数据结构:跳跃链表
本文转载自微信公众号「潜行前行」,作者cscw。转载本文请联系潜行前行公众号。
什么是跳跃链表
开发时经常使用的平衡数据结构有B数、红黑数,AVL数。但是如果让你实现其中一种,很难,实现起来费时间。而跳跃链表一种基于链表数组实现的快速查找数据结构,目前开源软件 Redis 和 LevelDB 都有用到它。它的效率和红黑树以及 AVL 树不相上下
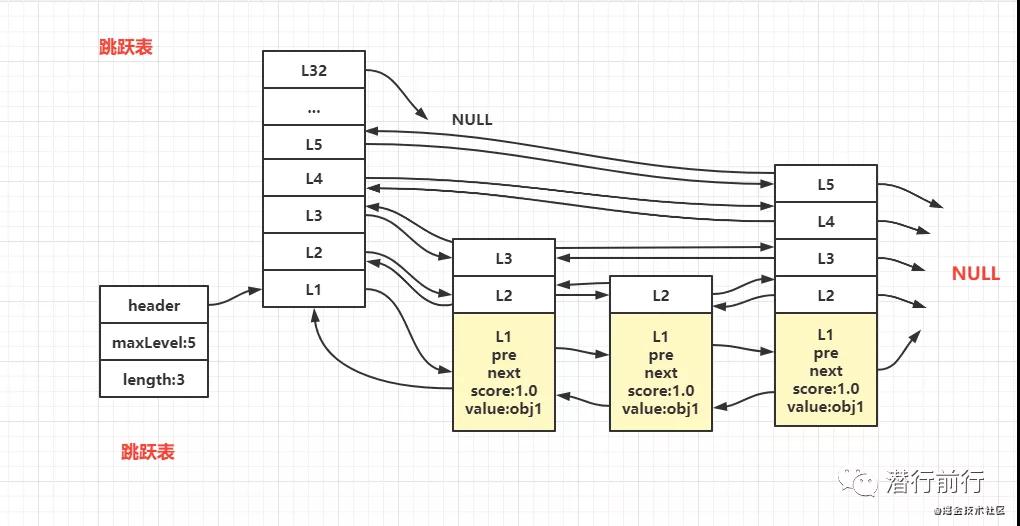
跳跃链表结构
结构
- public class SkipList<T> {
- //跳跃表的头尾
- private SkipListNode<T> head;
- //跳跃表含的元素长度
- private int length;
- //跳表的层数 的历史最大层数
- public int maxLevel;
- public SecureRandom random;
- private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 31;
- public SkipList() {
- //初始化头尾节点及两者的关系
- head = new SkipListNode<>(SkipListNode.HEAD_SCORE, null, MAX_LEVEL);
- //初始化大小,层,随机
- length = 0;
- maxLevel = 0; // 层数从零开始计算
- random = new SecureRandom();
- }
- ...
- header:指向跳跃表的头节点
- maxLevel:记录目前跳跃表,层数最大节点的层数
- length:链表存在的元素长度
节点
跳跃链表节点的组成:前节点、后节点、分值(map的key值)、及存储对象 value
- public class SkipListNode<T> {
- //在跳表中排序的 分数值
- public double score;
- public T value;
- public int level;
- // 前后节点
- public SkipListNode<T> next,pre;
- //上下节点形成的层
- public SkipListNode<T>[] levelNode;
- private SkipListNode(double score, int level){
- this.score = score;
- this.level = level;
- }
- public SkipListNode(double score, T value, int level) {
- this.score = score;
- this.value = value;
- this.level = level;
- this.levelNode = new SkipListNode[level+1];
- //初始化 SkipListNode 及 每一层的 node
- for (int i = level; i > 0; --i) {
- levelNode[i] = new SkipListNode<T>(score, level);
- levelNode[i].levelNode = levelNode;
- }
- this.levelNode[0] = this;
- }
- @Override
- public String toString() { return "Node[score=" + score + ", value=" + value + "]"; }
- }
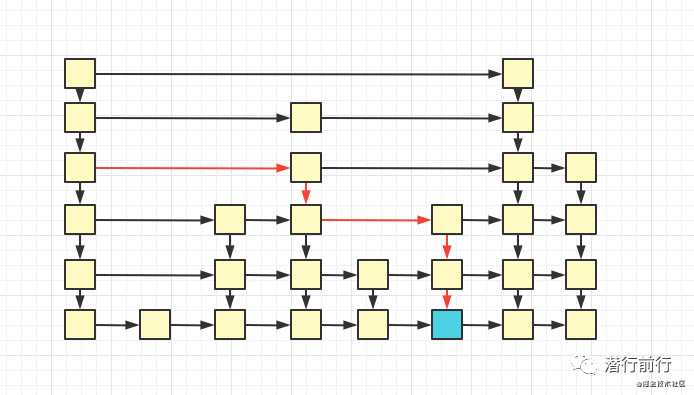
跳表是用空间来换时间
在我实现的跳跃链表节点,包括一个 levelNode 成员属性。它就是节点层。跳跃链表能实现快速访问的关键点就是它
平时访问一个数组,我们是顺序遍历的,而跳跃链表效率比数组链表高,是因为它使用节点层存储多级索引,形成一个稀疏索引,所以需要的更多的内存空间
跳跃链表有多快
如果一个链表有 n 个结点,每两个结点抽取出一个结点建立索引的话,那么第一层索引的结点数大约就是 n/2,第二层索引的结点数大约为 n/4,以此类推第 m 层索引的节点数大约为 n/(2^m)
访问数据时可以从 m 层索引查询定位到 m-1 层索引数据。而 m-1 大约是 m 层的1/2。也就是说最优的时间复杂度为O(log/N)
最差情况。在实际实现中,每一层索引是无法每次以数据数量对折一次实现一层索引。因此折中的方式,每一层的索引是随机用全量数据建一条。也就是说最差情况时间复杂度为O(N),但最优时间复杂度不变
查询
查询一开始是遍历最高层 maxLevel 的索引 m。按照以下步骤查询出等于 score 或者最接近 score 的左节点
1:如果同层索引的 next 节点分值小于查询分值,则跳到 next 节点。cur = next
2:如果 next 为空。或者next节点分值大于查询分值。则跳到下一层 m-1 索引,循环 2
循环 1、2 步骤直到访问到节点分值和查询分值一致,或者索引层为零
- // SkipList
- private SkipListNode<T> findNearestNode(double score) {
- int curLevel = maxLevel;
- SkipListNode<T> cur = head.levelNode[curLevel];
- SkipListNode<T> next = cur.next;
- // 和当前节点分数相同 或者 next 为 null
- while (score != cur.score && curLevel > 0) {
- // 1 向右 next 遍历
- if (next != null && score >= next.levelNode[0].score) {
- cur = next;
- }
- next = cur.levelNode[curLevel].next;
- // 2 向下遍历,层数减1
- while ((next == null || score < next.levelNode[0].score) && curLevel > 0) {
- next = cur.levelNode[--curLevel].next;
- }
- }
- // 最底层的 node。
- return cur.levelNode[0];
- }
- public SkipListNode<T> get(double score) {
- //返回跳表最底层中,最接近这个 score 的node
- SkipListNode<T> p = findNearestNode(score);
- //score 相同,返回这个node
- return p.score == score ? p : null;
- }
插入
如果分值存在则替换 value
如果分值对应节点不存在,则随机一个索引层数 level (取值 0~31)。然后依靠节点属性 levelNode 加入 0 到 level 层的索引
- //SkipList
- public T put(double score, T value) {
- //首先得到跳表最底层中,最接近这个key的node
- SkipListNode<T> p = findNearestNode(score);
- if (p.score == score) {
- // 在跳表中,只有最底层的node才有真正的value,只需修改最底层的value就行
- T old = p.value;
- p.value = value;
- return old;
- }
- // nowNode 为新建的最底层的node。索引层数 0 到 31
- int nodeLevel = (int) Math.round(random.nextDouble() * 32);
- SkipListNode<T> nowNode = new SkipListNode<T>(score, value, nodeLevel);
- //初始化每一层,并连接每一层前后节点
- int level = 0;
- while (nodeLevel >= p.level) {
- for (; level <= p.level; level++) {
- insertNodeHorizontally(p.levelNode[level], nowNode.levelNode[level]);
- }
- p = p.pre;
- }
- // 此时 p 的层数大于 nowNode 的层数才进入循环
- for (; level <= nodeLevel; level++) {
- insertNodeHorizontally(p.levelNode[level], nowNode.levelNode[level]);
- }
- this.length ++ ;
- if (this.maxLevel < nodeLevel) {
- maxLevel = nodeLevel;
- }
- return value;
- }
- private void insertNodeHorizontally(SkipListNode<T> pre, SkipListNode<T> now) {
- //先考虑now
- now.next = pre.next;
- now.pre = pre;
- //再考虑pre的next节点
- if (pre.next != null) {
- pre.next.pre = now;
- }
- //最后考虑pre
- pre.next = now;
- }
删除
使用 get 方法找到元素,然后解除节点属性 levelNode 在每一层索引的前后引用关系即可
- //SkipList
- public T remove(double score){
- //在底层找到对应这个key的节点
- SkipListNode<T> now = get(score);
- if (now == null) {
- return null;
- }
- SkipListNode<T> curNode, next;
- //解除节点属性 levelNode 在每一层索引的前后引用关系
- for (int i = 0; i <= now.level; i++){
- curNode = now.levelNode[i];
- next = curNode.next;
- if (next != null) {
- next.pre = curNode.pre;
- }
- curNode.pre.next = curNode.next;
- }
- this.length--; //更新size,返回旧值
- return now.value;
- }
使用示例
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- SkipList<String> list=new SkipList<>();
- list.printSkipList();
- list.put(1, "csc");
- list.printSkipList();
- list.put(3, "lwl");
- list.printSkipList();
- list.put(2, "hello world!");
- list.printSkipList();
- System.out.println(list.get(2));
- System.out.println(list.get(4));
- list.remove(2);
- list.printSkipList();
- }
欢迎指正文中错误
参考文章
- redis设计与实现
- 跳表(跳跃表,skipList)总结-java版[1]
- 数据结构与算法——跳表[2]
相关文章
- es实战-分片分配失败解决方案
- mysql 系列:日志
- 如何成为数据分析师系列(二):可视化图表进阶
- 数据安全审查综合解读|如何从被动合规到主动战略风控?
- 基于实时计算Flink版的场景解决方案demo
- 高手总结的15个技巧,让你轻松玩转数据可视化!
- 数据结构
- 从睫毛膏到太空垃圾,2018年度值得推荐的数据可视化作品都在这了!
- SpringBoot | 1.4 数据库事务处理
- Elasticsearch搜索(查询)性能优化
- PostgreSQL数据目录深度揭秘
- 阿里云产品8月刊
- mysql 系列:锁和它的运用
- 怎么快速的让网站被收录?搜索引擎的工作原理
- Logstash 同步 mysql 踩坑
- 云数据库选型必读:总有一款适合你!
- IDC《2017年中国BI市场的的跟踪报告》发布 中国厂商帆软软件位居第一
- 区域内有几个一二三类LSA计算
- 深入浅出 带你看懂数据可视化「美」的历程
- prometheus笔记