,t,now()); insert into t values (11000,t,now()); insert into t values (12000,t,now()); insert into t values (13000,t,now()); cat test.sql insert into test values (0,test,now()); insert into test values (1000,test,now()); insert into test values (2000,test,now()); insert into test values (3000,test,now()); insert into test values (4000,test,now()); insert into test values (5000,test,now()); insert into test values (6000,test,now()); insert into test values (7000,test,now()); insert into test values (8000,test,now()); insert into test values (9000,test,now()); insert into test values (10000,test,now()); insert into test values (11000,test,now()); insert into test values (12000,test,now()); insert into test values (13000,test,now()); pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 1 -f ./test.sql -c 16 -j 16 -T 120 tps = 5619.075687 (including connections establishing) tps = 5619.473688 (excluding connections establishing) pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 1 -f ./t.sql -c 16 -j 16 -T 120 tps = 3781.152246 (including connections establishing) tps = 3781.456820 (excluding connections establishing) cat t.sql insert into t values (13000,t,now()); cat test.sql insert into test values (13000,test,now()); pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 1 -f ./test.sql -c 16 -j 16 -T 120 tps = 75777.169561 (including connections establishing) tps = 75781.869815 (excluding connections establishing) pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 1 -f ./t.sql -c 16 -j 16 -T 120 tps = 50596.853557 (including connections establishing) tps = 50599.913130 (excluding connections establishing)
以上测试,软中断较多,并没有体现PG分区表代码层的优势。
使用copy 测试
效果立竿见影
date;psql -c "copy (select 0,test,now() from generate_series(1,5000000)) to stdout"|psql -c "copy test from stdin";date Sat Jun 11 19:12:50 CST 2016 COPY 5000000 Sat Jun 11 19:13:02 CST 2016 date;psql -c "copy (select 0,test,now() from generate_series(1,5000000)) to stdout"|psql -c "copy t from stdin";date Sat Jun 11 19:13:05 CST 2016 COPY 0 Sat Jun 11 19:14:35 CST 2016 date;psql -c "copy (select 13000,test,now() from generate_series(1,5000000)) to stdout"|psql -c "copy test from stdin";date Sat Jun 11 19:05:08 CST 2016 COPY 5000000 Sat Jun 11 19:05:22 CST 2016 date;psql -c "copy (select 13000,test,now() from generate_series(1,5000000)) to stdout"|psql -c "copy t from stdin";date Sat Jun 11 19:05:26 CST 2016 COPY 0 Sat Jun 11 19:07:55 CST 2016
PostgreSQL技术周刊第7期:PostgreSQL11新特性之分区表增加哈希分区 PostgreSQL(简称PG)的开发者们:云栖社区已有5000位PG开发者,发布了3000+PG文章(文章列表),沉淀了700+的PG精品问答(问答列表)。 PostgreSQL技术周刊会为大家介绍最新的PG技术与动态、预告活动、最热问答、直播教程等,欢迎大家订阅PostgreSQL技术周刊。
相关文章
- PostgreSQL快速导入千万条数据
- Postgresql数组、复合数组简单实例
- PostgreSQL 如何禁用全表扫描的方法介绍
- postgresql数据库基础 之 查询字符串中是否包含某字符的操作
- PostgreSQL常用优化技巧示例介绍
- Postgresql 存储过程(plpgsql)两层for循环的操作
- PostgreSQL 逻辑复制 配置操作
- PostgreSQL 22022: indicator_overflow 报错 故障修复 远程处理
- PostgreSQL 42P15: invalid_schema_definition 报错 故障修复 远程处理
- PostgreSQL 42P16: invalid_table_definition 报错 故障修复 远程处理
- postgresql 清空数据表数据详解数据库
- PostgreSQL使用localhost可以连接/使用IP无法连接的问题解决详解数据库
- MongoDB与PostgresQL无责任初步测试详解数据库
- PostgreSQL数据库同步实践(postgresql同步)
- 利用PostgreSQL视图创建灵活报表(postgresql视图)
- 体验PostgreSQL之精彩:驱动新体验(postgresql驱动)
- 优化PostgreSQL内核优化:提升数据库性能的必经之路(postgresql内核)
- PostgreSQL新建数据库:快速搭建实现数据存储 (postgresql新建数据库)
- 连接 PostgreSQL: 实现高效数据管理的关键技巧(连接postgresql)
- PostgreSQL.conf配置文件详解(postgresql.conf)
- 数据库PostgreSQL:开放源码的分布式数据库管理系统(postgresql开源)
- Postgresql操作指南:极致生产力体系构建(postgresql操作)
- 权限管理PostgreSQL访问权限安全控制管理(postgresql访问)
- PostgreSQL中建立数据表的技巧(postgresql建表)
- PostgreSQL连接的实践与思考(postgresql链接)
- 加入PostgreSQL社区,实现开发技术的进步!(postgresql社区)
- PostgreSQL 掌握精妙的数据类型(postgresql类型)

