双向链表
2023-02-18 16:34:54 时间
双向链表
1. 双向链表的简介&概念
单链表在很多时候已经可以胜任很多优秀的操作了,但是,单链表任然存在不足,所谓‘单链表’,是指结点中只有一个指向其后继的指针,具有单向性,有时需要搜索大量数据的时候,就必须要多次进行从头开始的遍历,这样的搜索不是很便利。
图:单链表示意图

对此在单链表的基础上,产生了双向链表的概念,即: 在单链表的基础上,对于每一个结点设计一个前驱结点,前驱结点与前一个结点相互连接,构成一个链表。
双向链表可以简称为双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。
图:双向链表示意图
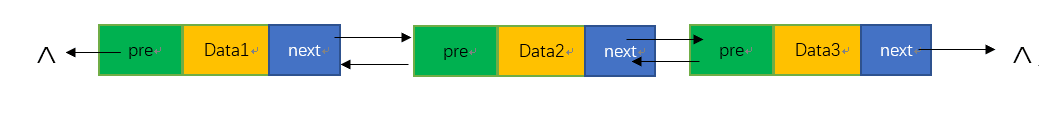
一个完整的双向链表应该是头结点的pre指针指为空,尾结点的next指针指向空,其余结点前后相链。
2. 双向链表的结点设计
对于每一个结点而言,有:
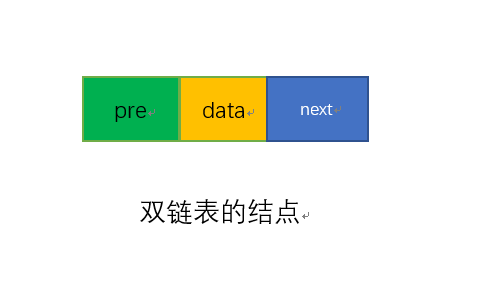
结构体
typedef char DataType;
struct DoubleNode{
DataType data;
DoubleNode* prev;
DoubleNode* next;
};
typedef DoubleNode* PDoubleNode;
初始化双链表
//初始化链表,大小为可以储存n个元素
PDoubleNode InitList(PDoubleNode head,int n){
PDoubleNode p,s;
head = (DoubleNode*)malloc(sizeof(DoubleNode));//分配内存
if(head==NULL){
return NULL;
}
//头节点的初始化
head->prev =NULL;
head->next = NULL;
p=head;
//输入n个元素
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
s= (PDoubleNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleNode));
if (s==NULL)
{
exit(0);
}
cout<<"Enter a value"<<endl;
cin>>s->data;
//指针指向
s->next=NULL;
p->next = s;
s->prev =p;
p=s;//p指向尾节点
}
return head;
}
插入元素
添加至表头
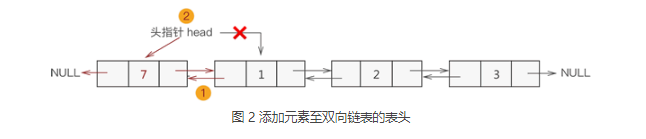
换句话说,假设新元素节点为 temp,表头节点为 head,则需要做以下 2 步操作即可:
- temp->next=head; head->prior=temp;
- 将 head 移至 temp,重新指向新的表头;
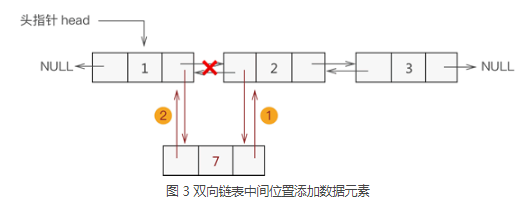
添加至表的中间位置
- 新节点先与其直接后继节点建立双层逻辑关系;
- 新节点的直接前驱节点与之建立双层逻辑关系;
添加至表尾
- 找到双链表中最后一个节点;
- 让新节点与最后一个节点进行双层逻辑关系;
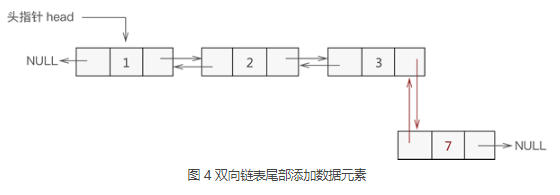
PDoubleNode insertNode(PDoubleNode head,DataType data,int pos){
PDoubleNode p=head;
PDoubleNode q =(PDoubleNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleNode));
q->data=data;
q->next=NULL;
q->prev=NULL;
//插入到表头需要特殊考虑
if(pos==1){
q->next=head;
head->prev=q;
head=q;
}else
{
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for (int i = 1; i < pos-1; i++)
{
p=p->next;
}
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if (p->next==NULL)
{
p->next=q;
q->prev=p;
}else
{
p->next->prev=q;
q->next=p->next;
p->next=q;
q->prev=p;
}
}
return head;
}
删除节点
双链表删除结点时,只需遍历链表找到要删除的结点,然后将该节点从表中摘除即可。
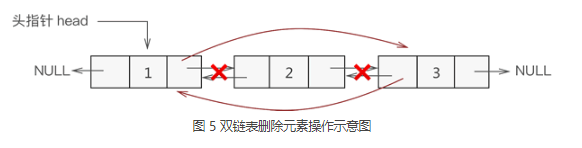
//删除节点
PDoubleNode deleteNode(PDoubleNode head,DataType data)
{
PDoubleNode p=head;
while (p)
{
if (p->data==data)
{
p->prev->next=p->next;
p->next->prev=p->prev;
free(p);
return head;
}
p=p->next;
}
cout<<"not found"<<endl;
return head;
}
查找节点
通常,双向链表同单链表一样,都仅有一个头指针。因此,双链表查找指定元素的实现同单链表类似,都是从表头依次遍历表中元素。
int selectElem(PDoubleNode head,DataType data){
PDoubleNode p = head;
int i=1;
while (p)
{
if(p->data==data){
return i;
}
i++;
p=p->next;
}
return -1;
}
修改节点
PDoubleNode amendElement(PDoubleNode head,int add,DataType newData){
PDoubleNode p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < add; i++)
{
p=p->data;
}
p->data=newData;
}
完整代码:

#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct line{
int data; //data
struct line *pre; //pre node
struct line *next; //next node
}line;
//分别表示该结点的前驱(pre),后继(next),以及当前数据(data)
//遍历双链表,同时打印元素数据
void printLine(line *head){
line *list = head;
int pos=1;
while(list){
printf("第%d个数据是:%d\n",pos++,list->data);
list=list->next;
}
}
//创建双链表
line* initLine(line * head){
int number,pos=1,input_data;
printf("请输入创建结点的大小\n");
scanf("%d",&number);
if(number<1){return NULL;} //输入非法直接结束
//////头结点创建///////
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
head->pre=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
printf("输入第%d个数据\n",pos++);
scanf("%d",&input_data);
head->data=input_data;
line * list=head;
while (pos<=number) {
line * body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->pre=NULL;
body->next=NULL;
printf("输入第%d个数据\n",pos++);
scanf("%d",&input_data);
body->data=input_data;
list->next=body;
body->pre=list;
list=list->next;
}
return head;
}
//插入数据
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add){
//三个参数分别为:进行此操作的双链表,插入的数据,插入的位置
//新建数据域为data的结点
line * temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->pre=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑
if (add==1) {
temp->next=head;
head->pre=temp;
head=temp;
}else{
line * body=head;
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for (int i=1; i<add-1; i++) {
body=body->next;
}
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if (body->next==NULL) {
body->next=temp;
temp->pre=body;
}else{
body->next->pre=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->pre=body;
}
}
return head;
}
//删除元素
line * deleteLine(line * head,int data){
//输入的参数分别为进行此操作的双链表,需要删除的数据
line * list=head;
//遍历链表
while (list) {
//判断是否与此元素相等
//删除该点方法为将该结点前一结点的next指向该节点后一结点
//同时将该结点的后一结点的pre指向该节点的前一结点
if (list->data==data) {
list->pre->next=list->next;
list->next->pre=list->pre;
free(list);
printf("--删除成功--\n");
return head;
}
list=list->next;
}
printf("Error:没有找到该元素,没有产生删除\n");
return head;
}
int main(){
line *head=NULL;
printf("创建双链表操作\n");
head=initLine(head);
printLine(head);
//////////create line////////////
printf("插入操作\n");
head=insertLine(head,40,2); //为了简化直接写参数了
printLine(head);
//////////insert Line////////////
printf("删除操作\n");
head=deleteLine(head,2); //为了简化直接写参数了
printLine(head);
//////////delete Line////////////
return 0;
}
相关文章
- 最长支持5小时!实时语音转写,直播也能同步字幕
- 运动健康者的福音,拍照即可获取食物卡路里和营养元素啦
- 日调用量超600亿次,HMS Core HiAI Foundation助力AI应用高效开发
- HMS Core地理围栏能力助你实现指定范围人群的精准消息推送
- 华为音频编辑服务实时变声,大叔音怪兽音随意变换
- HMS Core分析服务助您掌握用户分层密码,实现整体收益提升
- 全场景AI推理引擎MindSpore Lite, 助力HMS Core视频编辑服务打造更智能的剪辑体验
- 开发者问第一期问答分享来啦
- 上新啦!KIT!
- 【有奖调研】华为分析服务诚邀您参与,您的真实反馈可以让我们变得更好!
- 有奖调研 | 即时消息服务的产品需求规划就交给你了!
- 迁移学习(DANN)《Domain-Adversarial Training of Neural Networks》
- 【FAQ】接入HMS Core地图服务过程中常见问题总结
- 论文解读(CAN)《Contrastive Adaptation Network for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation》
- HMS Core电商解决方案之商品3D商品展示
- HMS Core Discovery第14期回顾长文|纵享丝滑剪辑,释放视频创作力
- 虚假新闻检测-迁移学习(CADM)《Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for COVID-19 Information Service with Contrastive Adversarial Domain Mixup》
- 谣言检测(ACLR)《Detect Rumors in Microblog Posts for Low-Resource Domains via Adversarial Contrastive Learning》
- 原来,这才是开发者打开世界读书日的正确姿势!
- 虚假新闻检测(CANMD)《Contrastive Domain Adaptation for Early Misinformation Detection: A Case Study on COVID-19》


