【Kotlin】类的继承 ② ( 使用 is 运算符进行类型检测 | 使用 as 运算符进行类型转换 | 智能类型转换 | Any 超类 )
一、使用 is 运算符进行类型检测
在 Kotlin 中 , 如果不确定一个 实例对象的类型 , 可以 使用 is 运算符进行判定 , 使用方法
实例对象 is 判定类型
上述用法可以判定 实例对象 是否是 判定类型 , 如果是 返回 true , 反之 返回 false ;
代码示例 : 在下面的代码中 , 调用 student is Person 判断 student 对象是否是 Person 类型 ;
open class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) {
fun info() {
println("name : $name, age : $age")
}
open fun sayHello(){
println("Hello World")
}
}
class Student : Person("Tom", 18){
override fun sayHello(){
println("Hello World Tom")
}
}
fun main() {
var student = Student()
var person = Person("Jerry", 12)
println("student is Person : ${student is Person}")
println("student is Student : ${student is Student}")
println("person is Person : ${person is Person}")
println("person is Student : ${person is Student}")
}
执行结果 :
student is Person : true
student is Student : true
person is Person : true
person is Student : false
二、使用 as 运算符进行类型转换 ( 智能类型转换 )
将 子类对象 声明为 父类类型 , 如果要 调用 子类 特有的方法 , 必须 使用 as 运算符进行 类型转换 ;
智能类型转换 : 使用 as 运算符进行 类型转换 , 只要进行一次类型转换 , 在后面还要调用子类成员时就可以直接调用 , 不再需要手动转换类型 ;
在下面的代码中 :
父类时 Person 类型 , 子类是 Student 类型 ;
创建 Student 对象 , 但是将其声明为 Person 类型 , 此时该对象只能调用 父类 Person 的成员 , 不能调用 Student 对象的特有成员 ;
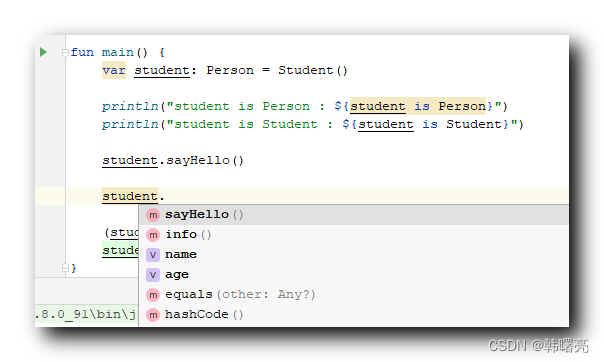
var student: Person = Student()
该 student 实例对象 , 可以调用 Person 类中的 sayHello 成员函数 , 但是不能调用 Student 类中的 helloStudent 成员函数 ; 下图中没有 helloStudent 函数的调用提示 ;
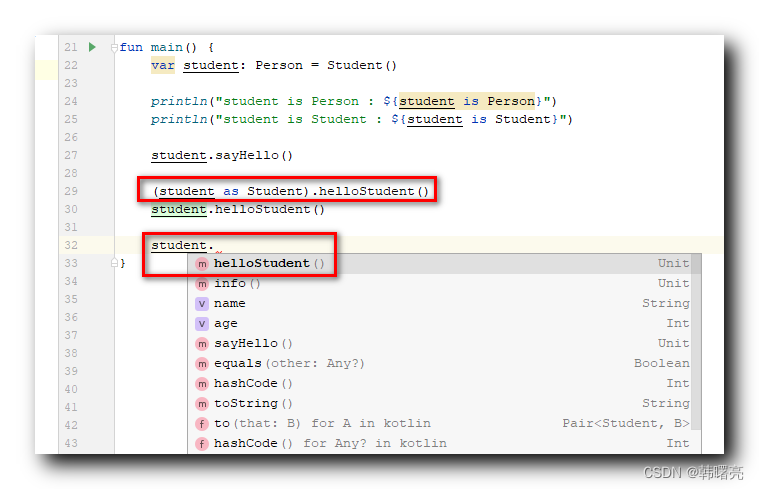
将 student 对象转为 Student 类型 , 即可调用 Student 类中的 helloStudent 成员函数 ;
(student as Student).helloStudent()
在进行第一次转换之后 , 后面 student 对象 可以直接调用 helloStudent 函数 , 不再需要进行先转换类型再调用 , 这就是 智能类型转换 ;
(student as Student).helloStudent()
student.helloStudent()
代码示例 :
open class Person(val name: String, val age: Int) {
fun info() {
println("name : $name, age : $age")
}
open fun sayHello(){
println("Hello World")
}
}
class Student : Person("Tom", 18){
override fun sayHello(){
println("Hello World Tom")
}
fun helloStudent(){
println("Hello Student")
}
}
fun main() {
var student: Person = Student()
println("student is Person : ${student is Person}")
println("student is Student : ${student is Student}")
student.sayHello()
(student as Student).helloStudent()
student.helloStudent()
}
执行结果 :
student is Person : true
student is Student : true
Hello World Tom
Hello Student
Hello Student
三、Any 超类
在 Java 中 , 所有的类都继承自 Object 类 ;
在 Kotlin 中 , 所有的类都继承自 Any 类 ;
Any 类原型如下 :
package kotlin
/**
* Kotlin类层次结构的根。每个Kotlin类都有[Any]作为超类。
*/
public open class Any {
public open operator fun equals(other: Any?): Boolean
public open fun hashCode(): Int
public open fun toString(): String
}
Kotlin 中的 equals , hashCode , toString 等函数在编译器中都已经实现 , 在不同平台的编译器中实现不同 ;
Kotlin 的跨平台能力比 Java 更强 , 为了支持跨平台 , Kotlin 在不同的平台中有不同的实现 ;
相关文章
- 无内核技术助力Java、Node.js、Go与Python应用
- 开源网络实时分析工具Skydive
- 十分钟理解 Java 中的动态代理
- Android Java层的anti-hooking技巧
- Spring知识点提炼
- 容器中的Java与内存限制:LXC、Docker与OpenVZ
- 程序员眼中的古典名画
- Java程序员需要注意的五大Docker误区
- 作为一个程序员我最大的遗憾
- 作为一个菜鸟程序员跳槽可行吗?
- C++中引用和匿名对象的理解和本质剖析
- 软件开发过程中安全代码的七大实践
- 为什么未来是全栈工程师的世界?
- 调查:Java程序员最伤心,C++程序员最年老
- Java中HttpURLConnection 与 PoLA 法则
- 面试感悟:3年工作经验程序员应有的技能
- 给未来程序员的15个顶级职业建议
- 为什么很少见工资高的程序员炫富?
- Java虚拟机体系结构深入研究总结
- 一个Bug,让我发现了Java界的.AJ(锥)!

