Prometheus 长期远程存储方案 VictoriaMetrics 入门实践

VictoriaMetrics(简称VM) 是一个支持高可用、经济高效且可扩展的监控解决方案和时间序列数据库,可用于 Prometheus 监控数据做长期远程存储。
前面章节我们介绍了 Thanos 方案也可以用来解决 Prometheus 的高可用和远程存储的问题,那么为什么我们还要使用 VictoriaMetrics 呢?相对于 Thanos,VictoriaMetrics 主要是一个可水平扩容的本地全量持久化存储方案,VictoriaMetrics 不仅仅是时序数据库,它的优势主要体现在以下几点。
- 对外支持 Prometheus 相关的 API,可以直接用于 Grafana 作为 Prometheus 数据源使用。
- 指标数据摄取和查询具备高性能和良好的可扩展性,性能比 InfluxDB 和 TimescaleDB 高出 20 倍。
- 这处理高基数时间序列时,内存方面也做了优化,比 InfluxDB 少 10x 倍,比 Prometheus、Thanos 或 Cortex 少 7 倍。
- 高性能的数据压缩方式,与 TimescaleDB 相比,可以将多达 70 倍的数据点存入有限的存储空间,与 Prometheus、Thanos 或 Cortex 相比,所需的存储空间减少 7 倍。
- 它针对具有高延迟 IO 和低 IOPS 的存储进行了优化。
- 提供全局的查询视图,多个 Prometheus 实例或任何其他数据源可能会将数据摄取到 VictoriaMetrics。
- 操作简单
- VictoriaMetrics 由一个没有外部依赖的小型可执行文件组成
- 所有的配置都是通过明确的命令行标志和合理的默认值完成的
- 所有数据都存储在 - storageDataPath 命令行参数指向的目录中
- 可以使用 vmbackup/vmrestore 工具轻松快速地从实时快照备份到 S3 或 GCS 对象存储中
- 支持从第三方时序数据库获取数据源
- 由于存储架构,它可以保护存储在非正常关机(即 OOM、硬件重置或 kill -9)时免受数据损坏
- 同样支持指标的 relabel 操作
架构
VM 分为单节点和集群两个方案,根据业务需求选择即可。单节点版直接运行一个二进制文件既,官方建议采集数据点(data points)低于 100w/s,推荐 VM 单节点版,简单好维护,但不支持告警。集群版支持数据水平拆分。下图是 VictoriaMetrics 集群版官方的架构图。
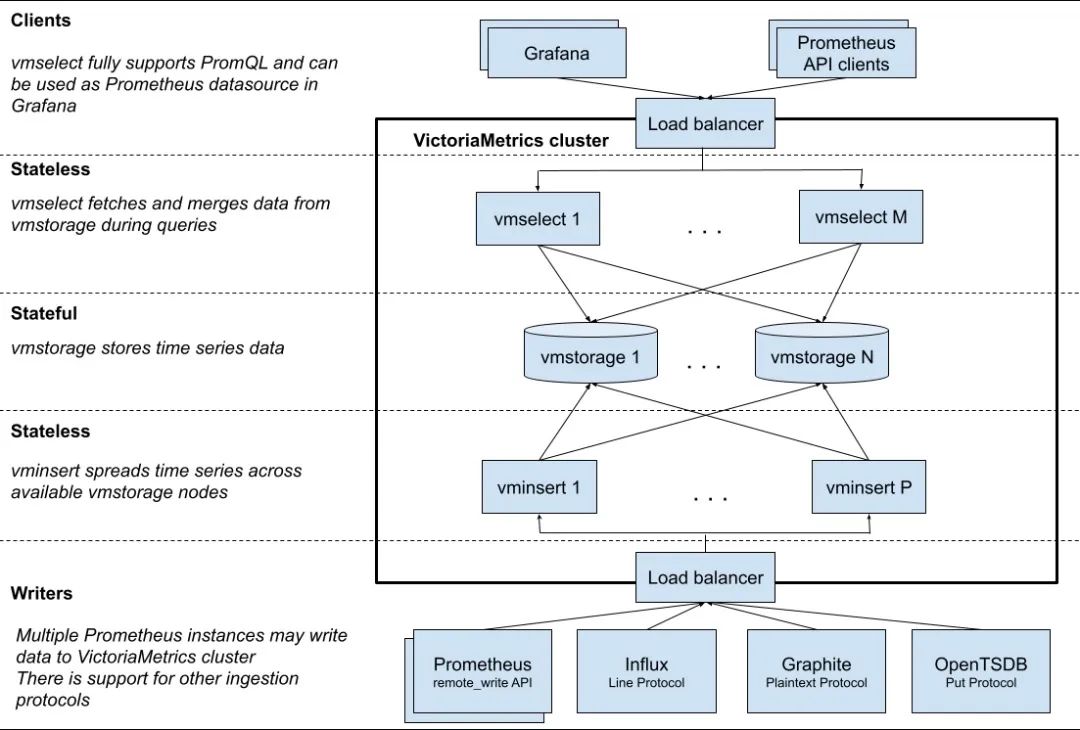
主要包含以下几个组件:
- vmstorage:数据存储以及查询结果返回,默认端口为 8482。
- vminsert:数据录入,可实现类似分片、副本功能,默认端口 8480。
- vmselect:数据查询,汇总和数据去重,默认端口 8481。
- vmagent:数据指标抓取,支持多种后端存储,会占用本地磁盘缓存,默认端口 8429。
- vmalert:报警相关组件,不如果不需要告警功能可以不使用该组件,默认端口为 8880。
集群方案把功能拆分为 vmstorage、 vminsert、vmselect 组件,如果要替换 Prometheus,还需要使用 vmagent、vmalert。从上图也可以看出 vminsert 以及 vmselect 都是无状态的,所以扩展很简单,只有 vmstorage 是有状态的。
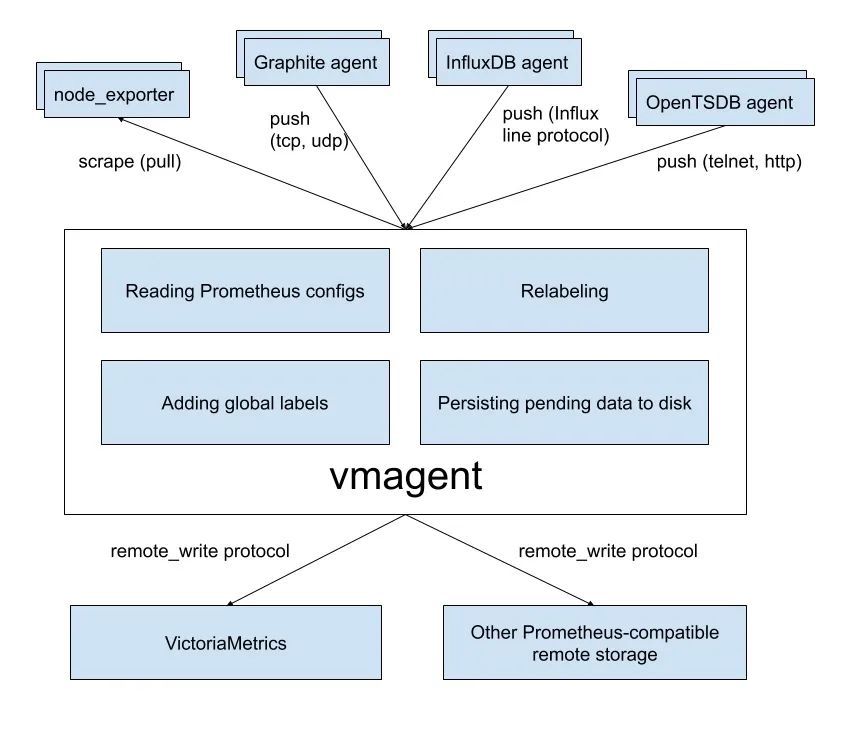
vmagent 的主要目的是用来收集指标数据然后存储到 VM 以及 Prometheus 兼容的存储系统中(支持 remote_write 协议即可)。
下图是 vmagent 的一个简单架构图,可以看出该组件也实现了 metrics 的 push 功能,此外还有很多其他特性:
- 替换 prometheus 的 scraping target
- 支持基于 prometheus relabeling 的模式添加、移除、修改 labels,可以方便在数据发送到远端存储之前进行数据的过滤
- 支持多种数据协议,influx line 协议,graphite 文本协议,opentsdb 协议,prometheus remote write 协议,json lines 协议,csv 数据
- 支持收集数据的同时,并复制到多种远端存储系统
- 支持不可靠远端存储(通过本地存储 -remoteWrite.tmpDataPath ),同时支持最大磁盘占用
- 相比 prometheus 使用较少的内存、cpu、磁盘 io 以及网络带宽
接下来我们就分别来介绍了 VM 的单节点和集群两个方案的使用。
单节点
这里我们采集 node-exporter 为例进行说明,首先使用 Prometheus 采集数据,然后将 Prometheus 数据远程写入 VM 远程存储,由于 VM 提供了 vmagent 组件,最后我们使用 VM 来完全替换 Prometheus,可以使架构更简单、更低的资源占用。
这里我们将所有资源运行在 kube-vm 命名空间之下:
☸ ➜ kubectl create ns kube-vm
首先我们这 kube-vm 命名空间下面使用 DaemonSet 控制器运行 node-exporter,对应的资源清单文件如下所示:
# vm-node-exporter.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: DaemonSet
metadata:
name: node-exporter
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: node-exporter
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: node-exporter
spec:
hostPID: true
hostIPC: true
hostNetwork: true
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
containers:
- name: node-exporter
image: prom/node-exporter:v1.3.1
args:
- --web.listen-address=$(HOSTIP):9111
- --path.procfs=/host/proc
- --path.sysfs=/host/sys
- --path.rootfs=/host/root
- --no-collector.hwmon # 禁用不需要的一些采集器
- --no-collector.nfs
- --no-collector.nfsd
- --no-collector.nvme
- --no-collector.dmi
- --no-collector.arp
- --collector.filesystem.ignored-mount-points=^/(dev|proc|sys|var/lib/containerd/.+|/var/lib/docker/.+|var/lib/kubelet/pods/.+)($|/)
- --collector.filesystem.ignored-fs-types=^(autofs|binfmt_misc|cgroup|configfs|debugfs|devpts|devtmpfs|fusectl|hugetlbfs|mqueue|overlay|proc|procfs|pstore|rpc_pipefs|securityfs|sysfs|tracefs)$
ports:
- containerPort: 9111
env:
- name: HOSTIP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
resources:
requests:
cpu: 150m
memory: 180Mi
limits:
cpu: 150m
memory: 180Mi
securityContext:
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534
volumeMounts:
- name: proc
mountPath: /host/proc
- name: sys
mountPath: /host/sys
- name: root
mountPath: /host/root
mountPropagation: HostToContainer
readOnly: true
tolerations: # 添加容忍
- operator: "Exists"
volumes:
- name: proc
hostPath:
path: /proc
- name: dev
hostPath:
path: /dev
- name: sys
hostPath:
path: /sys
- name: root
hostPath:
path: /
由于前面章节中我们也创建了 node-exporter,为了防止端口冲突,这里我们使用参数 --web.listen-address=$(HOSTIP):9111 配置端口为 9111。直接应用上面的资源清单即可。
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-node-exporter.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl get pods -n kube-vm -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
node-exporter-c4d76 1/1 Running 0 118s 192.168.0.109 node2 <none> <none>
node-exporter-hzt8s 1/1 Running 0 118s 192.168.0.111 master1 <none> <none>
node-exporter-zlxwb 1/1 Running 0 118s 192.168.0.110 node1 <none> <none>
然后重新部署一套独立的 Prometheus,为了简单我们直接使用 static_configs 静态配置方式来抓取 node-exporter 的指标,配置清单如下所示:
# vm-prom-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-config
namespace: kube-vm
data:
prometheus.yaml: |
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "nodes"
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.0.109:9111', '192.168.0.110:9111', '192.168.0.111:9111']
relabel_configs: # 通过 relabeling 从 __address__ 中提取 IP 信息,为了后面验证 VM 是否兼容 relabeling
- source_labels: [__address__]
regex: "(.*):(.*)"
replacement: "${1}"
target_label: 'ip'
action: replace
上面配置中通过 relabel 操作从 __address__ 中将 IP 信息提取出来,后面可以用来验证 VM 是否兼容 relabel 操作。
同样要给 Prometheus 数据做持久化,所以也需要创建一个对应的 PVC 资源对象:
# apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
# kind: StorageClass
# metadata:
# name: local-storage
# provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
# volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: prometheus-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
capacity:
storage: 20Gi
storageClassName: local-storage
local:
path: /data/k8s/prometheus
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- node2
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: prometheus-data
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
storageClassName: local-storage
然后直接创建 Prometheus 即可,将上面的 PVC 和 ConfigMap 挂载到容器中,通过 --config.file 参数指定配置文件文件路径,指定 TSDB 数据路径等,资源清单文件如下所示:
# vm-prom-deploy.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
spec:
volumes:
- name: data
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: prometheus-data
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: prometheus-config
containers:
- image: prom/prometheus:v2.35.0
name: prometheus
args:
- "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yaml"
- "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus" # 指定tsdb数据路径
- "--storage.tsdb.retention.time=2d"
- "--web.enable-lifecycle" # 支持热更新,直接执行localhost:9090/-/reload立即生效
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
name: http
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/etc/prometheus"
name: config-volume
- mountPath: "/prometheus"
name: data
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
app: prometheus
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: web
port: 9090
targetPort: http
直接应用上面的资源清单即可。
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-prom-config.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-prom-pvc.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-prom-deploy.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl get pods -n kube-vm -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
node-exporter-c4d76 1/1 Running 0 27m 192.168.0.109 node2 <none> <none>
node-exporter-hzt8s 1/1 Running 0 27m 192.168.0.111 master1 <none> <none>
node-exporter-zlxwb 1/1 Running 0 27m 192.168.0.110 node1 <none> <none>
prometheus-dfc9f6-2w2vf 1/1 Running 0 4m58s 10.244.2.102 node2 <none> <none>
☸ ➜ kubectl get svc -n kube-vm
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
prometheus NodePort 10.103.38.114 <none> 9090:31890/TCP 4m10s
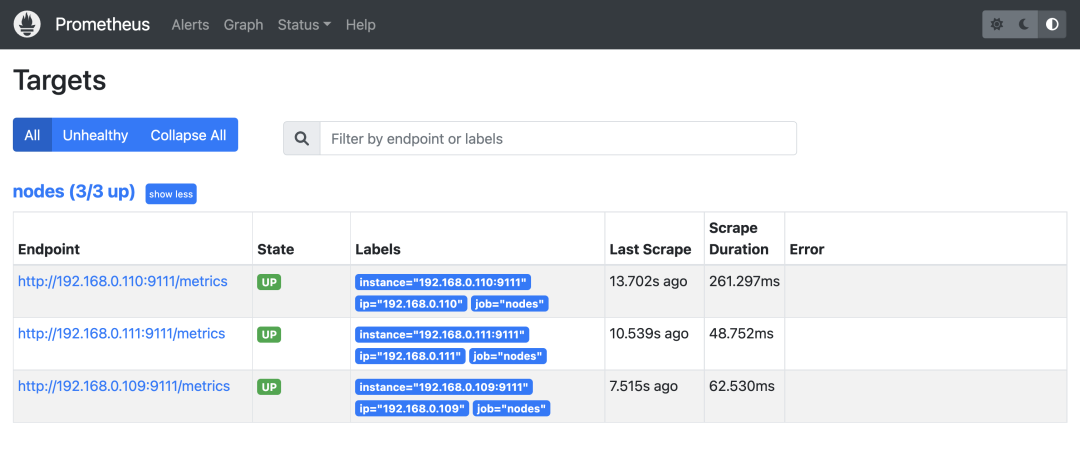
部署完成后可以通过 http://:31890 访问 Prometheus,正常可以看到采集的 3 个 node 节点的指标任务。

同样的方式重新部署 Grafana,资源清单如下所示:
# vm-grafana.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: grafana
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: grafana
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: grafana
spec:
volumes:
- name: storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: grafana-data
containers:
- name: grafana
image: grafana/grafana:main
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 3000
name: grafana
securityContext:
runAsUser: 0
env:
- name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER
value: admin
- name: GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD
value: admin321
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/grafana
name: storage
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: grafana
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 3000
selector:
app: grafana
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: grafana-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
capacity:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: local-storage
local:
path: /data/k8s/grafana
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- node2
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: grafana-data
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
storageClassName: local-storage
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-grafana.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl get svc -n kube-vm |grep grafana
grafana NodePort 10.97.111.153 <none> 3000:31800/TCP 62s
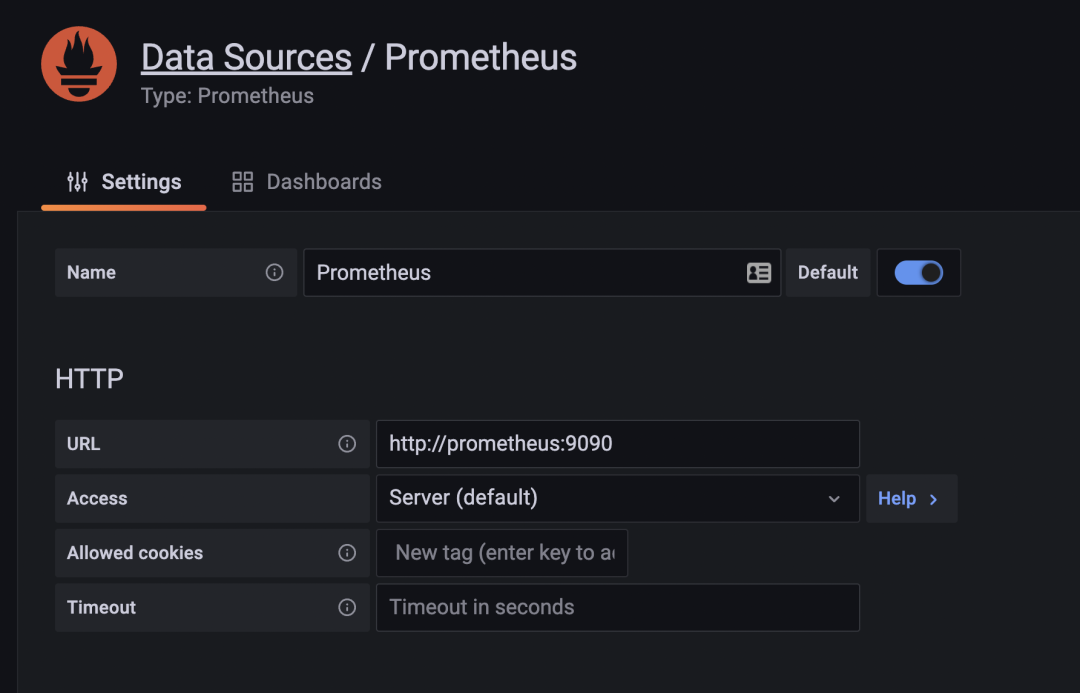
同样通过 http://:31800 就可以访问 Grafana 了,进入 Grafana 配置 Prometheus 数据源。

然后导入 16098 这个 Dashboard,导入后效果如下图所示。

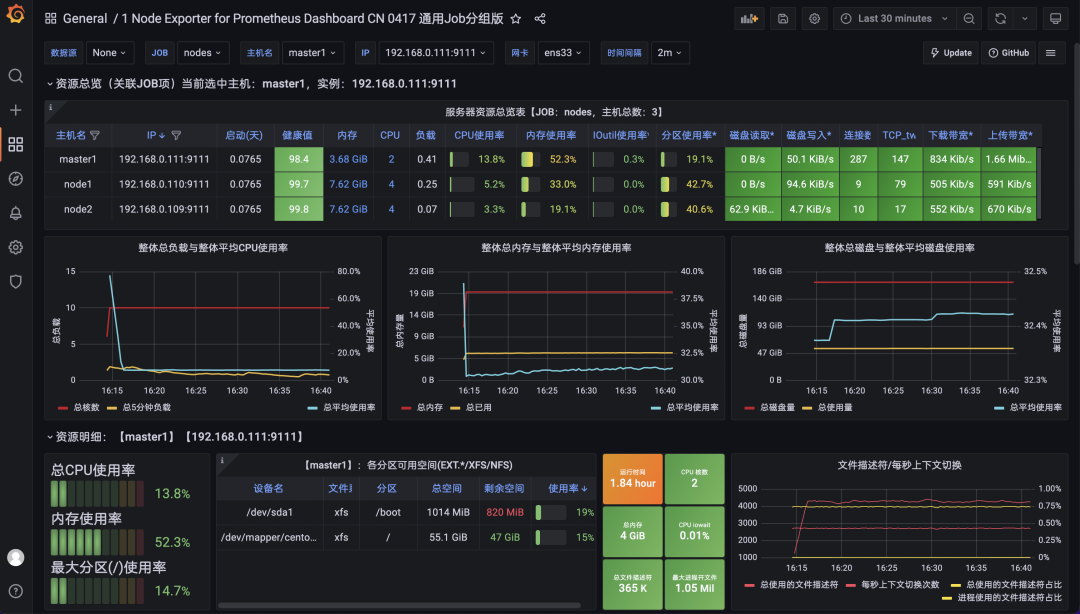
到这里就完成了使用 Prometheus 收集节点监控指标,接下来我们来使用 VM 来改造现有方案。
远程存储 VictoriaMetrics
首先需要一个单节点模式的 VM,运行 VM 很简单,可以直接下载对应的二进制文件启动,也可以使用 docker 镜像一键启动,我们这里同样部署到 Kubernetes 集群中。资源清单文件如下所示。
# vm-grafana.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: victoria-metrics
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: victoria-metrics
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: victoria-metrics
spec:
volumes:
- name: storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: victoria-metrics-data
containers:
- name: vm
image: victoriametrics/victoria-metrics:v1.76.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- -storageDataPath=/var/lib/victoria-metrics-data
- -retentionPeriod=1w
ports:
- containerPort: 8428
name: http
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/victoria-metrics-data
name: storage
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: victoria-metrics
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8428
selector:
app: victoria-metrics
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: victoria-metrics-data
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
capacity:
storage: 20Gi
storageClassName: local-storage
local:
path: /data/k8s/vm
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- node2
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: victoria-metrics-data
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
storageClassName: local-storage
这里我们使用 -storageDataPath 参数指定了数据存储目录,然后同样将该目录进行了持久化,-retentionPeriod 参数可以用来配置数据的保持周期。直接应用上面的资源清单即可。
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-single-node-deploy.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl get svc victoria-metrics -n kube-vm
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
victoria-metrics NodePort 10.106.216.248 <none> 8428:31953/TCP 75m
☸ ➜ kubectl get pods -n kube-vm -l app=victoria-metrics
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
victoria-metrics-57d47f4587-htb88 1/1 Running 0 3m12s
☸ ➜ kubectl logs -f victoria-metrics-57d47f4587-htb88 -n kube-vm
2022-04-22T08:59:14.431Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/logger/flag.go:12 build version: victoria-metrics-20220412-134346-tags-v1.76.1-0-gf8de318bf
2022-04-22T08:59:14.431Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/logger/flag.go:13 command line flags
2022-04-22T08:59:14.431Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/logger/flag.go:20 flag "retentionPeriod"="1w"
2022-04-22T08:59:14.431Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/logger/flag.go:20 flag "storageDataPath"="/var/lib/victoria-metrics-data"
2022-04-22T08:59:14.431Z info VictoriaMetrics/app/victoria-metrics/main.go:52 starting VictoriaMetrics at ":8428"...
2022-04-22T08:59:14.432Z info VictoriaMetrics/app/vmstorage/main.go:97 opening storage at "/var/lib/victoria-metrics-data" with -retentionPeriod=1w
......
2022-04-22T08:59:14.449Z info VictoriaMetrics/app/victoria-metrics/main.go:61 started VictoriaMetrics in 0.017 seconds
2022-04-22T08:59:14.449Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/httpserver/httpserver.go:91 starting http server at http://127.0.0.1:8428/
到这里我们单节点的 VictoriaMetrics 就部署成功了。接下来我们只需要在 Prometheus 中配置远程写入我们的 VM 即可,更改 Prometheus 配置:
# vm-prom-config2.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: prometheus-config
namespace: kube-vm
data:
prometheus.yaml: |
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_timeout: 15s
remote_write: # 远程写入到远程 VM 存储
- url: http://victoria-metrics:8428/api/v1/write
scrape_configs:
- job_name: "nodes"
static_configs:
- targets: ['192.168.0.109:9111', '192.168.0.110:9111', '192.168.0.111:9111']
relabel_configs: # 通过 relabeling 从 __address__ 中提取 IP 信息,为了后面验证 VM 是否兼容 relabeling
- source_labels: [__address__]
regex: "(.*):(.*)"
replacement: "${1}"
target_label: 'ip'
action: replace
重新更新 Prometheus 的配置资源对象:
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-prom-config2.yaml
# 更新后执行 reload 操作重新加载 prometheus 配置
☸ ➜ curl -X POST "http://192.168.0.111:31890/-/reload"
配置生效后 Prometheus 就会开始将数据远程写入 VM 中,我们可以查看 VM 的持久化数据目录是否有数据产生来验证:
☸ ➜ ll /data/k8s/vm/data/
total 0
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 38 Apr 22 17:15 big
r--r-- 1 root root 0 Apr 22 16:59 flock.lock
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 38 Apr 22 17:15 small
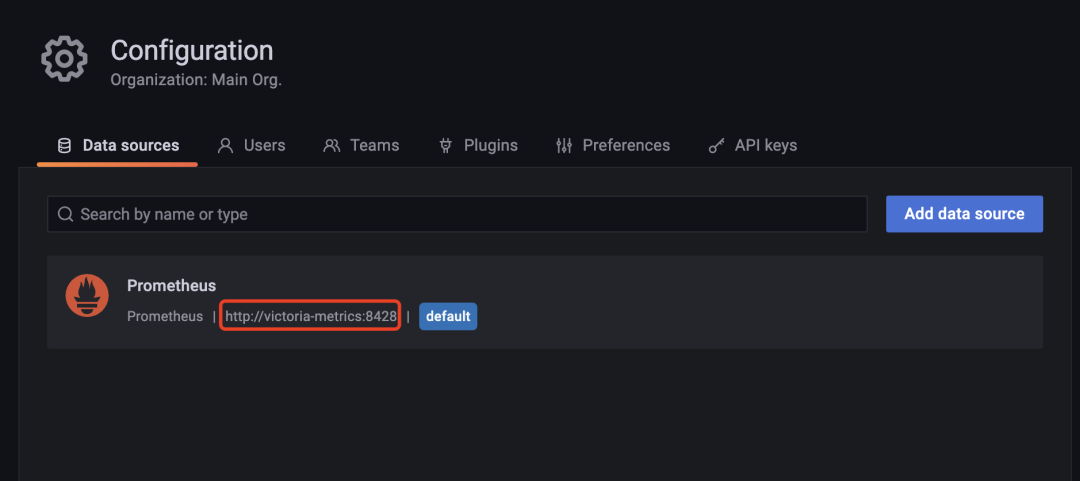
现在我们去直接将 Grafana 中的数据源地址修改成 VM 的地址:

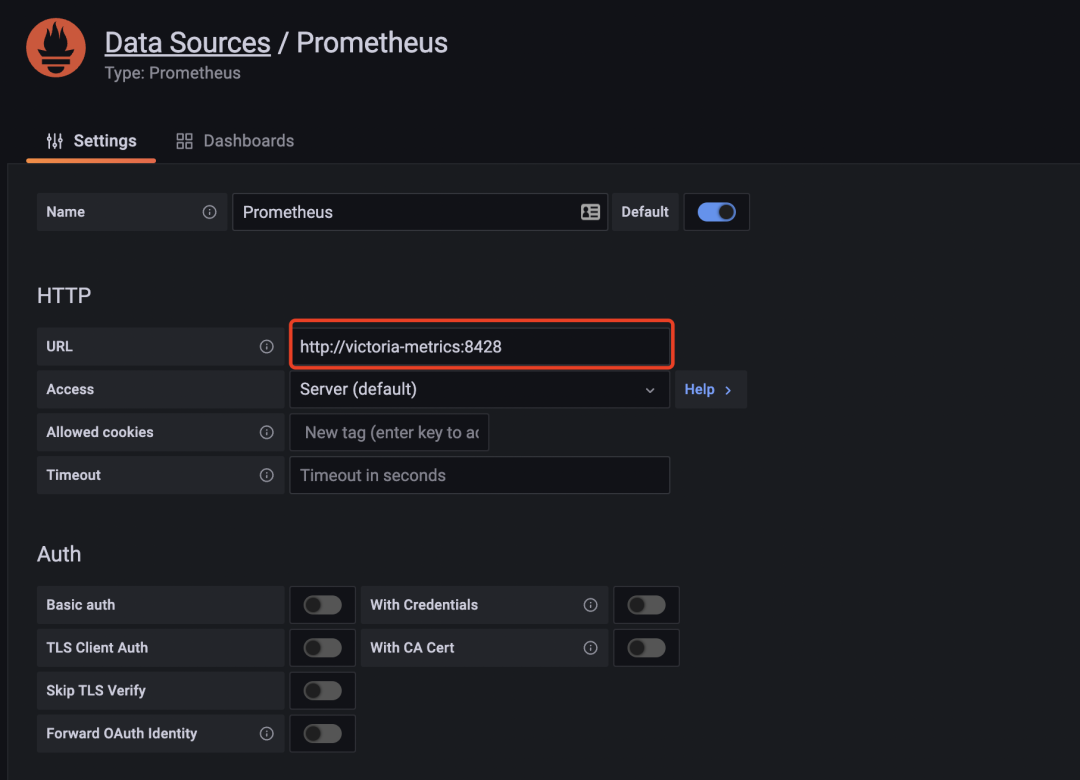
修改完成后重新访问 node-exporter 的 dashboard,正常可以显示,证明 VM 是兼容的。
替换 Prometheus
上面我们将 Prometheus 数据远程写入到了 VM,但是 Prometheus 开启 remote write 功能后会增加其本身的资源占用,理论上其实我们也可以完全用 VM 来替换掉 Prometheus,这样就不需要远程写入了,而且本身 VM 就比 Prometheus 占用更少的资源。
现在我们先停掉 Prometheus 的服务:
☸ ➜ kubectl scale deploy prometheus --replicas=0 -n kube-vm
然后将 Prometheus 的配置文件挂载到 VM 容器中,使用参数 -promscrape.config 来指定 Prometheus 的配置文件路径,如下所示:
# vm-single-node-deploy2.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: victoria-metrics
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: victoria-metrics
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: victoria-metrics
spec:
volumes:
- name: storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: victoria-metrics-data
- name: prometheus-config
configMap:
name: prometheus-config
containers:
- name: vm
image: victoriametrics/victoria-metrics:v1.76.1
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- -storageDataPath=/var/lib/victoria-metrics-data
- -retentionPeriod=1w
- -promscrape.config=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yaml
ports:
- containerPort: 8428
name: http
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/lib/victoria-metrics-data
name: storage
- mountPath: /etc/prometheus
name: prometheus-config
记得先将 Prometheus 配置文件中的 remote_write 模块去掉,然后重新更新 VM 即可:
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-prom-config.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-single-node-deploy2.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl get pods -n kube-vm -l app=victoria-metrics
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
victoria-metrics-8466844968-ncfnp 1/1 Running 2 (3m3s ago) 3m45s
☸ ➜ kubectl logs -f victoria-metrics-8466844968-ncfnp -n kube-vm
......
2022-04-22T10:01:59.837Z info VictoriaMetrics/app/victoria-metrics/main.go:61 started VictoriaMetrics in 0.022 seconds
2022-04-22T10:01:59.837Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/httpserver/httpserver.go:91 starting http server at http://127.0.0.1:8428/
2022-04-22T10:01:59.837Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/httpserver/httpserver.go:92 pprof handlers are exposed at http://127.0.0.1:8428/debug/pprof/
2022-04-22T10:01:59.838Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/promscrape/scraper.go:103 reading Prometheus configs from "/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yaml"
2022-04-22T10:01:59.838Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/promscrape/config.go:96 starting service discovery routines...
2022-04-22T10:01:59.839Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/promscrape/config.go:102 started service discovery routines in 0.000 seconds
2022-04-22T10:01:59.840Z info VictoriaMetrics/lib/promscrape/scraper.go:395 static_configs: added targets: 3, removed targets: 0; total targets: 3
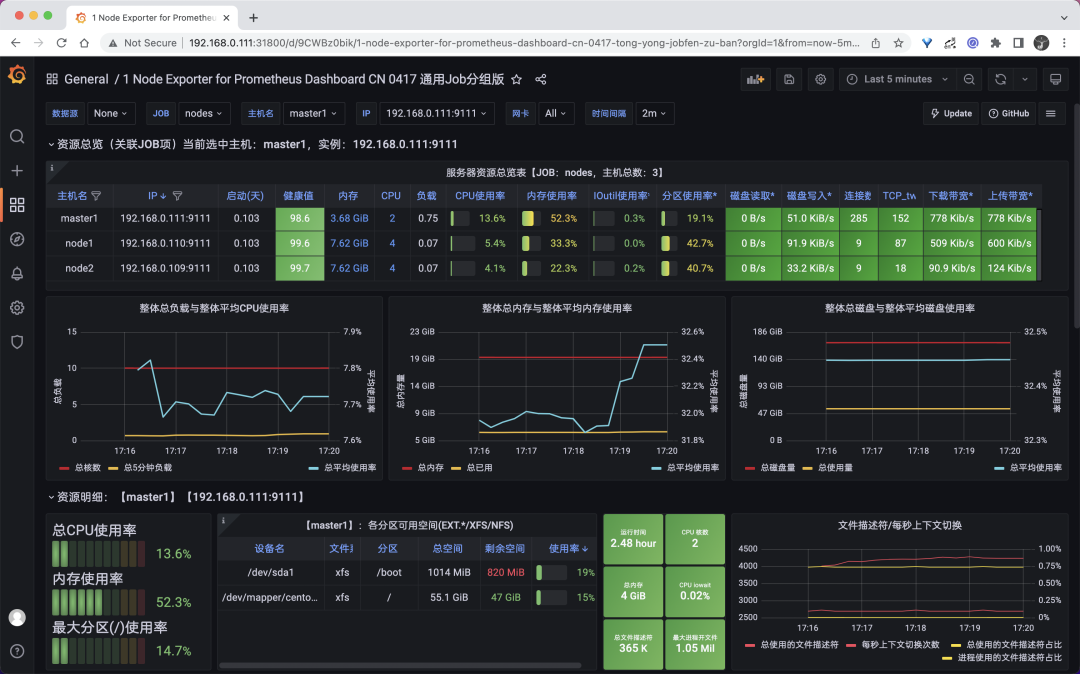
从 VM 日志中可以看出成功读取了 Prometheus 的配置,并抓取了 3 个指标(node-exporter)。现在我们再去 Grafana 查看 node-exporter 的 Dashboard 是否可以正常显示。先保证数据源是 VM 的地址。

这样我们就使用 VM 替换掉了 Prometheus,我们也可以这 Grafana 的 Explore 页面去探索采集到的指标。

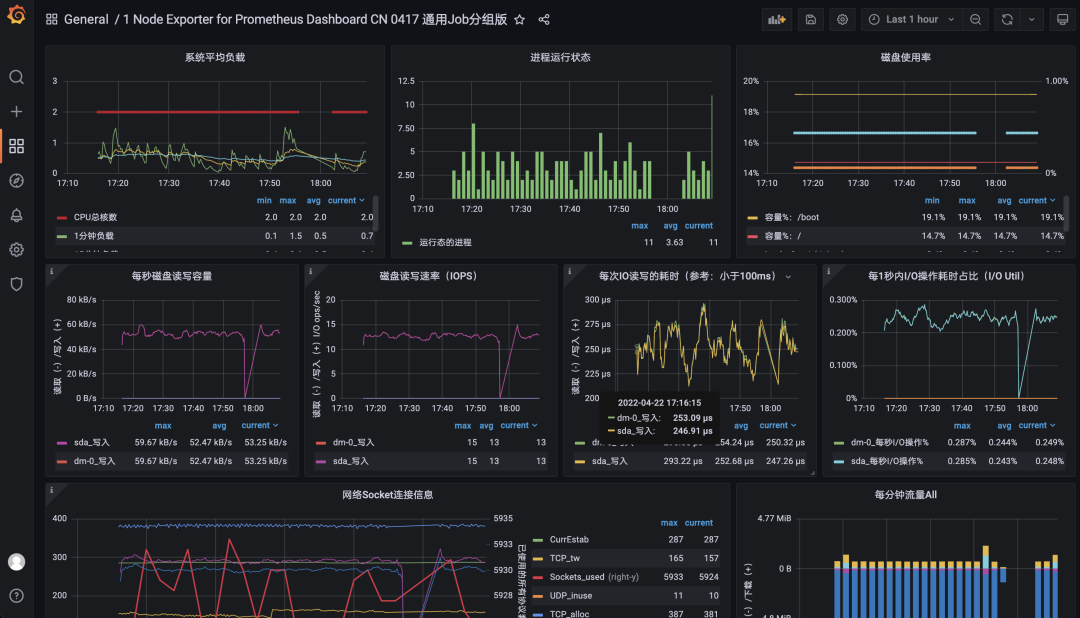
UI 界面
VM 单节点版本本身自带了一个 Web UI 界面 - vmui,不过目前功能比较简单,可以直接通过 VM 的 NodePort 端口进行访问。
☸ ➜ kubectl get svc victoria-metrics -n kube-vm
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
victoria-metrics NodePort 10.106.216.248 <none> 8428:31953/TCP 75m
我们这里可以通过 http://:31953 访问到 vmui:
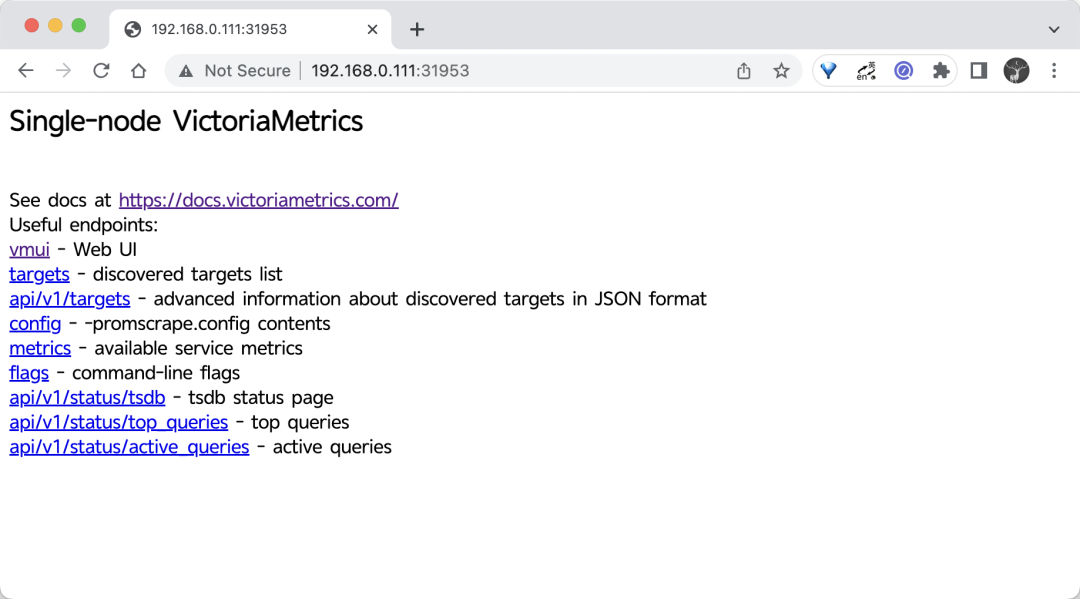
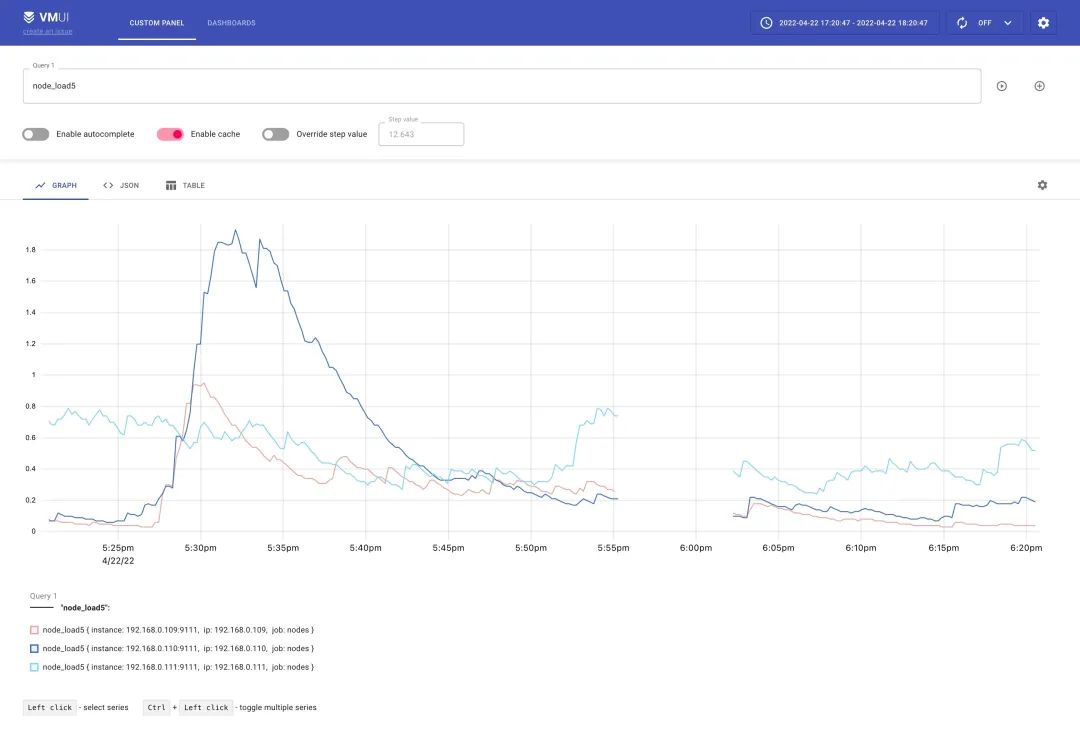
可以通过 /vmui 这个 endpoint 访问 UI 界面:
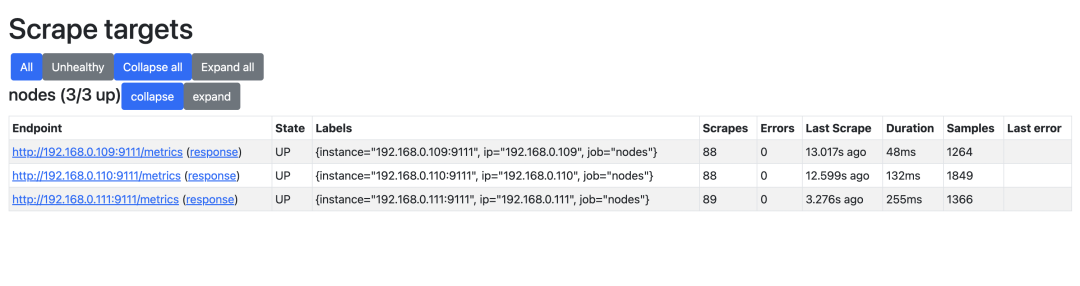
如果你想查看采集到的指标 targets,那么可以通过 /targets 这个 endpoint 来获取:

这些功能基本上可以满足我们的一些需求,但是还是太过简单,如果你习惯了 Prometheus 的 UI 界面,那么我们可以使用 promxy 来代替 vmui,而且 promxy 还可以进行多个 VM 单节点的数据聚合,以及 targets 查看等,对应的资源清单文件如下所示:
# vm-promxy.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: promxy-config
namespace: kube-vm
data:
config.yaml: |
promxy:
server_groups:
- static_configs:
- targets: [victoria-metrics:8428] # 指定vm地址,有多个则往后追加即可
path_prefix: /prometheus # 配置前缀
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: promxy
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: promxy
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: promxy
spec:
containers:
- args:
- "--config=/etc/promxy/config.yaml"
- "--web.enable-lifecycle"
- "--log-level=trace"
env:
- name: ROLE
value: "1"
command:
- "/bin/promxy"
image: quay.io/jacksontj/promxy
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: promxy
ports:
- containerPort: 8082
name: web
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/etc/promxy/"
name: promxy-config
readOnly: true
- args: # container to reload configs on configmap change
- "--volume-dir=/etc/promxy"
- "--webhook-url=http://localhost:8082/-/reload"
image: jimmidyson/configmap-reload:v0.1
name: promxy-server-configmap-reload
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/etc/promxy/"
name: promxy-config
readOnly: true
volumes:
- configMap:
name: promxy-config
name: promxy-config
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: promxy
namespace: kube-vm
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 8082
selector:
app: promxy
直接应用上面的资源对象即可:
☸ ➜ kubectl apply -f vm-promxy.yaml
☸ ➜ kubectl get pods -n kube-vm -l app=promxy
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
promxy-5f7dfdbc64-l4kjq 2/2 Running 0 6m45s
☸ ➜ kubectl get svc promxy -n kube-vm
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
promxy NodePort 10.110.19.254 <none> 8082:30618/TCP 6m12s
访问 Promxy 的页面效果和 Prometheus 自带的 Web UI 基本一致的。
这里面我们简单介绍了单机版的 victoriametrics 的基本使用。关于集群版的使用请关注后续文章。
相关文章
- 数据孤岛是业务效率的无声杀手
- 2023展望:新的一年将给大数据分析领域带来什么?
- 阿里云ADB基于Hudi构建Lakehouse的实践
- 大数据在医疗保健领域的使用案例
- 微软增加说明:KB5021751 更新扫描已经 / 即将过时 Office 过程中不会触碰用户隐私
- 2022 Gartner全球云数据库管理系统魔力象限发布 腾讯云数据库入选
- 场景化、重实操,分享一个实时数仓实践案例
- Arctic的湖仓一体践行之路
- 分布式计算MapReduce究竟是怎么一回事?
- 淘系数据模型治理优秀实践
- 大数据分析对医疗保健的影响
- 当我们说大数据Hadoop,究竟在说什么?
- 2022年及以后大数据的五个发展趋势
- 网易严选离线数仓治理实践
- 2023 年数据治理趋势
- 一份“靠谱”的年度经营计划,你学会了吗?
- 漫谈对大数据的思考
- 测试一下,读懂数据的能力,你有吗?
- 用艺术的眼光探索数据之美
- 聊聊数据分析成果如何落地

