java详解队列

一、队列是什么?
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out) 入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾(Tail/Rear) 出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头(Head/Front)
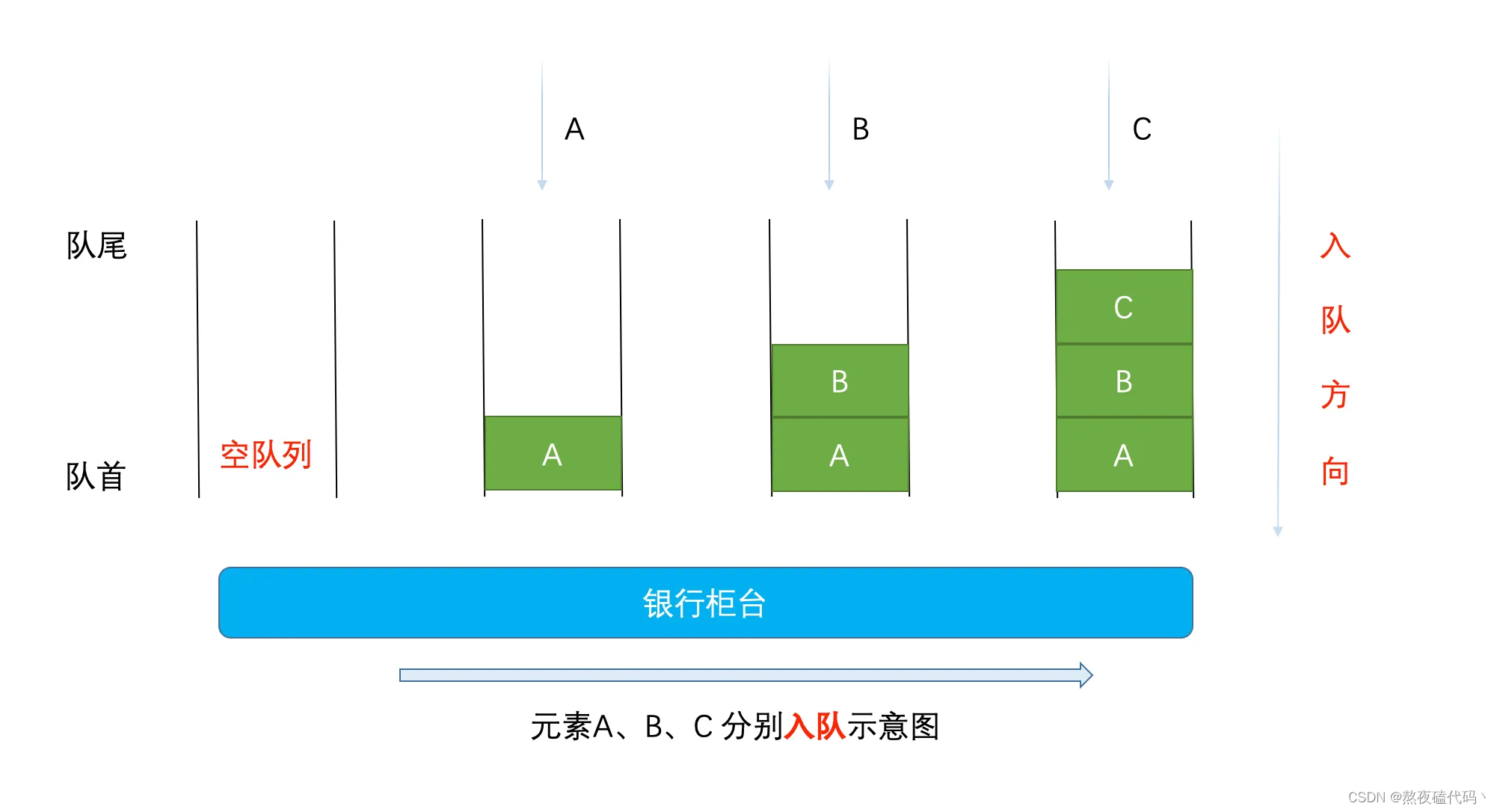

队列是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的前端进行删除操作,而在表的后端进行插入操作。
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
二、模拟实现队列
队列中既然可以存储元素,那底层肯定要有能够保存元素的空间,通过前面线性表的学习了解到常见的空间类型有两种:顺序结构 和 链式结构。同学们思考下:队列的实现使用顺序结构还是链式结构好?
因为队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,顺序表要想达到此目的,删除和取数据时间复杂度达到了O(n),那我们可不可以用单链表而且时间复杂度是O(1)呢?
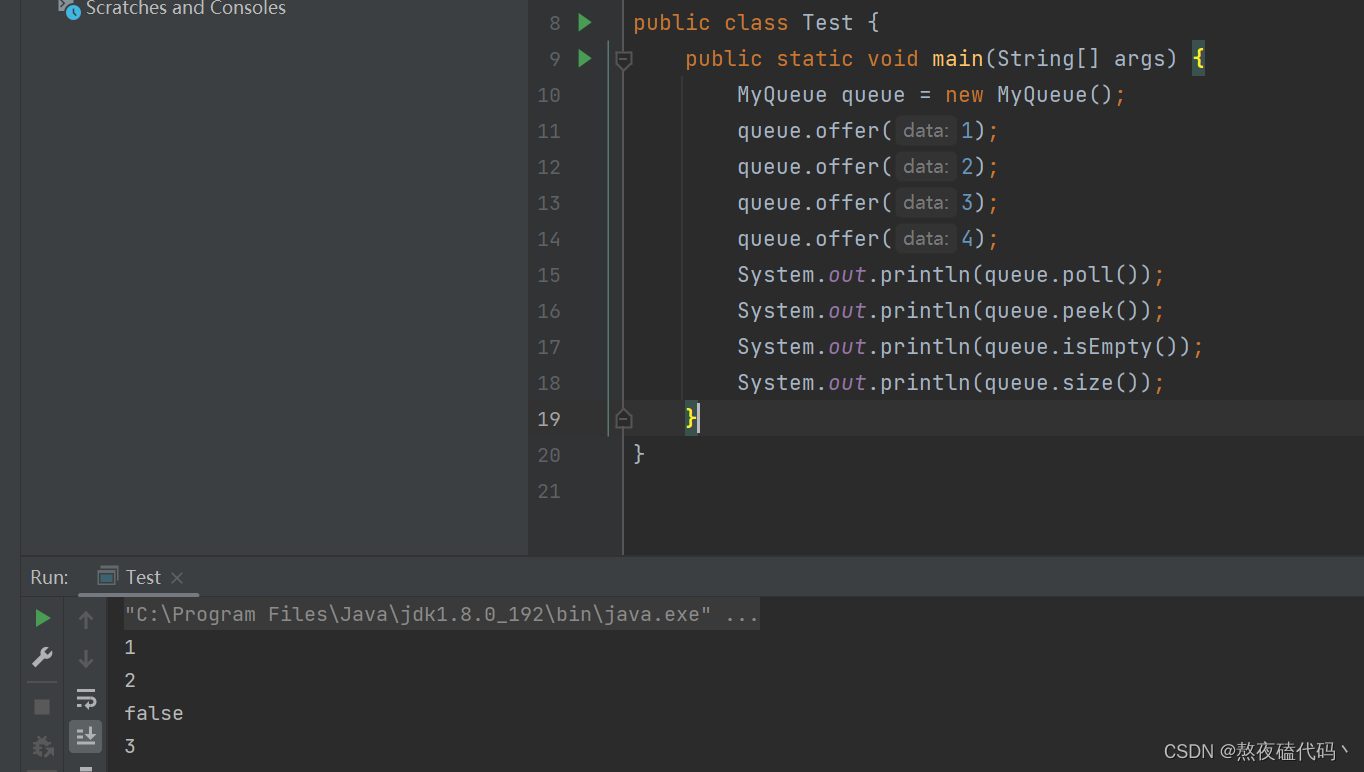
public class MyQueue {
static class ListNode {
public int value;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode tail;
//入队列
public void offer(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(head == null) {
head = node;
tail = node;
return;
}
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
}
//出队列
public int poll() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int ret = head.value;
head = head.next;
if(head == null) {
tail = null;
}
return ret;
}
//查看队列第一个元素
public int peek() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
int ret = head.value;
return ret;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size() == 0;
}
//获取队列大小
public int size() {
ListNode cur = head;
int count = 0;
while (cur != null) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
三、模拟实现循环队列
循环队列是把顺序队列首尾相连,把存储队列元素的表从逻辑上看成一个环,成为循环队列。
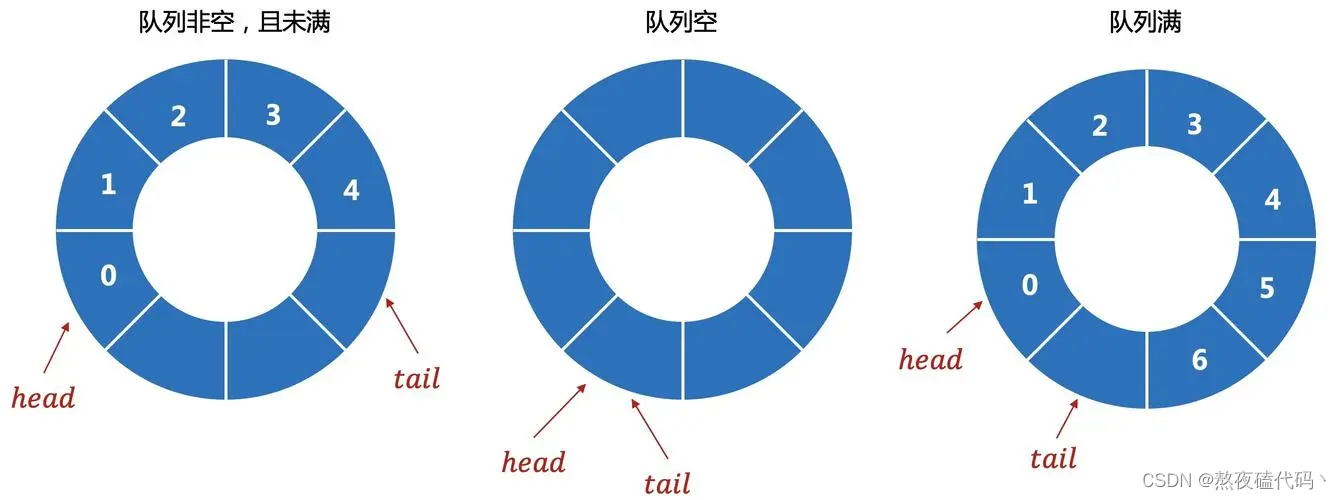
在实现循环队列时,我们主要面临的问题是,什么情况下队列为空,什么情况下队列为满,在判断满时:我们有两种方案,定义一个size变量,如果等于0为空,等于队列容量为满,这种过于简单,我们采用浪费一个空间的办法,如果head == tail队列为空,如果tail的下一个位置为head为满。
class MyCircularQueue {
public int[] arr;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
arr = new int[k+1];
}
public int front;
public int rear;
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()) {
return false;
}
arr[rear] = value;
rear = (rear + 1) % arr.length;
return true;
}
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
front = (front + 1) % arr.length;
return true;
}
public int Front() {
if(!isEmpty()) {
return arr[front];
}
return -1;
}
public int Rear() {
if(!isEmpty()) {
int ret = rear == 0 ? arr.length - 1 : rear - 1;
return arr[ret];
}
return -1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % arr.length == front;
}
}
四、用队列实现栈
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。

import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> qu1;
public Queue<Integer> qu2;
public MyStack() {
qu1 = new LinkedList<>();
qu2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(empty()) {
qu1.offer(x);
return;
}
if(qu1.isEmpty()) {
qu2.offer(x);
}else {
qu1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(qu1.isEmpty()) {
int x = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) {
qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
}
return qu2.poll();
}else {
int x = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) {
qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
}
return qu1.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(qu1.isEmpty()) {
int x = qu2.size();
for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) {
qu1.offer(qu2.poll());
}
int ret = qu2.poll();
qu1.offer(ret);
return ret;
}else {
int x = qu1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < x - 1; i++) {
qu2.offer(qu1.poll());
}
int ret = qu1.poll();
qu2.offer(ret);
return ret;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return qu1.isEmpty() && qu2.isEmpty();
}
}
五、用栈实现队列
请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾
int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int peek() 返回队列开头的元素
boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false

import java.util.Stack;
class MyQueue{
public Stack<Integer> s1;
public Stack<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new Stack<>();
s2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!s2.empty()) {
return s2.pop();
}else {
while(!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
return s2.pop();
}
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(!s2.empty()) {
return s2.peek();
}else {
while(!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
return s2.peek();
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.empty() && s2.empty();
}
}
相关文章
- Java枚举类
- 关于性能测试并发的设置,看这一篇就够了
- 安全优雅地停止Java线程
- Java 项目自动生成单元测试插件推荐
- Jenkins分布式构建和部署(master-slave)
- Java自动化测试,必备知识梳理及面试题分享
- Go并不需要Java风格的GC
- Java Review - 并发编程_独占锁ReentrantLock原理&源码剖析
- Java Review - 并发编程_读写锁ReentrantReadWriteLock的原理&源码剖析
- Java Review - 并发编程_抽象同步队列AQS
- Jmeter介绍
- Jenkins实战
- Java Review - 并发编程_ConcurrentLinkedQueue原理&源码剖析
- Java Review - 并发编程_StampedLock锁探究
- Java Review - 并发编程_LinkedBlockingQueue原理&源码剖析
- Java Review - 并发编程_ArrayBlockingQueue原理&源码剖析
- Java Review - 并发编程_PriorityBlockingQueue原理&源码剖析
- Java Review - 并发编程_DelayQueue原理&源码剖析
- springboot yml配置文件中换行问题
- 试试这款针对JAVA应用的开源防火墙!

